IBM 2006 Annual Report Download - page 80
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 80 of the 2006 IBM annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
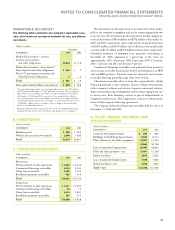
resulted in the receipt of $152 million of cash and a pre-tax gain of
$17 million. As a result of this transaction, the company’s equity in
Lenovo at September 30, 2005 represented 9.9 percent of ordinary
voting shares and 14.88 percent of total ownership.
Also, in the second half of the year, the company received an addi-
tional $23 million of cash from Lenovo related to working capital
adjustments, net of expenses related to employee matters. These
transactions were consistent with the company’s previous estimates.
Overall, including the gain on the equity sale recorded in the third
quarter, the company recorded an additional net pre-tax gain of $11
million; the resulting net pre-tax gain for the year ending December
31, 2005 is $1,108 million.
In addition, at December 31, 2005, the deferred income balance re-
lated to the services arrangements discussed previously is $169 million.
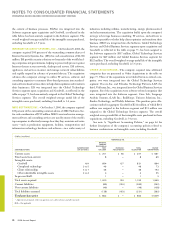
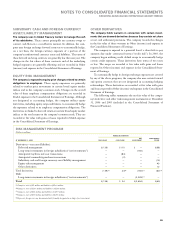
D. FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
(EXCLUDING DERIVATIVES)
FAIR VALUE OF FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
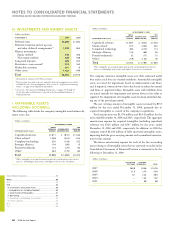
Cash and cash equivalents, marketable securities and derivative
financial instruments are recognized and measured at fair value in
the company’s financial statements. Notes and other accounts receiv-
able and other investments are financial assets with carrying values
that approximate fair value. Accounts payable, other accrued expenses
and short-term debt are financial liabilities with carrying values that
approximate fair value. The carrying amount of long-term debt is
approximately $13.8 billion and $15.4 billion and the estimated fair
value is $16.2 billion and $16.7 billion at December 31, 2006 and
2005, respectively.
In the absence of quoted prices in active markets, considerable
judgment is required in developing estimates of fair value. Estimates
are not necessarily indicative of the amounts the company could real-
ize in a current market transaction. The following methods and
assumptions were used to estimate fair values:
Loans and Financing Receivables
Estimates of fair value are based on discounted future cash flows using
current interest rates offered for similar loans to clients with similar
credit ratings for the same remaining maturities.
Restricted Securities
The fair value of restricted securities was estimated based on a quoted
price for an identical unrestricted security, adjusted to reflect the
effect of the restriction.
Long-Term Debt
For publicly-traded debt, estimates of fair value are based on market
prices. For other debt, fair value is estimated based on rates cur-
rently available to the company for debt with similar terms and
remaining maturities.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS MACHINES CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARY COMPANIES
78 2006 Annual Report
equity is subject to specific lock-up provisions that restrict the com-
pany from divesting the securities. These restrictions apply to specific
equity tranches and expire over a three-year period from the closing
date. The Lenovo equity was valued at $542 million at the closing
date and is recorded in Investments and sundry assets in the
Consolidated Statement of Financial Position. In addition, the com-
pany recorded an equity deferral of $112 million to reflect the value
of the lock-up provisions. This deferral was recorded as a contra-
investment in Investments and sundry assets.
As part of the agreements with Lenovo, the company will provide
certain services. These services include marketing support, informa-
tion technology, human resources support and learning services.
These service arrangements are primarily for periods of three years or
less and can be terminated earlier by Lenovo. The company estimated
the fair value of these service arrangements, and, as a result, has
deferred $262 million of the transaction gain. This amount will be
recorded as revenue, primarily in the company’s Global Services seg-
ments, as services are provided to Lenovo. The deferred amount was
recorded in deferred income in Other liabilities in the Consolidated
Statement of Financial Position.
The company also recorded direct and incremental expenses and
related provisions of $254 million associated with the divestiture,
consisting of $74 million for certain indemnities; $64 million for
employee-related charges; $40 million in real estate and information
technology costs; $20 million in transaction expenses; $22 million of
goodwill; and $34 million in other expenses. The company, as part of
the agreement, retained the right and will be given a preference to
provide maintenance, warranty and financing services to Lenovo.
The company retained the warranty liability for all Personal
Computing business products sold prior to the closing date. Lenovo
will have the right to use certain IBM trademarks under a Trademark
License Agreement for a term of five years. In addition, the company
entered into an arm’s-length supply agreement with Lenovo for a
term of five years, designed to provide the company with computers
for its internal use.
In the third quarter of 2005, as a result of the third-party invest-
ments described previously, Lenovo was required to repurchase the
first equity tranche at a specified share price. The equity repurchase
Consolidated Statements .........................................................
Notes .....................................................................................
A-G ......................................................................................... 62
A. Significant Accounting Policies ....................................... 62
B. Accounting Changes........................................................ 71
C. Acquisitions/Divestitures ................................................. 73
D. Financial Instruments (excluding derivatives) ................ 78
E. Inventories ....................................................................... 79
F. Financing Receivables ...................................................... 79
G. Plant, Rental Machines and Other Property ................... 79
H-M ......................................................................................... 80
N-S .......................................................................................... 88
T-X .......................................................................................... 96
Black
MAC
390 CG10