Volvo 2012 Annual Report Download - page 108
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 108 of the 2012 Volvo annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
USD 8.2
BRL 7.5
The Volvo Group’s global operations expose the company to financial risks
in the form of interest rate risks, currency risks, credit risks and liquidity
risks. Work on financial risks comprises an integrated element of the
Volvo Group’s business. Volvo Group strives to minimize these risks by
optimizing the Group’s capital costs by utilizing economies of scale, mini-
mize negative effects on income as a result of changes in currency or
interest rates and to optimize risk exposure. All risks are managed pursu-
ant to the Volvo Group’s established policies in these areas.
The Volvo Group’s risk management related to specific balance sheet
items are thus also described in other areas of the Annual Report, see refer-
ences in the Notes.
Read more about accounting principles for financial instruments in
Note 30, Financial Instruments.
FINANCIAL RISKS
CASH-FLOW RISKS
PRICE RISKS FINANCIAL CURRENCY
EXPOSURE
CURRENCY EXPOSURE
OF EQUITY
COMMERCIAL CURRENCY
EXPOSURE COMMERCIAL CREDIT RISK
FINANCIAL CREDIT RISK
FINANCIAL
COUNTERPARTY RISK
INTEREST-RATE RISKS A
Interest-rate risk refers to the risk that changed interest-rate levels will
affect consolidated earnings and cash flow (cash-flow risks) or the fair
value of financial assets and liabilities (price risks).
POLICY
Matching the interest-fixing terms of financial assets and liabilities
reduces the exposure. Interest-rate swaps are used to change/influence
the interest-fixing term the Volvo Group’s financial assets and liabilities.
Currency interest-rate swaps enable borrowing in foreign currencies from
different markets without introducing currency risk. The Volvo Group also
has standardized interest-rate forward contracts (futures) and FRAs
(forward-rate agreements). Most of these contracts are used to hedge
interest-rate levels for short-term borrowing or investments.
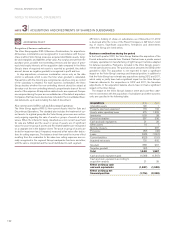
Cash-flow risks
The effect of changed interest rate levels on future currency and interest-
rate flows primarily pertains to the Volvo Group’s customer financing
operations and net financial items. Customer finance operations measure
the degree of matching interest rate fixing on borrowing and lending. The
calculation of the matching degree excludes equity, which amounted to
between 8 and 10% in the customer finance operations. At year-end
2012, the degree of such matching was 99% (97), which was in line with
the Volvo Group’s policy. At year-end 2012, in addition to the assets in its
customer-financing operations, the Volvo Group’s interest-bearing assets
consisted primarily of cash, cash equivalents and liquid assets invested in
short-term interest-bearing securities. The objective is to achieve an
interest-fixing term of three months for the liquid assets in the Volvo
Group’s industrial operations through the use of derivatives. On Decem-
ber 31, 2012, after taking derivatives into account, the average interest on
these assets was 1.1% (1.9). After taking derivatives into account, out-
standing loans had interest terms corresponding to an interest-rate fixing
term of three months and the average interest at year-end amounted to
3.2% (4.1), including the Volvo Group’s credit costs.
Price risks C
Exposure to price risks as result of changed interest-rate levels refers to
financial assets and liabilities with a longer interest-rate fixing term (fixed
interest).
The following table* D shows the effect on income before taxes in
Industrial Operations financial net position , including pensions and similar
net obligations, if interest rates were to increase by 1 percentage point,
(100 basis points) assuming an average interest-rate fixed term of three
months.
* The Note’s sensitivity analysis on interest rate risks is based on simplified
assumptions. It is not unreasonable for market interest rates to change by 1 per-
centage point (100 basis points) on an annual basis. However, in reality, these
rates often rise or decline at different points in time. The sensitivity analysis also
assumes a parallel deferment of the return curve, and that the interest rates on
assets and liabilities will be equally impacted by changes in market interest rates.
Accordingly, the impact of real interest-rate changes may differ from the analysis
presented above. D
INTEREST-RATE RISKS CURRENCY RISKS CREDIT RISKS LIQUIDITY RISKS
INTEREST-RATE RISKS
NOTE 4
GOALS AND POLICIES IN FINANCIAL RISK MANAGEMENT
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
FINANCIAL INFORMATION 2012
104