Berkshire Hathaway 2015 Annual Report Download - page 82
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 82 of the 2015 Berkshire Hathaway annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Management’s Discussion and Analysis (Continued)
Insurance—Underwriting (Continued)
Berkshire Hathaway Reinsurance Group (Continued)
Property/casualty (Continued)
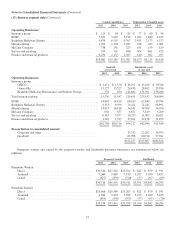
The property/casualty business generated pre-tax underwriting gains of $1.4 billion in 2014 compared to $1.2 billion in
2013. In each year, the underwriting gains were primarily attributable to our property business, which benefitted from relatively
low loss ratios, and the favorable run-off of prior years’ business, including the Swiss Re contract.
Retroactive reinsurance
Retroactive reinsurance policies provide indemnification of losses and loss adjustment expenses with respect to past loss
events, and related claims are generally expected to be paid over long periods of time. At the inception of a contract, deferred
charge assets are recorded for the excess, if any, of the estimated ultimate losses payable over the premiums earned. Deferred
charges are subsequently amortized over the estimated claims payment period based on estimates of the timing and amount of
future loss payments. The original estimates of the timing and amount of loss payments are periodically analyzed against actual
experience and revised based on an actuarial evaluation of the expected remaining losses. Amortization charges and deferred
charge adjustments resulting from changes to the estimated timing and amount of future loss payments are included in periodic
earnings.
Premiums earned from retroactive reinsurance contracts were not significant in 2015 or 2013, whereas premiums in 2014
included $3 billion from a single contract with Liberty Mutual Insurance Company (“LMIC”). Under the LMIC agreement, we
reinsure substantially all of LMIC’s unpaid losses and allocated loss adjustment expense liabilities related to (a) asbestos and
environmental claims from policies incepting prior to 2005 and (b) workers’ compensation claims occurrences arising prior to
January 1, 2014, in excess of an aggregate retention of approximately $12.5 billion and subject to an aggregate limit of $6.5
billion.
Pre-tax underwriting losses from retroactive reinsurance policies were $469 million in 2015, $632 million in 2014 and
$333 million in 2013. In each year, underwriting losses included deferred charge amortization and foreign currency transaction
gains or losses associated with foreign currency denominated reinsurance liabilities of U.S.-based subsidiaries. In 2015 and
2014, foreign currency exchange rate movements produced decreases in liabilities, generating pre-tax gains of $150 million and
$273 million, respectively. Foreign currency gains/losses were not significant in 2013.
Retroactive reinsurance underwriting results were also impacted during the last two years by increases in the estimated
ultimate liabilities for contracts written in prior years, partially offset by increases in related deferred charge balances. The
liability increases were approximately $550 million in 2015 and $825 million in 2014. In each year, the ultimate liability
increases primarily related to asbestos and environmental exposures. We also re-estimated the timing of future payments of such
liabilities as part of our actuarial analysis. The increase in ultimate liabilities, net of related deferred charge adjustments,
produced incremental pre-tax underwriting losses of approximately $90 million in 2015 and $450 million in 2014.
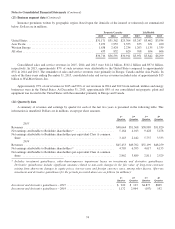
Gross unpaid losses from retroactive reinsurance contracts were approximately $23.7 billion at December 31, 2015, $24.3
billion at December 31, 2014 and $17.7 billion at December 31, 2013. Unamortized deferred charges related to BHRG’s
retroactive reinsurance contracts were approximately $7.6 billion at December 31, 2015, $7.7 billion at December 31, 2014 and
$4.25 billion at December 31, 2013. As of December 31, 2015, over 80% of unpaid losses and deferred charge balances were
concentrated in six contracts.
Life and annuity
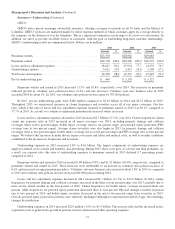
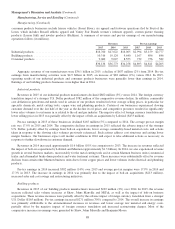
BHRG’s life and annuity underwriting results are summarized as follows (in millions).
Premiums earned Pre-tax underwriting gain (loss)
2015 2014 2013 2015 2014 2013
Periodic payment annuity .................................. $1,286 $1,105 $1,413 $(202) $(197) $(213)
Life reinsurance .......................................... 1,481 1,555 191 (45) (23) 336
Variable annuity guarantee ................................. 19 21 1,705 193 47 256
$2,786 $2,681 $3,309 $ (54) $(173) $ 379
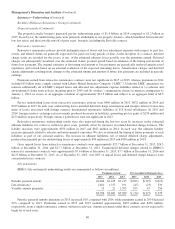
Periodic payment annuity premiums in 2015 increased 16% compared with 2014, while premiums earned in 2014 declined
22% compared to 2013. Premiums earned in 2015 and 2013 included approximately $425 million and $470 million,
respectively, from a single reinsurance contract written in each year. Annuity payments under these contracts are not expected to
begin for several years.
80