Berkshire Hathaway 2014 Annual Report Download - page 58
Download and view the complete annual report
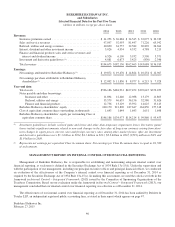
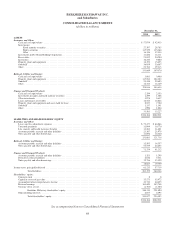
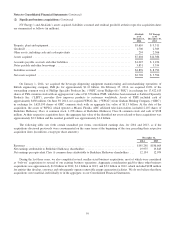
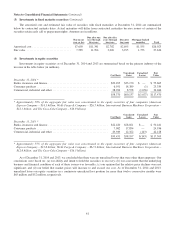
Please find page 58 of the 2014 Berkshire Hathaway annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
(1) Significant accounting policies and practices (Continued)
(k) Revenue recognition (Continued)
Railroad transportation revenues are recognized based upon the proportion of service provided as of the balance sheet
date. Customer incentives, which are primarily provided for shipping a specified cumulative volume or shipping to/
from specific locations, are recorded as pro-rata reductions to revenue based on actual or projected future customer
shipments. When using projected shipments, we rely on historic trends as well as economic and other indicators to
estimate the recorded liability for customer incentives.
Interest income from investments in fixed maturity securities and loans is earned under the interest method, which
reflects accrual of interest due under terms of the agreements as well as amortization of acquisition premiums,
accruable discounts and capitalized loan origination fees, as applicable. Dividends from equity securities are
recognized when earned, which is usually on the ex-dividend date.
(l) Losses and loss adjustment expenses
Liabilities for losses and loss adjustment expenses are established under property/casualty insurance and reinsurance
contracts issued by our insurance subsidiaries for losses that have occurred as of the balance sheet date. The liabilities
for losses and loss adjustment expenses are recorded at the estimated ultimate payment amounts, except that amounts
arising from certain workers’ compensation reinsurance business are discounted. Estimated ultimate payment amounts
are based upon (1) reports of losses from policyholders, (2) individual case estimates and (3) estimates of incurred but
not reported losses.
Provisions for losses and loss adjustment expenses are charged to earnings after deducting amounts recovered and
estimates of recoverable amounts under ceded reinsurance contracts. Reinsurance contracts do not relieve the ceding
company of its obligations to indemnify policyholders with respect to the underlying insurance and reinsurance
contracts.
The estimated liabilities of workers’ compensation claims assumed under certain reinsurance contracts are discounted
based upon an annual discount rate of 4.5% for claims arising prior to January 1, 2003 and 1% for claims arising
thereafter, consistent with discount rates used under insurance statutory accounting principles. The change in such
reserve discounts, including the periodic discount accretion is included in earnings as a component of losses and loss
adjustment expenses.
(m) Deferred charges reinsurance assumed
The excess, if any, of the estimated ultimate liabilities for claims and claim settlement costs over the premiums earned
with respect to retroactive property/casualty reinsurance contracts is recorded as a deferred charge at inception of the
contract. Deferred charges are subsequently amortized using the interest method over the expected claim settlement
periods. Changes to the estimated timing or amount of loss payments produce changes in periodic amortization.
Changes in such estimates are applied retrospectively and are included in insurance losses and loss adjustment
expenses in the period of the change. The unamortized deferred charge balances are included in other assets and were
$7,772 million and $4,359 million at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
(n) Insurance policy acquisition costs
Incremental costs that are directly related to the successful acquisition of insurance contracts are capitalized, subject to
ultimate recoverability, and are subsequently amortized to underwriting expenses as the related premiums are earned.
Direct incremental acquisition costs include commissions, premium taxes, and certain other costs associated with
successful efforts. All other underwriting costs are expensed as incurred. The recoverability of capitalized insurance
policy acquisition costs generally reflects anticipation of investment income. The unamortized balances are included in
other assets and were $1,722 million and $1,601 million at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
(p) Life, annuity and health insurance benefits
Liabilities for insurance benefits under life contracts are computed based upon estimated future investment yields,
expected mortality, morbidity, and lapse or withdrawal rates and reflects estimates for future premiums and expenses
under the contracts. These assumptions, as applicable, also include a margin for adverse deviation and may vary with
56