Blackberry 2015 Annual Report Download - page 121
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 121 of the 2015 Blackberry annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
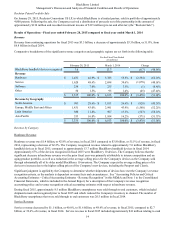
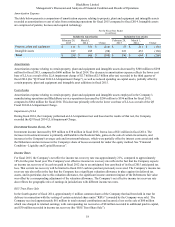
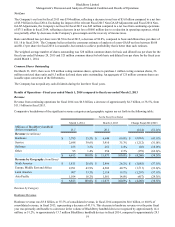
BlackBerry Limited
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
10
fiscal 2015, the Company was not able to reasonably estimate the amount of the potential sell-through programs that may be
offered on certain BlackBerry devices in future periods, resulting in revenues for BlackBerry 10 devices, and BlackBerry 7
devices in certain regions, being recognized only when the devices sold through to end customers.
Hardware
The Company’s use of customer incentives requires management to use significant judgment in evaluating whether prices for
handheld devices are fixed or determinable, which can impact the timing of when hardware revenue is recognized. When the
price isn’t considered fixed or determinable, the Company recognizes revenue when the product is sold through to its end users.
The Company must take into account its past history with its carrier and distribution partners to determine whether it can
reliably estimate whether any future concessions will be provided on products it has previously sold into the channel. The
Company also makes estimates of the level of channel inventory and the likelihood it will sell-through at the prices sold to its
distribution partners. The Company also has to consider external factors such as end customer demand, market acceptance of its
products, cannibalization of new product introductions, the competitive landscape, and technological obsolescence in
determining whether the price is fixed or determinable at the time of shipment. These factors could result in the Company
increasing its customer incentive programs which could impact the results of the Company’s operations. The Company
recognizes these customer incentives at the later of when the Company has recognized the product sale or when the program is
offered.
The Company also uses estimates in determining return provisions for its hardware sales. The Company has limited rights of
return for quality defects based on contractual terms and conditions. The Company’s historical experience is that returns for
defects are immaterial to the results of operations and represent only 0.5% to 1% of total units shipped. However, if defect rates
were to increase beyond those estimated, the Company would be required to recognize additional reductions to revenue. If the
defect rate were to change such that the Company could no longer reliably estimate the return rate, recognition of revenue
could be delayed until a reliable estimate could be made or the return period lapses.
Multiple Element Arrangements
The Company’s process for determining best estimated selling prices (“BESPs”) as it relates to when and if available upgrade
rights to the BlackBerry 10 devices exist involves management’s judgment and multiple factors are considered that may vary
over time depending upon the unique facts and circumstances related to each deliverable. The objective of BESP is to
determine the price at which the Company would transact a sale if the product or service was sold on a stand-alone basis.
Should future facts and circumstances change, the Company’s BESPs and the future rate of related amortization for software
upgrades and non-software services related to future sales of these devices could change. Factors subject to change include the
unspecified software upgrade rights offered, change in pricing of elements sold separately by the Company in the future, the
estimated value of unspecified software upgrade rights, the estimated or actual costs incurred to provide non-software services,
and the estimated period software upgrades and non-software services expected to be provided. Management does not expect
the estimate of BESP to increase in the future given the competitive nature of the industry and the downward trends on its
pricing. It is more likely to decrease in the future, which would result in a positive impact on the results of operations on a go-
forward basis. Management also uses historical data to determine the useful life of the device over which to amortize the
upgrade value. If the life of the device increased, the rate at which revenue is recognized would decrease. Conversely if the life
of the device decreased, the rate at which revenue is recognized would increase. Management reviews its estimates on an
annual basis unless other facts and circumstances arise to warrant a shorter review cycle.
Adoption of Accounting Policies
In April 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (the “FASB”) issued a new accounting standards update on the topic
of reporting discontinued operations and disclosures of disposals of components of an entity. The amendments change the
requirements for reporting discontinued operations by limiting discontinued operations reporting to disposals of components of
an entity that represent strategic shifts that have (or will have) a major effect on an entity's operations and financial results. The
amendments also require expanded disclosures for discontinued operations and certain other disposals that do not qualify for
discontinued operations. The amendments are effective for all disposals (or classifications as held for sale) of components of an
entity that occur within annual periods beginning on or after December 15, 2014 and interim periods within those years, with
early adoption permitted. The Company will adopt this guidance in the first quarter of fiscal 2016.
In May 2014, the FASB issued a new accounting standard on the topic of revenue contracts, which replaces the existing
revenue recognition standard. The new standard amends a number of requirements that an entity must consider in recognizing
revenue and requires improved disclosures to help readers of financial statements better understand the nature, amount, timing
and uncertainty of revenue recognized. For public entities, the new standard is effective for annual reporting periods beginning
after December 15, 2016, including interim periods within that reporting period. Early adoption is not permitted. The Company