Lexmark 2013 Annual Report Download - page 60
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 60 of the 2013 Lexmark annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
56
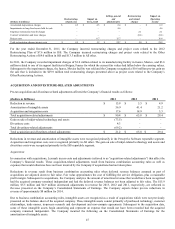
the Company’s future operating cash flows. Additionally, the $14.4 million payment made by the Company in February 2014 related
to the Molina litigation is not included in the table above. Refer to Part II, Item 8, Note 19 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial
Statements for additional information.
Capital Expenditures
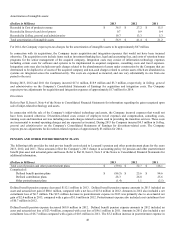
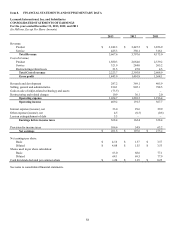
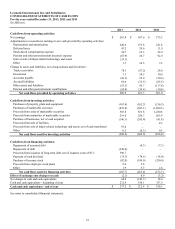
Capital expenditures totaled $167.4 million, $162.2 million, and $156.5 million in 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively. The capital
expenditures for 2013 principally related to building and improvements, infrastructure support (including internal-use software
expenditures) and new product development. The Company expects capital expenditures to be approximately $150 million for full
year 2014, attributable mostly to building and improvements, infrastructure support and new product development. Capital
expenditures in 2014 are expected to be funded through cash from operations; however, if necessary, the Company may use existing
cash and cash equivalents, proceeds from sales of marketable securities or additional sources of liquidity as discussed in the preceding
sections.
EFFECT OF CURRENCY EXCHANGE RATES AND EXCHANGE RATE RISK MANAGEMENT
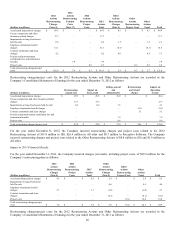
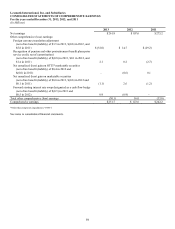
Revenue derived from international sales, including exports from the U.S., accounts for approximately 57% of the Company’s
consolidated revenue, with EMEA accounting for 37% of worldwide sales. Substantially all foreign subsidiaries maintain their
accounting records in their local currencies. Consequently, period-to-period comparability of results of operations is affected by
fluctuations in currency exchange rates. Certain of the Company’s Latin American and European entities use the U.S. dollar as their
functional currency.
Currency exchange rates had a negligible impact on international revenue in 2013 when compared to 2012. Currency exchange rates
had a 3% unfavorable impact on international revenue in 2012 when compared to 2011. The Company may act to mitigate the effects
of exchange rate fluctuations through the use of operational hedges, such as pricing actions and product sourcing decisions.
The Company’s exposure to exchange rate fluctuations generally cannot be minimized solely through the use of operational hedges.
Therefore, the Company utilizes financial instruments such as forward exchange contracts to reduce the impact of exchange rate
fluctuations on certain assets and liabilities, which arise from transactions denominated in currencies other than the functional
currency. The Company does not purchase currency-related financial instruments for purposes other than exchange rate risk
management.
RECENT ACCOUNTING PRONOUNCEMENTS
Refer to Part II, Item 8, Note 2 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for a discussion of recent accounting
pronouncements which is incorporated herein by reference. There are no known material changes and trends nor any recognized future
impact of new accounting guidance beyond the disclosures provided in Note 2.
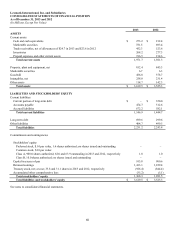
INFLATION
The Company is subject to the effects of changing prices and operates in an industry where product prices are very competitive and
subject to downward price pressures. As a result, future increases in production costs or raw material prices could have an adverse
effect on the Company’s business. In an effort to minimize the impact on earnings of any such increases, the Company must
continually manage its product costs and manufacturing processes. Additionally, monetary assets such as cash, cash equivalents and
marketable securities lose purchasing power during inflationary periods and thus, the Company’s cash and marketable securities
balances could be more susceptible to the effects of increasing inflation.
56