Lexmark 2013 Annual Report Download - page 125
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 125 of the 2013 Lexmark annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
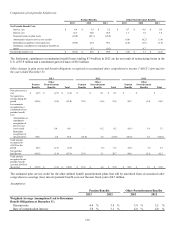
Related to Lexmark’s acquisition of the Information Products Corporation from IBM in 1991, IBM agreed to pay for its pro rata share
(currently estimated at $13.2 million) of future postretirement benefits for all the Company’s U.S. employees based on prorated years
of service with IBM and the Company.
Cash flows:
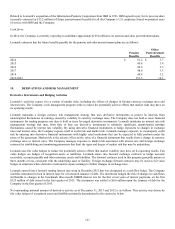
In 2014, the Company is currently expecting to contribute approximately $34 million to its pension and other postretirement plans.
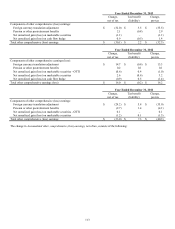
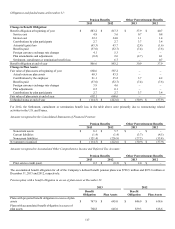
Lexmark estimates that the future benefits payable for the pension and other postretirement plans are as follows:
Pension
Benefits
Other
Postretirement
Benefits
2014 $ 51.2 $ 3.7
2015 49.8 3.4
2016 49.6 3.3
2017 48.8 3.3
2018 48.8 3.2
2019-2023 251.3 14.1
18. DERIVATIVES AND RISK MANAGEMENT
Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities
Lexmark’s activities expose it to a variety of market risks, including the effects of changes in foreign currency exchange rates and
interest rates. The Company’s risk management program seeks to reduce the potentially adverse effects that market risks may have on
its operating results.
Lexmark maintains a foreign currency risk management strategy that uses derivative instruments to protect its interests from
unanticipated fluctuations in earnings caused by volatility in currency exchange rates. The Company does not hold or issue financial
instruments for trading purposes nor does it hold or issue leveraged derivative instruments. Lexmark maintains an interest rate risk
management strategy that may, from time to time use derivative instruments to minimize significant, unanticipated earnings
fluctuations caused by interest rate volatility. By using derivative financial instruments to hedge exposures to changes in exchange
rates and interest rates, the Company exposes itself to credit risk and market risk. Lexmark manages exposure to counterparty credit
risk by entering into derivative financial instruments with highly rated institutions that can be expected to fully perform under the
terms of the agreement. Market risk is the adverse effect on the value of a financial instrument that results from a change in currency
exchange rates or interest rates. The Company manages exposure to market risk associated with interest rate and foreign exchange
contracts by establishing and monitoring parameters that limit the types and degree of market risk that may be undertaken.
Lexmark uses fair value hedges to reduce the potentially adverse effects that market volatility may have on its operating results. Fair
value hedges are hedges of recognized assets or liabilities. Lexmark enters into forward exchange contracts to hedge accounts
receivable, accounts payable and other monetary assets and liabilities. The forward contracts used in this program generally mature in
three months or less, consistent with the underlying asset or liability. Foreign exchange forward contracts may be used as fair value
hedges in situations where derivative instruments expose earnings to further changes in exchange rates.
Lexmark entered into a forward starting interest rate swap in December 2012 that was designated as a cash flow hedge. The Company
used this instrument to lock in interest rates for a forecasted issuance of debt. The instrument hedged the risk of changes in cash flows
attributable to changes in the benchmark three-month LIBOR interest rate for the first seven years of interest payments, on the first
$325 million of debt issued in the first quarter of 2013. The instrument was settled at $0.0 million upon the issuance of debt by the
Company in the first quarter of 2013.
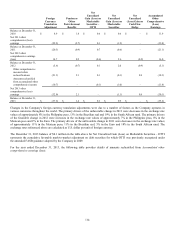
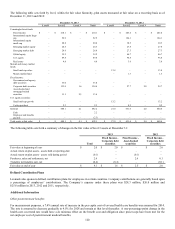
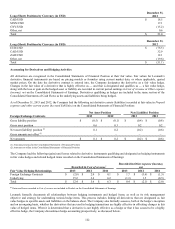
Net outstanding notional amount of derivative activity as of December 31, 2013 and 2012 is as follows. This activity was driven by
fair value hedges of recognized assets and liabilities primarily denominated in the currencies below.
121