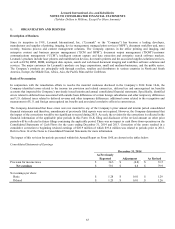
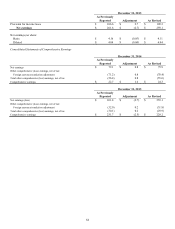
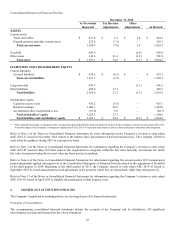
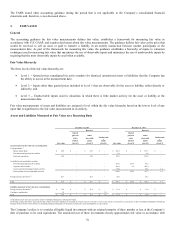
Lexmark 2015 Annual Report Download - page 77
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 77 of the 2015 Lexmark annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.73
Restructuring:
Lexmark records a liability for a cost associated with an exit or disposal activity at its fair value in the period in which the liability is
incurred, except for liabilities for certain employee termination benefit charges that are accrued over time. Employee termination
benefits associated with an exit or disposal activity are accrued when the obligation is probable and estimable as a postemployment
benefit obligation when local statutory requirements stipulate minimum involuntary termination benefits or when a mutual
understanding of termination benefits has been established through written policies or past practice. Specifically for termination
benefits under a one-time benefit arrangement, the timing of recognition and related measurement of a liability depends on whether
employees are required to render service until they are terminated in order to receive the termination benefits and, if so, whether
employees will be retained to render service beyond a minimum retention period. For employees who are not required to render
service until they are terminated in order to receive the termination benefits or employees who will not provide service beyond the
minimum retention period, the Company records a liability for the termination benefits at the communication date. If employees are
required to render service until they are terminated in order to receive the termination benefits and will be retained to render service
beyond the minimum retention period, the Company measures the liability for termination benefits at the communication date and
recognizes the expense and liability ratably over the future service period. For contract termination costs, which primarily includes
leases, Lexmark records a liability for costs to terminate a contract before the end of its term when the Company terminates the
agreement in accordance with the contract terms or when the Company ceases using the rights conveyed by the contract. The
Company records a liability for other costs associated with an exit or disposal activity in the period in which the liability is incurred.
Income Taxes:
The provision for income taxes is determined based on pre-tax income included in the Consolidated Statement of Earnings and current
tax laws in the jurisdictions in which the Company operates. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined under the liability
method based on the differences between the financial statement carrying amounts and tax bases of assets and liabilities measured by
enacted tax rates in effect for the years in which the differences are expected to reverse. A valuation allowance is established to offset
any deferred tax assets if, based upon the available evidence, it is more likely than not that some or all of the deferred tax assets will
not be realized. The Company considers historical profitability, future market growth, future taxable income, the expected timing of
the reversals of existing temporary differences and tax planning strategies in determining the need for a deferred tax valuation
allowance.
The evaluation of tax positions in accordance with the accounting guidance for uncertainty in income taxes is a two-step process. The
first step is recognition, whereby the Company determines whether it is more likely than not, based solely on the technical merits of
the position, that such position will be sustained upon examination, including resolution of any litigation. A tax position that meets the
more likely than not recognition threshold is measured in the second step to determine the amount of benefit to recognize in the
financial statements. The tax position is measured at the largest amount of benefit that is greater than 50 percent likely of being
realized upon ultimate resolution. The Company recognizes interest and penalties on unrecognized tax benefits as part of its income
tax provision.
Derivatives:
All derivatives, including foreign currency exchange contracts, are recognized in the Statements of Financial Position at fair value. For
those agreements subject to master netting agreements or similar arrangements, the Company nets the fair values of its derivative
assets and liabilities for presentation purposes as permitted under the accounting guidance for offsetting. Derivatives that are not
hedges must be recorded at fair value through earnings. If a derivative is a hedge, depending on the nature of the hedge, changes in the
fair value of the derivative are either offset against the change in fair value of underlying assets or liabilities through earnings or
recognized in Accumulated other comprehensive loss until the underlying hedged item is recognized in earnings. Any ineffective
portion of a derivative’s change in fair value is immediately recognized in earnings. Derivatives qualifying as hedges are included in
the same section of the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows as the underlying assets and liabilities being hedged. Changes in the
fair value of the derivatives for fair value hedges are offset against the changes in fair value of the underlying assets or liabilities
through earnings. Changes in the fair value of cash flow hedges are recorded in Accumulated other comprehensive loss, until earnings
are affected by the variability of cash flows of the hedged transaction.
Net (Loss) Earnings Per Share:
Basic net (loss) earnings per share is calculated by dividing net (loss) income by the weighted average number of shares outstanding
during the reported period. The calculation of diluted net (loss) earnings per share is similar to basic, except that the weighted average
number of shares outstanding includes the additional dilution from potential common stock such as stock options, restricted stock
units, and dividend equivalents.