SunTrust 2005 Annual Report Download - page 37
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 37 of the 2005 SunTrust annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.SUNTRUST ANNUAL REPORT 35
As part of its risk governance framework, the Company has also estab-
lished various risk management-related committees. These committees
are jointly responsible for ensuring adequate risk measurement and man-
agement in their respective areas of authority. These committees include:
ALCO, Corporate Product Risk Assessment Committee (“PRAC”), Credit
Management Committee, Operational Risk Committee and SERP Steering
Committee. Additionally, the Company has established an Enterprise Risk
Committee (“ERC”), chaired by the CRO, which is responsible for support-
ing the CRO in managing the Company’s aggregate risk profile. The ERC
consists of various senior executives throughout the Company and meets
on a monthly basis.
The Board of Directors is wholly responsible for oversight of the
Company’s corporate risk governance process. In , the Company
formed the Risk Committee of the Board, which assists the Board of
Directors in executing this responsibility.
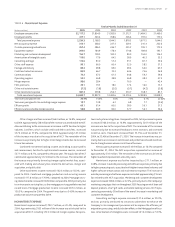
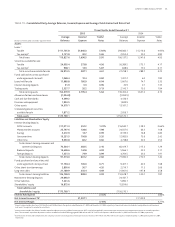
CREDIT RISK MANAGEMENT
Credit risk refers to the potential for economic loss arising from the fail-
ure of SunTrust clients to meet their contractual agreements on all credit
instruments, including on-balance sheet exposures from loans and leases,
contingent exposures from unfunded commitments, letters of credit, credit
derivatives, and counterparty risk under interest rate and foreign exchange
derivative products. As credit risk is an essential component of many of the
products and services provided by the Company to its clients, the ability
to accurately measure and manage credit risk is integral to maintain both
the long-run profitability of its lines of business and capital adequacy of the
enterprise.
SunTrust manages and monitors extensions of credit risk through
initial underwriting processes and periodic reviews. SunTrust maintains
underwriting standards in accordance with credit policies and procedures,
and Credit Risk Management conducts independent risk reviews to ensure
active compliance with all policies and procedures. Credit Risk Management
periodically reviews its lines of business to monitor asset quality trends and
the appropriateness of credit policies. In particular, total borrower exposure
limits are established and concentration risk is monitored. SunTrust has
made a major commitment to maintain and enhance comprehensive credit
systems in order to be compliant with business requirements and evolv-
ing regulatory standards. As part of a continuous improvement process,
SunTrust Credit Risk Management evaluates potential enhancements to its
risk measurement and management tools, implementing them as appropri-
ate along with amended credit policies and procedures.
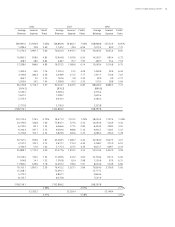
Borrower/counterparty (obligor) risk and facility risk are evaluated
using the Company’s risk rating methodology, which has been implemented
in the lines of business representing the largest total credit exposures.
SunTrust uses various risk models in the estimation of expected and unex-
pected losses. These models incorporate both internal and external default
and loss experience. To the extent possible, the Company collects internal
data to ensure the validity, reliability, and accuracy of its risk models used in
default and loss estimation.
OPERATIONAL RISK MANAGEMENT
SunTrust faces ongoing and emerging risk and regulatory pressure related
to the activities that surround the delivery of banking and financial prod-
ucts. Coupled with external influences such as market conditions, fraudu-
lent activities, disasters, security risks, country, and legal risk, the potential
for operational and reputational loss has increased significantly.
SunTrust believes that effective management of operational risk
plays a major role in both the level and the stability of the profitability of
the institution. Operational risk is the risk of monetary loss resulting from
inadequate or failed internal processes, people and systems, or from exter-
nal events. To meet the demands of today’s business risk environment,
SunTrust has established a corporate level Operational Risk Management
function, headed by the CRO, to implement a “best in class” operational
risk management program that will reduce the risk of operational losses
and enhance shareholder value.
Two committees have been formed to manage operational risk in the
organization-the Operational Risk Committee (“ORC”) and the Operational
Risk Forum (“ORF”). The ORC is composed of senior managers who review
and discuss potential material operational risk issues faced by the Company.
The ORF operates as a communications group disseminating operational
risk information to the Risk Managers for the Lines of Business/Functions of
the Company, and providing feedback to corporate risk management and
executive risk committees on risk-related strategies and issues.
The corporate governance structure also includes a Risk Manager and
support staff embedded within each line of business and corporate func-
tion. These risk managers, while reporting directly to their respective line or
function, facilitate communications with the Company’s risk functions and
execute the requirements of the corporate framework and policy. The Risk
Manager works closely with the corporate Operational Risk Management
function to ensure consistency and best practices.
A key component of the SERP is the implementation of a robust
Operational Risk Management framework that organizationally identifies,
assesses, controls, quantifies, monitors, and reports on operational risks
companywide. The goal of this framework is to implement effective opera-
tional risk techniques and strategies, minimize operational losses through
enhanced collection and reporting of loss event data, and strengthen
SunTrust’s performance by minimizing operational capital allocation
requirements.
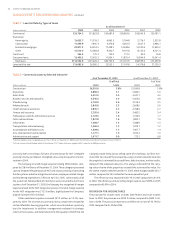
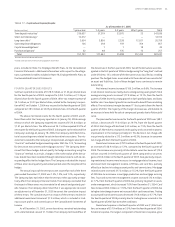
MARKET RISK MANAGEMENT
Market risk refers to potential losses arising from changes in interest rates,
foreign exchange rates, equity prices, commodity prices and other relevant
market rates or prices. Interest rate risk, defined as the exposure of net
interest income and Economic Value of Equity (“EVE”) to adverse move-
ments in interest rates, is SunTrust’s primary market risk, and mainly arises
from the structure of the balance sheet (non-trading activities). SunTrust
is also exposed to market risk in its trading activities, mortgage servicing
rights, mortgage warehouse and pipeline, and equity holdings of The Coca-
Cola Company common stock. ALCO meets regularly and is responsible
for reviewing the interest-rate sensitivity position of the Company and
establishing policies to monitor and limit exposure to interest rate risk. The
policies established by ALCO are reviewed and approved by the Company’s
Board of Directors.
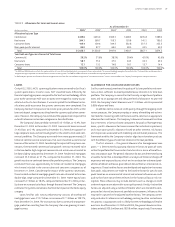
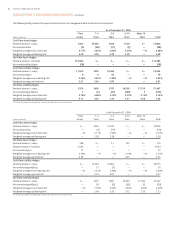
Market Risk From Non-trading Activities
The primary goal of interest rate risk management is to control exposure
to interest rate risk, both within policy limits approved by ALCO and the
Board and within narrower guidelines established by ALCO. These limits
and guidelines reflect SunTrust’s tolerance for interest rate risk over both
short-term and long-term horizons.
The major sources of the Company’s non-trading interest rate risk are
timing differences in the maturity and repricing characteristics of assets