SunTrust 2005 Annual Report Download - page 91
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 91 of the 2005 SunTrust annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
SUNTRUST ANNUAL REPORT 89
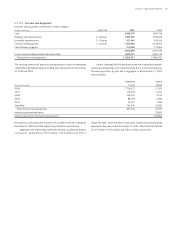
The accumulated benefit obligation for the Retirement Benefits at the
end of and was . billion and . billion, respectively. For
the Supplemental Retirement Benefits, the accumulated benefit obliga-
tion at the end of and was . million and . million,
respectively.
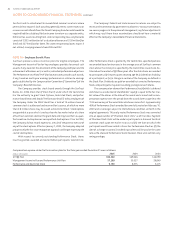
(Dollars in thousands) % Increase % Decrease
Effect on Post Retirement benefit obligation , (,)
Assumed healthcare cost trend rates have a significant effect on the
amounts reported for the post retirement plans. As of December , ,
SunTrust assumed that retiree health care costs will increase at an initial
rate of .% per year. SunTrust assumed a healthcare cost trend that rec-
ognizes expected medical inflation, technology advancements, rising cost
of prescription drugs, regulatory requirements and Medicare cost shifting.
SunTrust expects this annual cost increase to decrease over a -year period
to .% per year. Due to changing medical inflation, it is important to
understand the effect of a one-percent point change in assumed healthcare
cost trend rates. These amounts are shown below:
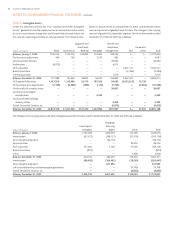
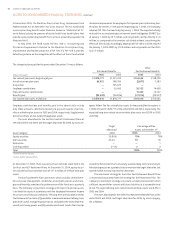
The change in benefit obligations for the years ended December was as follows:
Supplemental Other
Retirement Benefits Retirement Benefits Post Retirement Benefits
(Dollars in thousands)
Benefit obligation, beginning of year ,, ,, , , , ,
Service cost , , , , , ,
Interest cost , , , , , ,
Plan participants’ contributions — — — — , ,
Amendments — — , , — —
Actuarial loss (gain) , , , , , (,)
NCF acquisition — , — , , ,
Benefits paid (,) (,) (,) (,) (,) (,)
Benefit obligation, end of year ,, ,, , , , ,
Supplemental Other
(Weighted average assumptions used to Retirement Benefits Retirement Benefits Post Retirement Benefits
determine benefit obligations, end of year)
Discount rate .% .% .% .% .% .%
Rate of compensation increase . . . . N/A N/A
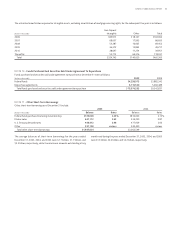
A discount rate is used to determine the present value of future ben-
efit obligations. The discount rate for each plan is determined by matching
the expected cash flows of each plan to a yield curve based on long term,
high quality fixed income debt instruments available as of the measure-
ment date. A string of benefit payments projected to be paid by the plan
for the next years is developed based on most recent census data, plan
provisions and assumptions. The benefit payments at each future maturity
are discounted by the year-appropriate spot interest rates (which are devel-
oped from a yield curve of approximately Aa quality bonds with similar
maturities as the benefit payments). The model then solves for the constant
discount rate that produces the same present value of the projected benefit
payments as generated by discounting each year’s payments by the spot
rate. This assumption is reviewed by the SunTrust Benefit Plan Committee
and updated every year for each plan.
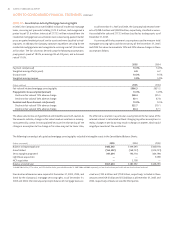
A rate of compensation growth is used to determine future benefit
obligations for those plans whose benefits vary by pay. Based on a
study of recent SunTrust salary increase experience and projections of real
inflation, wage growth, and merit increases, SunTrust has increased its
compensation increase assumption from .% to .% from year end
to year end .
Actuarial gains and losses are created when actual experience deviates
from assumptions. The main sources of actuarial losses for result from
lower discount rates, higher salary increase assumptions, changes made to
refine turnover and retirement assumptions, and the use of a more current
mortality table.