Rogers 2009 Annual Report Download - page 104
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 104 of the 2009 Rogers annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
108 ROGERS COMMUNICATIONS INC. 2009 ANNUAL REPORT
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
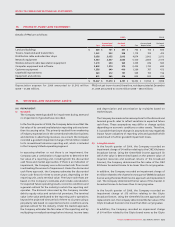
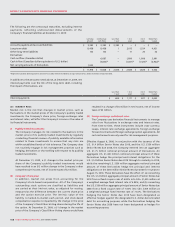
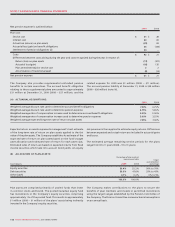
The following are the contractual maturities, excluding interest
payments, reflecting undiscounted disbursements of the
Company’s financial liabilities at December 31, 2009:
Carrying
amount
Contractual
cash flows
Less than
1 year
1 to 3
years
4 to 5
years
More than
5 years
Accounts payable and accrued liabilities $ 2,383 $ 2,383 $ 2,383 $ – $ – $ –
Long-term debt 8,458 8,458 12,012 1,524 4,921
Other long-term liabilities 133 133 –71 20 42
Derivatives:
Cash outflow (Canadian dollar) 6,687 –1,890 1,806 2,991
Cash inflow (Canadian dollar equivalent of U.S. dollar) (5,833)* –(1,387)* (1,524)* (2,922)*
Net carrying amounts of Derivatives 1,002
$ 11,976 $ 11,828 $ 2,384 $ 2,586 $ 1,826 $ 5,032
*Represents Canadian dollar equivalent amount of U.S. dollar inflows matched to an equal amount of U.S. dollar maturities in long-term debt.
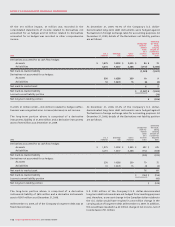
In addition to the amounts noted above, at December 31, 2009, net
interest payments over the life of the long-term debt, including
the impact of Derivatives, are:
Less than
1 year
1 to 3
years
4 to 5
years
More than
5 years
Interest payments $ 680 $ 1,171 $ 827 $ 2,443
(D) MARKET RISK:
Market risk is the risk that changes in market prices, such as
fluctuations in the market prices of the Company’s publicly traded
investments, the Company’s share price, foreign exchange rates
and interest rates, will affect the Company’s income or the value of
its financial instruments.
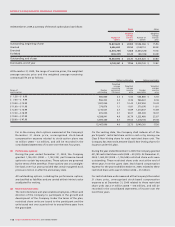
(i) Publicly traded investments:
The Company manages its risk related to fluctuations in the
market prices of its publicly traded investments by regularly
conducting financial reviews of publicly available information
related to these investments to ensure that any risks are
within established levels of risk tolerance. The Company does
not routinely engage in risk management practices such as
hedging, derivatives or short selling with respect to its publicly
traded investments.
At December 31, 2009, a $1 change in the market price per
share of the Company’s publicly traded investments would
have resulted in an $13 million change in the Company’s other
comprehensive income, net of income taxes of $2 million.
(ii) Company’s share price:
In addition, market risk arises from accounting for the
Company’s stock-based compensation. All of the Company’s
outstanding stock options are classified as liabilities and
are carried at their intrinsic value, as adjusted for vesting,
measured as the difference between the current share price
and the option exercise price. The intrinsic value of the
liability is marked-to-market each period, and stock-based
compensation expense is impacted by the change in the price
of the Company’s Class B Non-Voting shares during the life of
the option. At December 31, 2009, a $1 change in the market
price of the Company’s Class B Non-Voting shares would have
resulted in a change of $6 million in net income, net of income
taxes of $3 million.
(iii) Foreign exchange and interest rates:
The Company uses derivative financial instruments to manage
risks from fluctuations in exchange rates and interest rates.
From time-to-time, these instruments include cross-currency
swaps, interest rate exchange agreements, foreign exchange
forward contracts and foreign exchange option agreements. All
such instruments are only used for risk management purposes.
Effective August 6, 2008, in conjunction with the issuance of the
U.S. $1.4 billion Senior Notes due 2018, and the U.S. $350 million
Senior Notes due 2038, the Company entered into an aggregate
U.S. $1.75 billion notional principal amount of Derivatives. An
aggregate U.S. $1,400 million notional principal amount of these
Derivatives hedge the principal and interest obligations for the
U.S. $1.4 billion Senior Notes due 2018 through to maturity in 2018,
while the remaining U.S. $350 million aggregate notional principal
amount of these Derivatives hedge the principal and interest
obligations on the $350 million Senior Notes due 2038 for 10 years to
August 15, 2018. These Derivatives have the effect of: (a) converting
the U.S. $1.4 billion aggregate principal amount of Senior Notes due
2018 from a fixed coupon rate of 6.80% into Cdn. $1,435 million at
a weighted average fixed interest rate of 6.80%; and (b) converting
the U.S. $350 million aggregate principal amount of Senior Notes due
2038 from a fixed coupon rate of 7.50% into Cdn. $359 million at
a weighted average fixed interest rate of 7.53%. The Derivatives
hedging the Senior Notes due 2018 have been designated as
effective hedges against the designated U.S. dollar-denominated
debt for accounting purposes, while the Derivatives hedging the
Senior Notes due 2038 have not been designated as hedges for
accounting purposes.