IBM 2004 Annual Report Download - page 19
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 19 of the 2004 IBM annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
MANAGEMENT DISCUSSION
International Business Machines Corporation and Subsidiary Companies
17
ibm annual report 2004
key business drivers
The following are some of the key drivers of the company’s business.
Economic Environment and Corporate IT Spending Budgets
If overall demand for hardware, software and services changes, whether due to general
economic conditions or a shift in corporate buying patterns, sales performance could be
impacted. IBM’s diverse portfolio of products and offerings is designed to gain market
share in strong and weak economic climates. The company accomplishes this by not only
having a mix of offerings with long-term cash and income streams as well as cyclical trans-
action-based sales, but also by continually developing competitive products and solutions
and effectively managing a skilled resource base. IBM continues to transform itself to take
advantage of shifting demand trends, focusing on client or industry-specific solutions,
business performance and open standards.
Internal Business Transformation and Efficiency Initiatives
IBM continues to drive greater productivity and cost savings as it transforms itself into an
on demand enterprise. This includes the internal supply chain initiatives discussed above,
as well as driving collaboration across the IBM enterprise to stimulate innovation and drive
growth. Transformation efforts are improving the company’s management of its costs
worldwide: rebalancing of skills, optimizing its workforce to drive growth, keeping the com-
pany’s compensation programs competitive, and creating a cost-efficient and cutting-edge
IT infrastructure to support its transformation. IBM is extending its supply chain initiatives
to labor costs and other internal processes. Continued success in this area will impact the
company’s cost structure improvements, as well as the amount of competitive leverage it
can apply by passing savings along to clients.
Innovation Initiatives
IBM invests for new and innovative capabilities, products and services. IBM has been moving
away from commoditized categories of the IT industry and into areas in which it can differ-
entiate itself through innovation and by leveraging its investments in R&D. Examples
include IBM’s leadership position in the design and fabrication of ASICs; the design of
smaller, faster and energy-efficient semiconductor devices; the design of “grid” comput-
ing networks that allow computers to share processing power; the transformation and
integration of business processes; and the company’s efforts to advance open technology
standards and to engage with governments, academia, think tanks and nongovernmental
organizations on emerging trends in technology, society and culture. In the highly compet-
itive IT industry, with large diversified competitors as well as smaller and nimble single-
technology competitors, IBM’s ability to continue its cutting-edge innovation is critical to
maintaining and increasing market share. IBM is managing this risk by more closely linking
its R&D organization to industry-specific and client-specific needs, as discussed in
Description of Business —IBM Worldwide Organizations.
Open Standards
The broad adoption of open standards is essential to the computing model for an on
demand business and is a significant driver of collaborative innovation across all industries.
Without interoperability among all manner of computing platforms, the integration of any
client’s internal systems, applications and processes remains a monumental and expensive
task. The broad-based acceptance of open standards— rather than closed, proprietary
architectures— also allows the computing infrastructure to more easily absorb (and thus
benefit from) new technical innovations. IBM is committed to fostering open standards
because they are vital to the On Demand Operating Environment, and because their
acceptance will expand growth opportunities across the entire business services and IT
industry. There are a number of competitors in the IT industry with significant resources
and investments who are committed to closed and proprietary platforms as a way to lock
customers into a particular architecture. This competition will result in increased pricing
pressure and/or IP claims and proceedings. IBM’s support of open standards is evidenced
by the enabling of its products to support open standards such as Linux, and the develop-
ment of Rational software development tools, which can be used to develop and upgrade
any other company’s software products.
Emerging Business Opportunities
The company is continuing to refocus its business on the higher value segments of enter-
prise computing— providing technology and transformation services to clients’ businesses.
Consistent with that focus, the company continues to significantly invest in Emerging
Business Opportunities, as a way to drive revenue growth and market share gain. Areas of
investment include strategic acquisitions, primarily in software and services, information-
based medicine, on demand retail, sensor and actuator solutions, Business Performance
Transformation Services, key technologies (POWER5 and POWERBlade) and emerging
growth countries such as China, Russia, India and Brazil.
Year in Review
results of continuing operations
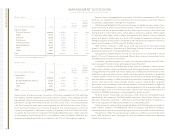
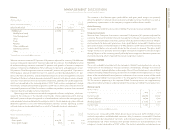
Revenue
(Dollars in millions)
Yr. to Yr.
Percent
Yr. to Yr. Change
Percent Constant
FOR THE YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31: 2004 2003 Change Currency
Statement of Earnings
Revenue Presentation:
Global Services $«46,213 $«42,635 8.4% 3.1%
Hardware 31,154 28,239 10.3 6.5
Software 15,094 14,311 5.5 0.6
Global Financing 2,608 2,826 (7.7) (11.5)
Enterprise Investments/Other 1,224 1,120 9.3 5.2
Total $«96,293 $«89,131 8.0% 3.4%