Berkshire Hathaway 2015 Annual Report Download - page 9
Download and view the complete annual report
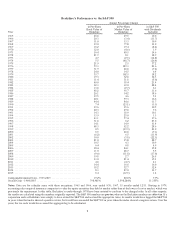
Please find page 9 of the 2015 Berkshire Hathaway annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.‹Berkshire increased its ownership interest last year in each of its “Big Four” investments – American
Express, Coca-Cola, IBM and Wells Fargo. We purchased additional shares of IBM (increasing our
ownership to 8.4% versus 7.8% at yearend 2014) and Wells Fargo (going to 9.8% from 9.4%). At the other
two companies, Coca-Cola and American Express, stock repurchases raised our percentage ownership. Our
equity in Coca-Cola grew from 9.2% to 9.3%, and our interest in American Express increased from 14.8%
to 15.6%. In case you think these seemingly small changes aren’t important, consider this math: For the
four companies in aggregate, each increase of one percentage point in our ownership raises Berkshire’s
portion of their annual earnings by about $500 million.
These four investees possess excellent businesses and are run by managers who are both talented and
shareholder-oriented. Their returns on tangible equity range from excellent to staggering. At Berkshire, we
much prefer owning a non-controlling but substantial portion of a wonderful company to owning 100% of
a so-so business. It’s better to have a partial interest in the Hope Diamond than to own all of a rhinestone.
If Berkshire’s yearend holdings are used as the marker, our portion of the “Big Four’s” 2015 earnings
amounted to $4.7 billion. In the earnings we report to you, however, we include only the dividends they
pay us – about $1.8 billion last year. But make no mistake: The nearly $3 billion of these companies’
earnings we don’t report are every bit as valuable to us as the portion Berkshire records.
The earnings our investees retain are often used for repurchases of their own stock – a move that increases
Berkshire’s share of future earnings without requiring us to lay out a dime. The retained earnings of these
companies also fund business opportunities that usually turn out to be advantageous. All that leads us to
expect that the per-share earnings of these four investees, in aggregate, will grow substantially over time. If
gains do indeed materialize, dividends to Berkshire will increase and so, too, will our unrealized capital
gains.
Our flexibility in capital allocation – our willingness to invest large sums passively in non-controlled
businesses – gives us a significant edge over companies that limit themselves to acquisitions they will
operate. Woody Allen once explained that the advantage of being bi-sexual is that it doubles your chance
of finding a date on Saturday night. In like manner – well, not exactly like manner – our appetite for either
operating businesses or passive investments doubles our chances of finding sensible uses for Berkshire’s
endless gusher of cash. Beyond that, having a huge portfolio of marketable securities gives us a stockpile
of funds that can be tapped when an elephant-sized acquisition is offered to us.
************
It’s an election year, and candidates can’t stop speaking about our country’s problems (which, of course,
only they can solve). As a result of this negative drumbeat, many Americans now believe that their children will not
live as well as they themselves do.
That view is dead wrong: The babies being born in America today are the luckiest crop in history.
American GDP per capita is now about $56,000. As I mentioned last year that – in real terms – is a
staggering six times the amount in 1930, the year I was born, a leap far beyond the wildest dreams of my parents or
their contemporaries. U.S. citizens are not intrinsically more intelligent today, nor do they work harder than did
Americans in 1930. Rather, they work far more efficiently and thereby produce far more. This all-powerful trend is
certain to continue: America’s economic magic remains alive and well.
Some commentators bemoan our current 2% per year growth in real GDP – and, yes, we would all like to
see a higher rate. But let’s do some simple math using the much-lamented 2% figure. That rate, we will see, delivers
astounding gains.
7