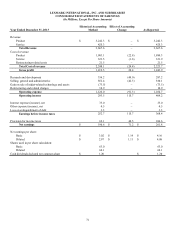
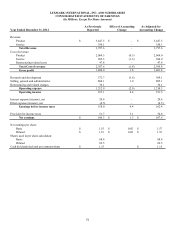
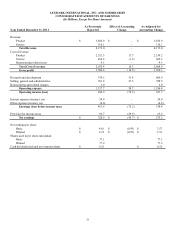
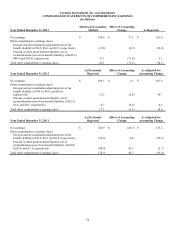
Lexmark 2013 Annual Report Download - page 83
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 83 of the 2013 Lexmark annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
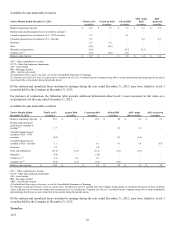
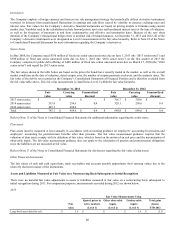
79
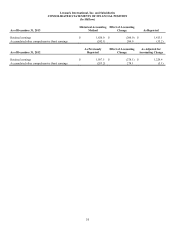
Liability Classified
Cash-based long-term incentive awards based on the Company’s relative total shareholder return were granted in 2012 and 2013. The
fair value of the awards is determined each period under a Monte Carlo simulation, which can result in greater variability in expense
over the period earned. Refer to Note 6 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for more information regarding stock-based
compensation.
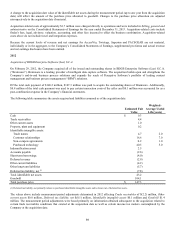
Restructuring:
Lexmark records a liability for a cost associated with an exit or disposal activity at its fair value in the period in which the liability is
incurred, except for liabilities for certain employee termination benefit charges that are accrued over time. Employee termination
benefits associated with an exit or disposal activity are accrued when the obligation is probable and estimable as a postemployment
benefit obligation when local statutory requirements stipulate minimum involuntary termination benefits or, in the absence of local
statutory requirements, termination benefits to be provided are similar to benefits provided in prior restructuring activities. Specifically
for termination benefits under a one-time benefit arrangement, the timing of recognition and related measurement of a liability
depends on whether employees are required to render service until they are terminated in order to receive the termination benefits and,
if so, whether employees will be retained to render service beyond a minimum retention period. For employees who are not required
to render service until they are terminated in order to receive the termination benefits or employees who will not provide service
beyond the minimum retention period, the Company records a liability for the termination benefits at the communication date. If
employees are required to render service until they are terminated in order to receive the termination benefits and will be retained to
render service beyond the minimum retention period, the Company measures the liability for termination benefits at the
communication date and recognizes the expense and liability ratably over the future service period. For contract termination costs,
Lexmark records a liability for costs to terminate a contract before the end of its term when the Company terminates the agreement in
accordance with the contract terms or when the Company ceases using the rights conveyed by the contract. The Company records a
liability for other costs associated with an exit or disposal activity in the period in which the liability is incurred.
Income Taxes:
The provision for income taxes is computed based on pre-tax income included in the Consolidated Statements of Earnings. The
Company estimates its tax liability based on current tax laws in the statutory jurisdictions in which it operates. These estimates include
judgments about the recognition and realization of deferred tax assets and liabilities resulting from the expected future tax
consequences of events that have been included in the financial statements. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are
determined based on the difference between the financial statement carrying amounts and tax bases of assets and liabilities using
enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the differences are expected to reverse.
The Company determines its effective tax rate by dividing its income tax expense by its income before taxes as reported in its
Consolidated Statements of Earnings. For reporting periods prior to the end of the Company’s fiscal year, the Company records
income tax expense based upon an estimated annual effective tax rate. This rate is computed using the statutory tax rate and an
estimate of annual net income by geographic region adjusted for an estimate of non-deductible expenses and available tax credits.
The evaluation of a tax position in accordance with the accounting guidance for uncertainty in income taxes is a two-step process. The
first step is recognition: The enterprise determines whether it is more likely than not that a tax position will be sustained upon
examination, including resolution of any litigation. The second step is measurement: A tax position that meets the more-likely-than-
not recognition threshold is measured to determine the amount of benefit to recognize in the financial statements. The tax position is
measured at the largest amount of benefit that is greater than 50 percent likely of being realized upon ultimate resolution. The
Company recognizes accrued interest and penalties associated with uncertain tax positions as part of its income tax provision.
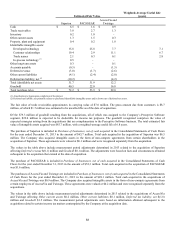
Derivatives:
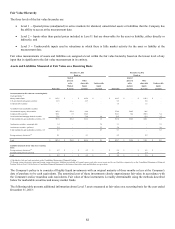
All derivatives, including foreign currency exchange contracts, are recognized in the Statements of Financial Position at fair value.
The Company nets the fair values of its derivative assets and liabilities for presentation purposes as permitted under the accounting
guidance for offsetting. Derivatives that are not hedges must be recorded at fair value through earnings. If a derivative is a hedge,
depending on the nature of the hedge, changes in the fair value of the derivative are either offset against the change in fair value of
underlying assets or liabilities through earnings or recognized in Accumulated other comprehensive earnings (loss) until the
underlying hedged item is recognized in earnings. Any ineffective portion of a derivative’s change in fair value is immediately
recognized in earnings. Derivatives qualifying as hedges are included in the same section of the Consolidated Statements of Cash
Flows as the underlying assets and liabilities being hedged. Changes in the fair value of the derivatives for the fair value hedges were
offset against the changes in fair value of the underlying assets or liabilities through earnings. Changes in the fair value of the cash
flow hedge are recorded in Accumulated other comprehensive earnings (loss), until earnings are affected by the variability of cash
flows of the hedged transaction.
79