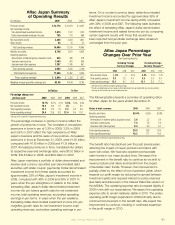
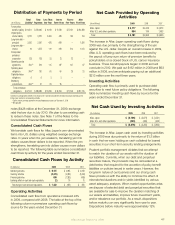
Aflac 2009 Annual Report Download - page 42
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 42 of the 2009 Aflac annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
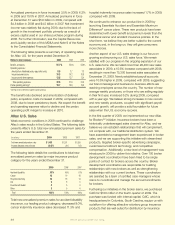
We attempt to match the duration of our assets with the
duration of our liabilities. The following table presents the
approximate duration of Aac Japan’s yen-denominated assets
and liabilities, along with premiums, as of December 31.
The following table presents the approximate duration of
Aac U.S. dollar-denominated assets and liabilities, along
with premiums, as of December 31.
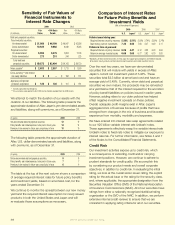
The table at the top of the next column shows a comparison
of average required interest rates for future policy benets
and investment yields, based on amortized cost, for the
years ended December 31.
We continue to monitor the spread between our new money
yield and the required interest assumption for newly issued
products in both the United States and Japan and will
re-evaluate those assumptions as necessary.
Over the next two years, we have yen-denominated
securities that will mature with yields in excess of Aac
Japan’s current net investment yield of 3.43%. These
securities total $3.3 billion at amortized cost and have an
average yield of 5.49%. Currently, when debt and perpetual
securities we own mature, the proceeds may be reinvested
at a yield below that of the interest required for the accretion
of policy benet liabilities on policies issued in earlier years.
However, adding riders to our older policies has helped
offset negative investment spreads on these policies.
Overall, adequate prot margins exist in Aac Japan’s
aggregate block of business because of prots that have
emerged from changes in the mix of business and favorable
experience from mortality, morbidity and expenses.
We have entered into interest rate swap agreements related
to our ¥20 billion variable interest rate Uridashi notes.
These agreements effectively swap the variable interest rate
Uridashi notes to xed rate notes to mitigate our exposure to
interest rate risk. For further information, see Notes 4 and 7
of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
Credit Risk
Our investment activities expose us to credit risk, which
is a consequence of extending credit and/or carrying
investment positions. However, we continue to adhere to
prudent standards for credit quality. We accomplish this
by considering our product needs and overall corporate
objectives, in addition to credit risk. In evaluating the initial
rating, we look at the overall senior issuer rating, the explicit
rating for the actual issue or the rating for the security class,
and, where applicable, the appropriate designation from the
Securities Valuation Ofce (SVO) of the National Association
of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC). All of our securities have
ratings from either a nationally recognized statistical rating
organization or the SVO of the NAIC. In addition, we perform
extensive internal credit reviews to ensure that we are
consistent in applying rating criteria for all of our securities.
(In years)
2009
2008
Yen-denominated debt and perpetual securities 12 12
Policy benefits and related expenses to be paid in future years 14 14
Premiums to be received in future years on policies in force 10 10
(In years)
2009
2008
Dollar-denominated debt and perpetual securities 9 8
Policy benefits and related expenses to be paid in future years 7 7
Premiums to be received in future years on policies in force 6 6
Sensitivity of Fair Values of
Financial Instruments to
Interest Rate Changes
2009
2008
Fair
+100
Basis Fair +100 Basis
(In millions) Value Points Value Points
Debt and perpetual securities:
Fixed-maturity securities:
Yen-denominated $ 51,989 $ 46,199 $ 49,047 $ 43,556
Dollar-denominated 10,620 9,668 9,048 8,246
Perpetual securities:
Yen-denominated 6,990 6,376 7,804 7,103
Dollar-denominated 273 251 244 225
Total debt and
perpetual securities $ 69,872 $ 62,494 $ 66,143 $ 59,130
Notes payable* $ 2,683 $ 2,557 $ 1,713 $ 1,530
Cross-currency** and interest
rate swap liabilities $ 3 $ – $ 158 $ 151
Japanese policyholder
protection corporation $ 128 $ 128 $ 161 $ 161
* Excludes capitalized lease obligations
** Cross-currency swaps expired in April 2009 and are therefore excluded from the 2009 column.
Comparison of Interest Rates
for Future Policy Benets and
Investment Yields
(Net of Investment Expenses)
2009 2008 2007
U.S. *Japan* U.S. *Japan* U.S. *Japan*
Policies issued during year:
Required interest on policy reserves 5.50% 2.51% 5.50% 2.74% 5.50% 2.74%
New money yield on investments 7.22 2.88 7.56 3.27 6.40 3.11
Policies in force at year-end:
Required interest on policy reserves 6.06 4.47 6.12 4.55 6.20 4.63
Return on average invested assets 6.66 3.65 6.77 3.82 6.79 3.83
* Represents yen-denominated investments for Aflac Japan that support policy obligations and therefore excludes
Aflac Japan’s annuity products, and dollar-denominated investments and related investment income
We’ve got you under our wing.
38