Aflac 2009 Annual Report Download - page 40
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 40 of the 2009 Aflac annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Market Risks of Financial Instruments
Our investment philosophy is to maximize investment
income while emphasizing liquidity, safety and quality. Our
investment objective, subject to appropriate risk constraints,
is to fund policyholder obligations and other liabilities in a
manner that enhances shareholders’ equity. We seek to
achieve this objective through a diversied portfolio of xed-
income investments that reects the characteristics of the
liabilities it supports. Aac invests primarily within the xed
income securities markets.
The following table details investment securities by segment
as of December 31.
Because we invest in xed-income securities, our nancial
instruments are exposed primarily to three types of market
risks: currency risk, interest rate risk and credit risk.
Currency Risk
The functional currency of Aac Japan’s insurance
operation is the Japanese yen. All of Aac Japan’s
premiums, claims and commissions are received or paid
in yen, as are most of its investment income and other
expenses. Furthermore, most of Aac Japan’s investments,
cash and liabilities are yen-denominated. When yen-
denominated securities mature or are sold, the proceeds
are generally reinvested in yen-denominated securities.
Aac Japan holds these yen-denominated assets to fund
its yen-denominated policy obligations. In addition, Aac
Incorporated has yen-denominated debt obligations.
Although we generally do not convert yen into dollars, we
do translate nancial statement amounts from yen into
dollars for nancial reporting purposes. Therefore, reported
amounts are affected by foreign currency uctuations. We
report unrealized foreign currency translation gains and
losses in accumulated other comprehensive income.
Aac Japan maintains a portfolio of reverse-dual currency
securities (yen-denominated debt securities with dollar
coupon payments), which exposes Aac to changes in
foreign exchange rates. This foreign currency effect is
accounted for as a component of unrealized gains or
losses on available-for-sale securities in accumulated other
comprehensive income. When the yen strengthens against
the dollar, shareholders’ equity is negatively impacted
and, conversely, when the yen weakens against the dollar,
shareholders’ equity is positively impacted. Aac Japan
invests a portion of its assets in reverse-dual currency
securities to provide a higher yield than those available on
Japanese government or other public corporate bonds,
while still adhering to prudent standards of credit quality.
The yen/dollar exchange rate would have to strengthen
to approximately 55 before the yield on these instruments
would equal that of a comparable yen-denominated
instrument.
On a consolidated basis, we attempt to minimize the
exposure of shareholders’ equity to foreign currency
translation uctuations. We accomplish this by investing
a portion of Aac Japan’s investment portfolio in dollar-
denominated securities and by the Parent Company’s
issuance of yen-denominated debt (for additional
information, see the discussion under Hedging Activities
as follows in this section of MD&A). As a result, the effect
of currency uctuations on our net assets is reduced. The
dollar values of our yen-denominated net assets, which
are subject to foreign currency translation uctuations for
nancial reporting purposes, are summarized as follows
(translated at end-of-period exchange rates) for the years
ended December 31:
(In millions) 2009 2008
Aflac Japan yen-denominated net assets $ 2,736 $ 2,528
Parent Company yen-denominated net liabilities (962) (1,876)
Consolidated yen-denominated net assets (liabilities)
subject to foreign currency translation fluctuations $ 1,774 $ 652
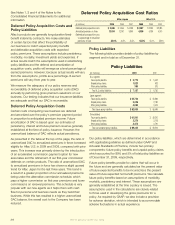
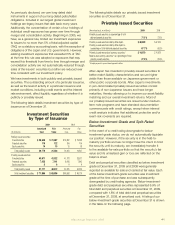
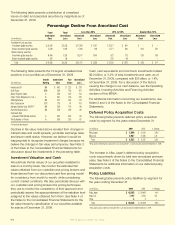
Investment Securities by Segment
Aflac Japan Aflac U.S.
(In millions) 2009 2008 2009 2008
Securities available for sale,
at fair value:
Fixed maturities $ 29,952 $ 29,140 $ 6,712* $ 5,772*
Perpetual securities 7,041 7,843 222 204
Equity securities 24 27 – –
Total available for sale 37,017 37,010 6,934 5,976
Securities held to maturity,
at amortized cost:
Fixed maturities 26,487 24,236 200 200
Total held to maturity 26,487 24,236 200 200
Total investment securities $ 63,504 $ 61,246 $ 7,134 $ 6,176
* Excludes investment-grade, available-for-sale fixed-maturity securities held by the Parent Company of $117 in 2009
and $100 in 2008.
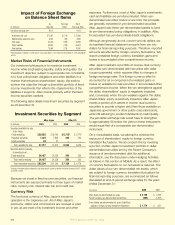
Impact of Foreign Exchange
on Balance Sheet Items
As Exchange Net of
(In millions) Reported Effect Exchange Effect
Yen/dollar exchange rate* 92.10 91.03
Investments and cash $ 73,192 $ (714) $ 73,906
Deferred policy acquisition costs 8,533 (69) 8,602
Total assets 84,106 (799) 84,905
Policy liabilities 69,245 (729) 69,974
Total liabilities 75,689 (778) 76,467
* The exchange rate at December 31, 2009, was 92.10 yen to one dollar, or 1.2% weaker than the December 31, 2008, exchange rate
of 91.03.
We’ve got you under our wing.
36