Aflac 2009 Annual Report Download - page 82
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 82 of the 2009 Aflac annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
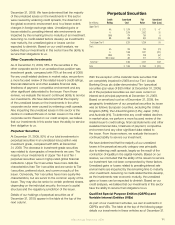
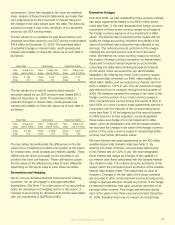
The components of the fair value of the cross-currency and
interest rate swap agreements were reected as an asset or
(liability) in the balance sheet as follows:
(In millions) 2009 2008
Interest rate component $ (3) $ 2
Foreign currency component – (164)
Accrued interest component – 4
Total fair value of cross-currency and interest rate swaps $ (3) $ (158)
The cross-currency swaps expired in April 2009, at which
time we settled the foreign exchange liability balance of
$106 million for these swaps with the applicable swap
counterparties.
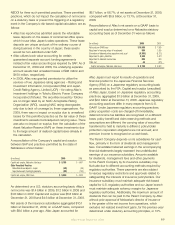
The following is a reconciliation of the foreign currency
component of the cross-currency swaps included in
accumulated other comprehensive income for the years
ended December 31.
(In millions) 2009 2008 2007
Balance, beginning of period $ (164) $ (47) $ (17)
Increase (decrease) in fair value of cross-currency swaps 51 (122) (26)
Interest rate component not qualifying for hedge accounting
reclassified to net earnings – 5 (4)
Balance, end of period $ (113) $ (164) $ (47)
Because the cross-currency swaps were de-designated
as a hedge of the net investment in Aac Japan for the
second quarter of 2009 prior to their expiration, the
foreign exchange loss recorded in accumulated other
comprehensive income for these swaps remained
unchanged from the balance as of March 31, 2009. This
unrealized loss of $113 million would need to be reversed
out of accumulated other comprehensive income and
recognized in earnings if we ever divested of our investment
in Aac Japan. Subsequent to March 31, 2009 and upon
expiration of these swaps, the fair value of the foreign
currency component of the cross-currency swaps increased
by $7 million, therefore we realized this amount as a foreign
exchange gain in earnings during the quarter ended June
30, 2009.
The change in fair value of the interest rate swaps, included
in accumulated other comprehensive income, was
immaterial during each of the years in the three-year period
ended December 31, 2009.
Our exposure to credit risk in the event of nonperformance
by counterparties to our derivatives as of December 31,
2009, was immaterial.
Nonderivative Hedges
During each of the years in the three-year period ended
December 31, 2009, we designated our yen-denominated
Samurai and Uridashi notes and yen-denominated loans
(see Note 7) as nonderivative hedges of the foreign currency
exposure of our investment in Aac Japan.
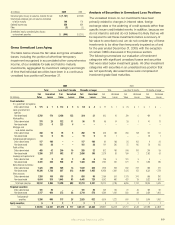
5. DEFERRED POLICY ACQUISITION
COSTS AND INSURANCE EXPENSES
Deferred Policy Acquisition Costs and Insurance
Expenses: Consolidated policy acquisition costs deferred
were $1.30 billion in 2009, compared with $1.24 billion in
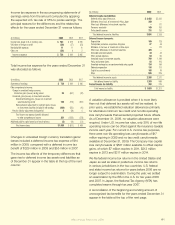
2008 and $1.09 billion in 2007. The following table presents
a rollforward of deferred policy acquisition costs by segment
for the years ended December 31.
2009 2008
(In millions) Japan U.S. Japan U.S.
Deferred policy acquisition costs:
Balance, beginning of year $ 5,644 $ 2,593 $ 4,269 $ 2,385
Capitalization 787 513 658 578
Amortization (523) (419) (405) (370)
Foreign currency translation and other (62) – 1,122 –
Balance, end of year $ 5,846 $ 2,687 $ 5,644 $ 2,593
Commissions deferred as a percentage of total acquisition
costs deferred were 76% in both 2009 and 2008 and 74%
i n 2 0 0 7.
Personnel, compensation and benet expenses as a
percentage of insurance expenses were 43% in both 2009
and 2008 and 44% in 2007. Advertising expense, which
is included in insurance expenses in the consolidated
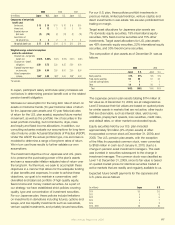
statements of earnings, was as follows for the years ended
December 31:
(In millions) 2009 2008 2007
Advertising expense:
Aflac Japan $ 106 $ 86 $ 83
Aflac U.S. 107 118 95
Total advertising expense $ 213 $ 204 $ 178
Depreciation and other amortization expenses, which
are included in insurance expenses in the consolidated
statements of earnings for the years ended December 31,
appear in the table at the top of the following page.
We’ve got you under our wing.
78