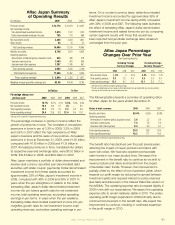
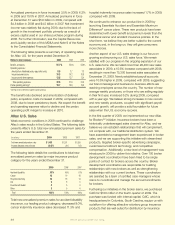
Aflac 2009 Annual Report Download - page 41
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 41 of the 2009 Aflac annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
The increase in our yen-denominated net asset position
was due primarily to the redemption in 2009 of the Parent
Company’s $450 million senior notes (economically yen
debt due to conversion using cross-currency swaps) and
the holding of ¥35.8 billion in cash by the Parent Company
as of December 31, 2009, for the redemption of our yen-
denominated Samurai notes due July 2010.
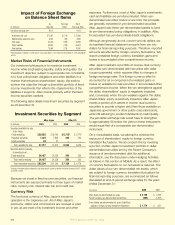
The following table demonstrates the effect of foreign
currency uctuations by presenting the dollar values of our
yen-denominated assets and liabilities, and our consolidated
yen-denominated net asset exposure at selected exchange
rates as of December 31.
We are exposed to economic currency risk only when yen
funds are actually converted into dollars. This primarily
occurs when we repatriate funds from Aac Japan to Aac
U.S., which is generally done annually. The exchange rates
prevailing at the time of repatriation will differ from the
exchange rates prevailing at the time the yen prots were
earned. A portion of the repatriation may be used to service
Aac Incorporated’s yen-denominated notes payable with
the remainder converted into dollars.
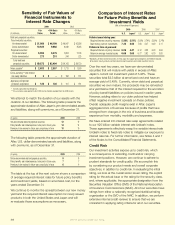
Interest Rate Risk
Our primary interest rate exposure is to the impact of
changes in interest rates on the fair value of our investments
in debt and perpetual securities. We use a modied
duration analysis modeling approach, which measures price
percentage volatility, to estimate the sensitivity of the fair
values of our investments to interest rate changes
on the debt and perpetual securities we own. For
example, if the current duration of a debt security
or perpetual security is 10, then the fair value of
that security will increase by approximately 10%
if market interest rates decrease by 100 basis
points, assuming all other factors remain constant.
Likewise, the fair value of the debt security or
perpetual security will decrease by approximately
10% if market interest rates increase by 100 basis
points, assuming all other factors remain constant.
The estimated effect of potential increases in
interest rates on the fair values of debt and
perpetual securities we own, notes payable,
cross-currency and interest rate swaps and our
obligation to the Japanese policyholder protection
corporation as of December 31 appears in the
table at the top of the following page.
There are various factors that affect the fair value
of our investment in debt and perpetual securities.
Included in those factors are changes in the
prevailing interest rate environment. Changes in
the interest rate environment directly affect the
balance of unrealized gains or losses for a given
period in relation to a prior period. Decreases in
market yields generally improve the fair value of
debt and perpetual securities while increases in
market yields generally have a negative impact on
the fair value of our debt and perpetual securities.
However, we do not expect to realize a majority of
any unrealized gains or losses because we have
the intent and ability to hold such securities until
a recovery of value, which may be maturity. For additional
information on unrealized losses on debt and perpetual
securities, see Note 3 of the Notes to the Consolidated
Financial Statements.
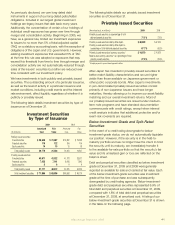
Dollar Value of Yen-Denominated Assets
and Liabilities at Selected Exchange Rates
(In millions) December 31, 2009 December 31, 2008
Yen/dollar exchange rates 77.10 92.10* 107.10 76.03 91.03* 106.03
Yen-denominated financial
instruments:
Assets:
Securities available for sale:
Fixed maturities $ 31,373 $ 26,263 $ 22,585 $ 31,145 $ 26,013 $ 22,333
Perpetual securities 8,350 6,990 6,011 9,343 7,804 6,700
Equity securities 23 19 17 26 22 19
Securities held to maturity:
Fixed maturities 31,640 26,487 22,777 29,018 24,236 20,808
Cash and cash equivalents 1,088 911 783 456 381 327
Other financial instruments 111 93 80 97 80 69
Subtotal 72,585 60,763 52,253 70,085 58,536 50,256
Liabilities:
Notes payable 1,616 1,353 1,163 1,522 1,271 1,091
Cross-currency swaps – – – 731 610 524
Japanese policyholder
protection corporation 153 128 110 192 161 138
Subtotal 1,769 1,481 1,273 2,445 2,042 1,753
Net yen-denominated
financial instruments 70,816 59,282 50,980 67,640 56,494 48,503
Other yen-denominated
assets 8,630 7,225 6,213 8,605 7,187 6,170
Other yen-denominated
liabilities 77,327 64,733 55,667 75,465 63,029 54,113
Consolidated yen-denominated
net assets subject to foreign
currency fluctuation $ 2,119 $ 1,774 $ 1,526 $ 780 $ 652 $ 560
*Actual year-end exchange rate
Aflac Annual Report for 2009 37