IBM 2006 Annual Report Download - page 23
Download and view the complete annual report
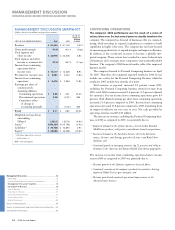
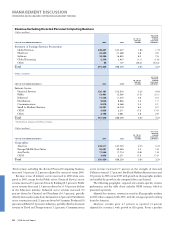
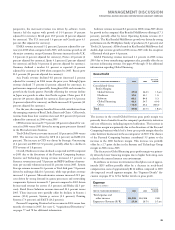
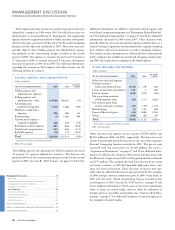
Please find page 23 of the 2006 IBM annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.KEY BUSINESS DRIVERS
The following are some of the key drivers of the company’s business.
Economic Environment and
Corporate Spending Budgets
If overall demand for systems, software and services changes, whether
due to general economic conditions or a shift in corporate buying
patterns, sales performance could be impacted. IBM’s diverse set of
products and offerings is designed to provide more consistent results
in both strong and weak economic environments. The company
accomplishes this by not only having a mix of offerings with long-
term cash and income streams, as well as cyclical transaction-based
sales, but also by continually developing competitive products and
solutions and effectively managing a skilled resource base. IBM con-
tinues to transform itself to take advantage of shifting demand trends,
focusing on client- or industry-specific solutions, business perfor-
mance and open standards.
Internal Business Transformation and
Global Integration Initiatives
IBM continues to drive greater productivity, flexibility and cost sav-
ings by transforming and globally integrating its own business pro-
cesses and functions. In 2006, the company continued the global
integration of its internal support functions—such as Legal, Finance,
Human Resources, Information Technology and Real Estate Site
Operations—which had been previously replicated for many of the
individual countries where IBM operates. In addition to eliminating
redundancies and overhead structures to drive productivity, this inte-
gration has improved IBM’s capacity to innovate by providing greater
clarity of key priorities around shared goals and objectives and led
to a sharper focus for the company on learning, development and
knowledge sharing. The company will continue to focus on global
integration initiatives to improve productivity in its integrated supply
chain, service delivery and internal support functions.
Innovation Initiatives
IBM invests to improve its ability to help its clients innovate.
Investment may occur in the research and development of new prod-
ucts and services, as well as in the establishment of new collaborative
and co-creation relationships with developers, other companies and
other institutions. Examples include IBM’s leadership position in the
design and fabrication of game processors; the design of smaller, faster
and energy-efficient semiconductor devices; and the design of “grid”
computing networks that allow computers to share processing power.
MANAGEMENT DISCUSSION
INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS MACHIN ES CORPORATION AND SUBSI DIARY COMPANIES
21
Through the Global Innovation Outlook (GIO), IBM has opened
up its technical and business forecasting processes to include external
leaders from business, academia, the public sector, nongovernmental
organizations and other influential constituents of the world com-
munity. The GIO takes a deep look at some of the most pressing
issues facing the world and works toward providing solutions to those
needs. In 2006, IBM also announced that it will invest $100 million
over the next two years to pursue 10 new businesses generated by
InnovationJam, an on-line brainstorming session which brought
together more than 150,000 people from 104 countries, including
IBM employees, family members, universities, business partners and
clients from 67 companies. Over two 72-hour sessions, participants
posted more than 46,000 ideas as they explored IBM’s most advanced
research technologies and considered their application to real-world
problems and emerging business opportunities.
Open Standards
The broad adoption of open standards is essential to the computing
model for an on demand business and is a significant driver of col-
laborative innovation across all industries. Without interoperability
among all manner of computing platforms, the integration of any
client’s internal systems, applications and processes remains a monu-
mental and expensive task. The broad-based acceptance of open
standards—rather than closed, proprietary architectures—also allows
the computing infrastructure to more easily absorb (and thus benefit
from) new technical innovations. IBM’s support of open standards is
evidenced by the enabling of its products to support open standards
such as Linux, and the development of Rational software development
tools, which can be used to develop and upgrade other companies’
software products.
Investing in Growth Opportunities
The company is continuing to refocus its business on the higher value
segments of enterprise computing—providing technology and trans-
formation services to clients’ businesses. Consistent with that focus,
the company continues to significantly invest in growth opportunities
as a way to drive revenue growth and market share gains. Areas of
investment include strategic acquisitions, primarily in software and
services, focused client- and industry-specific solutions, maintaining
technology leadership and emerging growth countries such as China,
Russia, India and Brazil.
Black
MAC
CG10