3M 2010 Annual Report Download - page 58
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 58 of the 2010 3M annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
52
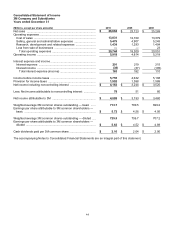
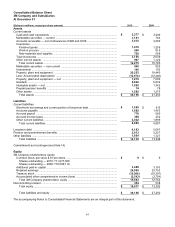
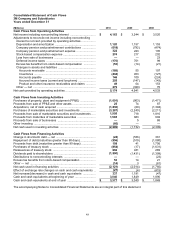
totaled $1.434 billion in 2010, $1.293 billion in 2009 and $1.404 billion in 2008. Research and development
expenses, covering basic scientific research and the application of scientific advances in the development of new
and improved products and their uses, totaled $919 million in 2010, $838 million in 2009 and $851 million in 2008.
Related expenses primarily include technical support provided by 3M to customers who are using existing 3M
products; internally developed patent costs, which include costs and fees incurred to prepare, file, secure and
maintain patents; and amortization of acquired patents.
Internal-use software: The Company capitalizes direct costs of materials and services used in the development of
internal-use software. Amounts capitalized are amortized over a period of three to seven years, generally on a
straight-line basis, unless another systematic and rational basis is more representative of the software’s use.
Amounts are reported as a component of either machinery and equipment or capital leases within property, plant and
equipment.
Environmental: Environmental expenditures relating to existing conditions caused by past operations that do not
contribute to current or future revenues are expensed. Reserves for liabilities related to anticipated remediation costs
are recorded on an undiscounted basis when they are probable and reasonably estimable, generally no later than the
completion of feasibility studies or the Company’s commitment to a plan of action. Environmental expenditures for
capital projects that contribute to current or future operations generally are capitalized and depreciated over their
estimated useful lives.
Income taxes: The provision for income taxes is determined using the asset and liability approach. Under this
approach, deferred income taxes represent the expected future tax consequences of temporary differences between
the carrying amounts and tax basis of assets and liabilities. The Company records a valuation allowance to reduce its
deferred tax assets when uncertainty regarding their realizability exists. As of December 31, 2010 and 2009, the
Company recorded $128 million and $23 million, respectively, of valuation allowances. The Company follows
accounting guidance related to accounting for uncertainty in income taxes to record uncertainties and judgments in
the application of complex tax regulations in a multitude of jurisdictions (refer to Note 8 for additional information).
Earnings per share: The difference in the weighted average 3M shares outstanding for calculating basic and diluted
earnings per share attributable to 3M common shareholders is the result of the dilution associated with the
Company’s stock-based compensation plans. Certain options outstanding under these stock-based compensation
plans during the years 2010, 2009 and 2008 were not included in the computation of diluted earnings per share
attributable to 3M common shareholders because they would not have had a dilutive effect (26.3 million average
options for 2010, 54.3 million average options for 2009, 41.0 million average options for 2008). As discussed in Note
10, the conditions for conversion related to the Company’s Convertible Notes have never been met. If the conditions
for conversion are met, 3M may choose to pay in cash and/or common stock; however, if this occurs, the Company
has the intent and ability to settle this debt security in cash. Accordingly, there was no impact on diluted earnings per
share attributable to 3M common shareholders. The computations for basic and diluted earnings per share for the
years ended December 31 follow:
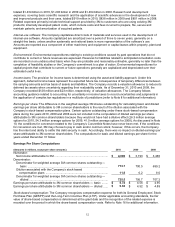
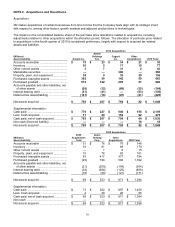
Earnings Per Share Computations
(Amounts in millions, except per share amounts)
2010
2009
2008
Numerator:
Net income attributable to 3M ....................................................................
$
4,085
$
3,193
$
3,460
Denominator:
Denominator for weighted average 3M common shares outstanding —
basic ......................................................................................................
713.7
700.5
699.2
Dilution associated with the Company’s stock-based
compensation plans ...............................................................................
11.8
6.2
8.0
Denominator for weighted average 3M common shares outstanding —
diluted ....................................................................................................
725.5
706.7
707.2
Earnings per share attributable to 3M common shareholders — basic ........
$
5.72
$
4.56
$
4.95
Earnings per share attributable to 3M common shareholders — diluted ......
$
5.63
$
4.52
$
4.89
Stock-based compensation: The Company recognizes compensation expense for both its General Employees’ Stock
Purchase Plan (GESPP) and the Long-Term Incentive Plan (LTIP). Under applicable accounting standards, the fair
value of share-based compensation is determined at the grant date and the recognition of the related expense is
recorded over the period in which the share-based compensation vests. Refer to Note 16 for additional information.