3M 2010 Annual Report Download - page 59
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 59 of the 2010 3M annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.53
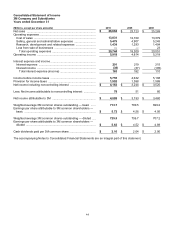
Comprehensive income: Total comprehensive income and the components of accumulated other comprehensive
income (loss) are presented in the Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity and Comprehensive Income.
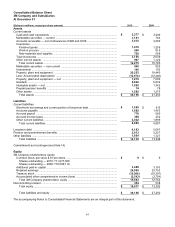
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) is composed of foreign currency translation effects (including
hedges of net investments in international companies), defined benefit pension and postretirement plan adjustments,
unrealized gains and losses on available-for-sale debt and equity securities, and unrealized gains and losses on
cash flow hedging instruments.
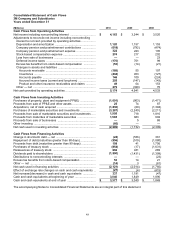
Derivatives and hedging activities: All derivative instruments within the scope of ASC 815, Derivatives and Hedging,
are recorded on the balance sheet at fair value. The Company uses interest rate swaps, currency and commodity
price swaps, and foreign currency forward and option contracts to manage risks generally associated with foreign
exchange rate, interest rate and commodity market volatility. All hedging instruments that qualify for hedge
accounting are designated and effective as hedges, in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting
principles. If the underlying hedged transaction ceases to exist, all changes in fair value of the related derivatives that
have not been settled are recognized in current earnings. Instruments that do not qualify for hedge accounting are
marked to market with changes recognized in current earnings. Cash flows from derivative instruments are classified
in the statement of cash flows in the same category as the cash flows from the items subject to designated hedge or
undesignated (economic) hedge relationships. The Company does not hold or issue derivative financial instruments
for trading purposes and is not a party to leveraged derivatives. However, the Company does have contingently
convertible debt that, if conditions for conversion are met, is convertible into shares of 3M common stock (refer to
Note 10 in this document).
Fair value measurements: 3M follows ASC 820, Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures, with respect to assets
and liabilities that are measured at fair value on a recurring basis and nonrecurring basis. Under the standard, fair
value is defined as the exit price, or the amount that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in
an orderly transaction between market participants as of the measurement date. The standard also establishes a
hierarchy for inputs used in measuring fair value that maximizes the use of observable inputs and minimizes the use
of unobservable inputs by requiring that the most observable inputs be used when available. Observable inputs are
inputs market participants would use in valuing the asset or liability developed based on market data obtained from
sources independent of the Company. Unobservable inputs are inputs that reflect the Company’s assumptions about
the factors market participants would use in valuing the asset or liability developed based upon the best information
available in the circumstances. The hierarchy is broken down into three levels. Level 1 inputs are quoted prices
(unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. Level 2 inputs include quoted prices for similar assets
or liabilities in active markets, quoted prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in markets that are not active,
and inputs (other than quoted prices) that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly. Level 3
inputs are unobservable inputs for the asset or liability. Categorization within the valuation hierarchy is based upon
the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement.
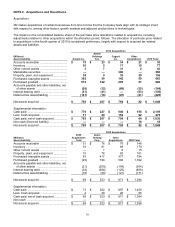
Acquisitions: The Company accounts for business acquisitions in accordance with ASC 805, Business Combinations.
This standard requires the acquiring entity in a business combination to recognize all (and only) the assets acquired
and liabilities assumed in the transaction and establishes the acquisition-date fair value as the measurement
objective for all assets acquired and liabilities assumed in a business combination. Certain provisions of this standard
prescribe, among other things, the determination of acquisition-date fair value of consideration paid in a business
combination (including contingent consideration) and the exclusion of transaction and acquisition-related
restructuring costs from acquisition accounting. 3M applies this standard to business combinations and adjustments
to an acquired entity’s deferred tax asset and liability balances occurring after December 31, 2008. Pre-2009
business combinations were accounted for under a former standard which, among other aspects, required
transaction and acquisition-related restructuring costs to be included in the acquisition purchase accounting and did
not require the recognition of certain contingent consideration as of the acquisition date.
New Accounting Pronouncements
In November 2008, the Financial Accountings Standards Board (FASB) ratified a standard related to certain equity
method investment accounting considerations. The standard indicates, among other things, that transaction costs for
an investment should be included in the cost of the equity-method investment (and not expensed) and shares
subsequently issued by the equity-method investee that reduce the investor’s ownership percentage should be
accounted for as if the investor had sold a proportionate share of its investment, with gains or losses recorded
through earnings. For 3M, the standard was effective for transactions occurring after December 31, 2008. The
adoption of this standard did not have a material impact on 3M’s consolidated results of operations or financial
condition.