Vodafone 2003 Annual Report Download - page 15
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 15 of the 2003 Vodafone annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
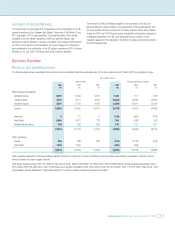
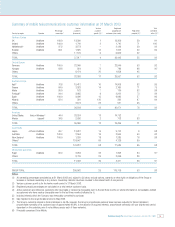
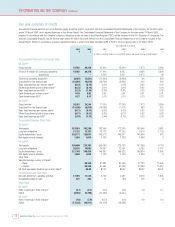
Vodafone Group Plc Annual Report & Accounts and Form 20-F 2003 13
conditions. Price Communications Wireless provided 800 MHz wireless service to
approximately 411,000 customers in the South East of the United States.
In December 2002, Verizon Wireless signed an agreement with Northcoast
Communications LLC, to purchase 50 Personal Communications (“PCS”)
(1800MHz – 1900MHz) licences and related network assets, for approximately
$750 million in cash. The licences cover portions of the East Coast and Midwest,
and serve approximately 47.2 million people. The transaction completed in
May 2003.
Verizon Wireless was the first major US carrier to launch CDMA2000 1XRTT
technology in major metropolitan markets and during the 2003 financial year
Verizon Wireless continued to roll-out its network, extending total coverage to
approximately 85% of the Verizon Wireless footprint, with coverage expected to
reach nearly 100% later in the year.
During the year ended 31 March 2003, Verizon Wireless continued to focus on
gaining and retaining high value customers through new customer additions, the
migration of existing analogue customers to digital price plans and churn
management programmes. Next generation services are expected to provide
business customers with the functionality to use the Verizon Wireless network as
an extension of their corporate Local Area Network or intranet, allowing them to
work from any location where there is coverage. The services will also allow for a
range of multimedia services to be offered, including services such as video and
audio streaming and interactive gaming.
In January 2003, Verizon Wireless withdrew its Registration Statement with the
SEC relating to a proposed initial public offering of a minority stake in the
partnership, stating that it currently has no significant funding needs that would
require it to proceed with the offering. On 10 July 2002, the Cellco Partnership,
doing business as Verizon Wireless, and Verizon Wireless Capital LLC, a wholly
owned subsidiary of the Cellco Partnership, filed a registration statement on
Form S-4 to exchange $4 billion privately placed notes for a new issue of notes
with identical terms registered under the US Securities Act of 1933. The
exchange offer closed on 12 November 2002.
In December 2002, the Federal Communications Commission (“FCC”) refunded
the remaining $261 million on deposit, which represented 15% of the initial
deposit made in relation to the re-auction of licences for 1.9GHz spectrum and
relieved Verizon Wireless of its remaining obligations with respect to the auction.
Mexico
On 4 April 2001, the Group acquired a 34.5% interest in Iusacell. Iusacell
currently provides wireless services in seven of Mexico’s nine regions, covering a
population of 90 million people and representing approximately 90% of the
country’s total population. Roaming is provided in the two remaining regions.
Mexico’s cellular market has continued to expand, with customer growth largely
driven by prepaid products. At 31 March 2003, Iusacell had 2,036,000
registered customers, an increase of 2% since 31 March 2002. Of the total
registered customer base, 83% were prepaid customers.
Iusacell’s financial performance continued to decline in the year despite a
modest increase in its customer base and management’s efforts to restructure
the business through substantial headcount reductions and tight cost and cash
management.
In order to alleviate certain of the resulting financial pressures, Iusacell began a
debt restructuring effort in December 2002 and, in May 2003, secured a
temporary waiver related to its $266 million secured bank credit facility. Iusacell
will continue to work with its financial advisor to restructure the terms and
payment schedules of its various debt agreements and instruments. It is likely
that Iusacell will require additional funding in order to grow its operations.
However, there is no assurance that such funding could be obtained at all or, if
obtainable, on terms which would be acceptable to Iusacell.
As a result of Iusacell’s deteriorating financial performance, the Group has
written off its investment and is currently considering its options with respect to
its investment, including disposal.
Globalstar
In August 2002, the sale of two Globalstar service provider companies,
Globalstar US and Globalstar Caribbean, was finalised. In November 2002, the
Globalstar service provider, Globalstar de Mexico, was sold.
Asia Pacific
The Group’s interests in the Asia Pacific region comprise subsidiary undertakings
in Japan, Australia and New Zealand, associated undertakings in Fiji and India,
and the Group’s interests in China.
Below is a description of the business developments and activities of the Group’s
business activities in the major telecommunications markets in the Asia Pacific
region.
Japan
Through a series of transactions undertaken during the last two financial years,
the Group has an effective 69.7% interest in J-Phone Vodafone.
Japan’s mobile telecommunications market remained robust as mobile services
continued to expand, with market penetration increasing by five percentage
points to 59% at 31 March 2003, compared with 54% at 31 March 2002.
At 31 March 2003, J-Phone Vodafone had approximately 13,912,000 registered
customers and a market share of over 18%. J-Phone Vodafone continued to
capture monthly market share above its cumulative share, with 1,727,000 net
customer additions recorded in the year ended 31 March 2003. One of the key
drivers of this recent growth has been the increase in J-Sky web usage and
content revenue, together with the continued success of J-Phone Vodafone’s
other data offerings, “Sha-mail”, the popular photo-messaging service and the
video-clip messaging service “movie sha-mail”.
At 31 March 2003, J-Phone Vodafone’s PDC (2G) network comprised 101 MSCs
and 13,890 base stations, giving population coverage of 99.7%.
On 30 June 2000, the Ministry of Post and Telecommunications awarded one of
three 3G licences to J-Phone Vodafone (then called J-Phone Communications).
No fees were required by the Japanese government for the licences. J-Phone
Vodafone was the first network operator in the Group to open its 3G network for
service, having commenced nationwide service on 20 December 2002. J-Phone
Vodafone’s 3G network is compatible with the global W-CDMA standard,
providing capability of international W-CDMA and GSM SIM enabled roaming to
Japan for the first time. At 31 March 2003, J-Phone Vodafone had concluded 69
roaming agreements in 62 countries and regions.
The use of micro cell technology has allowed the rapid and cost effective
deployment of J-Phone Vodafone’s 3G network. As at 31 March 2003, J-Phone
Vodafone had 3,644 operational 3G base stations covering over 71% of the
population. By the second half of the 2003 calendar year, J-Phone Vodafone
aims to have 13,275 operational 3G base stations covering over 95% of the
population.