SunTrust 2005 Annual Report Download - page 40
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 40 of the 2005 SunTrust annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
SUNTRUST ANNUAL REPORT38
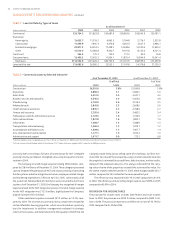
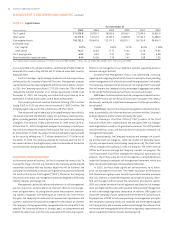
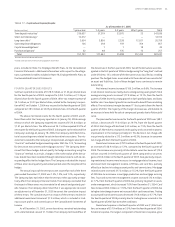
TABLE • Risk Management Derivative Financial Instruments
The Company monitors its sensitivity to changes in interest rates and may
use derivative instruments to limit the volatility of net interest income.
Derivative instruments increased net interest income in and by
. million and . million, respectively, or seven basis points and
basis points, respectively. The following tables summarize the deriva-
tive instruments entered into by the Company as an end-user. See Note
, Derivatives And Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements, to the Consolidated
Financial Statements for a complete description of the derivative instru-
ments and activities for and .
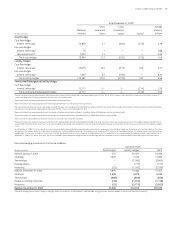
As of December ,
Gross Gross Average
Notional Unrealized Unrealized Maturity
(Dollars in millions) Amount Gains Losses Equity in Years
Asset Hedges
Cash flow hedges
Interest rate swaps , — () () .
Fair value hedges
Forward contracts , — () — .
Total asset hedges , — () () .
Liability Hedges
Cash flow hedges
Interest rate swaps and swaptions , — .
Fair value hedges
Interest rate swaps , () — .
Total liability hedges , () .
Terminated/Dedesignated Liability Hedges
Cash flow hedges
Interest rate swaps , — — () .
Fair value hedges
Interest rate swaps — — .
Total terminated/dedesignated hedges , — () .
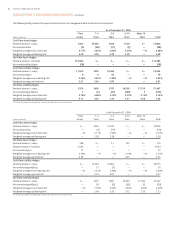
Includes only derivative financial instruments which are currently, or previously designated as, qualifying hedges under SFAS No. . All of the Company’s other derivative instruments are classified as trading. All interest
rate swaps have variable pay or receive rates with resets of six months or less.
Represents interest rate swaps designated as cash flow hedges of commercial loans.
Forward contracts are designated as fair value hedges of closed mortgage loans, including both fixed and floating, which are held for sale. Certain other forward contracts which are effective for risk management purposes,
but which are not in designated hedging relationships under SFAS No. , are not incorporated in this table.
Represents interest rate swaps and options designated as cash flow hedges of floating rate certificates of deposit, Global Bank Notes, FHLB Advances and other variable rate debt.
Represents interest rate swaps designated as fair value hedges of trust preferred securities, subordinated notes, FHLB Advances, certificate and time deposits and other fixed rate debt.
Represents the fair value of derivative financial instruments less accrued interest receivable or payable.
Represents interest rate swaps that have been terminated and/or dedesignated as derivatives that qualified for hedge accounting. The interest rate swaps were designated as cash flow hedges of floating rate debt and tax
exempt bonds. The . million of net losses, net of taxes, recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income will be reclassified into earnings as interest expense over the life of the respective hedged items.
Represents interest rate swaps that have been terminated as derivatives that qualified for hedge accounting. The interest rate swaps were designated as fair value hedges of fixed rate debt. The . million of pre-tax net
gains recorded in a valuation account in long-term debt will be reclassified into earnings as a yield adjustment of the hedged item in the same period that the hedged cash flows impact earnings. As of December , ,
. million of pre-tax net gains are expected to be reclassified as interest expense or interest income during the next twelve months.
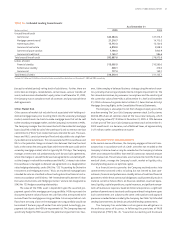
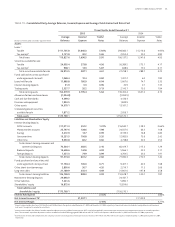
As of December , , the net unrealized loss on derivatives included in accumulated other comprehensive income, which is a component of stockholders’ equity, was . million, net of income taxes. Of this net
of tax amount, a . million loss represents the effective portion of the net losses on derivatives that currently qualify as cash flow hedges, and an . million loss relates to previous qualifying cash flow hedging rela-
tionships that have been terminated or dedesignated. Gains or losses on hedges of interest rate risk will be classified into interest income or expense as a yield adjustment of the hedged item in the same period that the
hedged cash flows impact earnings. As of December , , . million of net losses, net of taxes, recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income are expected to be reclassified as interest income or interest
expense during the next twelve months.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS continued