HSBC 2014 Annual Report Download - page 153
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 153 of the 2014 HSBC annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
HSBC BANK PLC
Notes on the Financial Statements (continued)
151
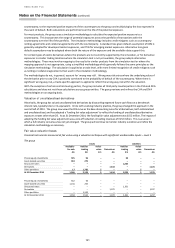
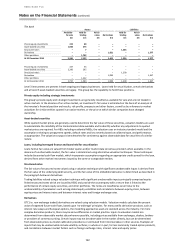
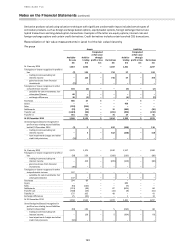
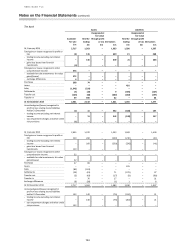
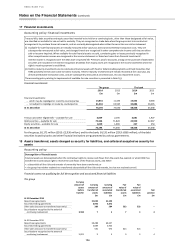
15 Derivatives
Accounting policy
Derivatives
Derivatives are initially recognised, and are subsequently remeasured, at fair value. Fair values of derivatives are obtained either from
quoted market prices or by using valuation techniques. Derivative assets and liabilities arising from different transactions are only
offset for accounting purposes if the offsetting criteria presented in Note 30 are met.
Embedded derivatives are bifurcated from the last contract when their economic characteristics and risks are not clearly and closely
related to those of the host non-derivative contract, their contractual terms would otherwise meet the definition of a stand-alone
derivative and the combined contract is not held for trading or designated at fair value. The bifurcated embedded derivatives are
measured at fair value with changes therein recognised in the income statement.
Derivatives are classified as assets when their fair value is positive, or as liabilities when their fair value is negative.
Gains and losses from changes in the fair value of derivatives, including the contractual interest, that do not qualify for hedge
accounting are reported in ‘Net trading income’ except for derivatives managed in conjunction with financial instruments designated
at fair value, where gains and losses are reported in ‘Net income from financial instruments designated at fair value’ together with the
gains and losses on the economically hedged items. Where the derivatives are managed with debt securities issued by HSBC and
designated at fair value, the contractual interest is shown in ‘Interest expense’ together with the interest payable on the issued debt.
When derivatives are designated as hedges, HSBC classifies them as either: (i) hedges of the change in fair value of recognised assets
or liabilities or firm commitments (‘fair value hedges’); (ii) hedges of the variability in highly probable future cash flows attributable to
a recognised asset or liability, or a forecast transaction (‘cash flow hedges’); or (iii) a hedge of a net investment in a foreign operation
(‘net investment hedges’).
Hedge accounting
At the inception of a hedging relationship, HSBC documents the relationship between the hedging instruments and the hedged items,
its risk management objective and its strategy for undertaking the hedge. HSBC requires documented assessment, both at hedge
inception and on an ongoing basis, of whether or not the hedging instruments are highly effective in offsetting the changes
attributable to the hedged risks in the fair values or cash flows of the hedged items.
Fair value hedge
Changes in the fair value of derivatives that are designated and qualify as fair value hedging instruments are recorded in the income
statement, along with changes in the fair value of the hedged assets, liabilities or group that contain the hedged risk. If a hedging
relationship no longer meets the criteria for hedge accounting, the hedge accounting is discontinued: the cumulative adjustment to
the carrying amount of the hedged item is amortised to the income statement on a recalculated effective interest rate over the
residual period to maturity, unless the hedged item has been derecognised.
Cash flow hedge
The effective portion of changes in the fair value of derivatives that are designated and qualify as cash flow hedges is recognised in
other comprehensive income; the ineffective portion of the change in fair value is recognised immediately in the income statement.
The accumulated gains and losses recognised in other comprehensive income are reclassified to the income statement in the periods
in which the hedged item affects profit or loss. In hedges of forecasted transactions that result in recognition of a non-financial asset
or liability, previous gains and losses recognised in other comprehensive income are included in the initial measurement of the asset
or liability.
When a hedging relationship is discontinued, any cumulative gain or loss recognised in other comprehensive income remains in equity
until the forecast transaction is recognised in the income statement. When a forecast transaction is no longer expected to occur, the
cumulative gain or loss previously recognised in other comprehensive income is immediately reclassified to the income statement.
Net investment hedge
Hedges of net investments in foreign operations are accounted for in a similar way to cash flow hedges. A gain or loss on the effective
portion of the hedging instrument is recognised in other comprehensive income; the residual change in fair value is recognised
immediately in the income statement. Gains and losses previously recognised in other comprehensive income are reclassified to the
income statement on the disposal, or part disposal, of the foreign operation.
Hedge effectiveness testing
To qualify for hedge accounting, HSBC requires that at the inception of the hedge and throughout its life each hedge must be expected
to be highly effective, both prospectively and retrospectively, on an ongoing basis.
The documentation of each hedging relationship sets out how the effectiveness of the hedge is assessed and the method adopted by
an entity to assess hedge effectiveness will depend on its risk management strategy. For prospective effectiveness, the hedging
instrument must be expected to be highly effective in offsetting changes in fair value or cash flows attributable to the hedged risk
during the period for which the hedge is designated, with the effectiveness range being defined as 80% to 125%. Hedge ineffectiveness
is recognised in the income statement in ‘Net trading income’.
Derivatives that do not qualify for hedge accounting
Non-qualifying hedges are economic hedges entered into as part of documented interest rate management strategies for which hedge
accounting was not applied. Changes in fair value of non-qualifying hedges do not alter the cash flows expected as part of the
documented management strategies for both the non-qualifying hedge instruments and the related assets and liabilities.