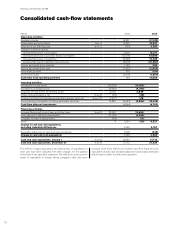
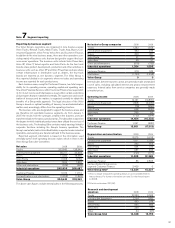
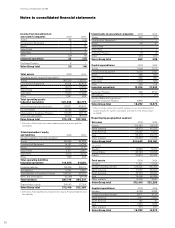
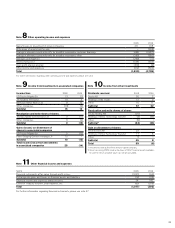
Volvo 2009 Annual Report Download - page 77
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 77 of the 2009 Volvo annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
derivatives that Volvo has decided not to apply hedge accounting on,
and derivates that are not part of an evidently effective hedge account-
ing. Gains and losses on these assets are recognized in the income
statement. Short-term investments that are reported at fair value
through profit and loss mainly consist of interest-bearing financial
instruments and are reported in note 21.
Derivatives used for hedging interest-rate exposure in the customer
financing portfolio are included in this category as it is not practically
possible to apply hedge accounting in accordance with IAS 39 due to
the large number of contracts that the customer finance portfolio con-
sist of. Volvo intends to keep these derivatives to maturity, why, over
time, the market valuation will be offset as a consequence of the inter-
est-rate fixing on borrowing and lending for the customer finance
operations, and accordingly not affect result or cash flow.
Financial assets held to maturity
Held-to-maturity investments are non-derivative assets with fixed
payments and term and that Volvo intends and is able to hold to matur-
ity. After initial recognition, these assets are measured in accordance
with the effective interest method, with adjustment for any impair-
ment. Gains and losses are recognized in the income statement when
assets are divested or impaired as well as in pace with the accrued
interested being reported. At present Volvo has no financial instru-
ments classified in this category.
Loan receivables and other receivables
Loans and receivables are non-derivative financial assets with fixed or
determinable payments, originated or acquired, that are not quoted in
an active market. After initial recognition, loans and receivables are
measured in accordance with the effective interest method. Gains and
losses are recognized in the income statement when the loans or
receivables are divested or impaired as well as in pace with the
accrued interested being reported.
Accounts receivables are recognized initially at fair value, which
normally corresponds to the nominal value. In the event that the pay-
ment terms exceed one year, the receivable is recognized at the dis-
counted present value.
Assessment of impairment – loan receivables and other receivables
Volvo conducts routine controls to ensure that the carrying value of
assets valued at amortized cost, such as loans and receivables, has
not decreased, which would result in an impairment loss reported in
the income statement. Allowances for doubtful receivables are con-
tinuously reported based on an assessment of a possible change in
the customer’s ability to pay.
Impairments consist of the difference between carrying value and
current value of the estimated future payment flow attributable to the
specific asset with consideration to the fair value of any collateral.
Discounting of future cash flow is based on the effective rate used
initially. Initially, the impairment requirement is evaluated for each
respective asset. If, based on objective grounds, it cannot be deter-
mined that one or more assets are subject to an impairment loss, the
assets are grouped in units based, for example, on similar credit risks
to evaluate the impairment loss requirement collectively. Individually
written down assets or assets written down during previous periods
are not included when grouping assets for impairment test. If the con-
ditions for a completed impairment loss later prove to no longer be
present, and that can be related to a specific event after the impair-
ment event, the impairment loss is reversed in the income statement
as long as the carrying value does not exceed the amortized cost at
the time of the reversal.
Volvo discloses loan receivables and accounts receivables in the
notes 16, 17, 19 and 20.
Available-for-sale assets
This category includes assets available for sales or those that have
not been classified in any of the other three categories. These assets
are initially measured at fair value including transaction costs. Fair
value changes are recognized directly in shareholders’ equity. The
cumulative gain or loss that was recognized in equity is recognized in
profit or loss when an available-for-sale financial asset is sold. Unreal-
ized value declines are recognized in equity, unless the decline is
significant or prolonged. Then the impairment is recognized in the
income statement. If the event causing the impairment no longer
exists, impairment can be reversed in the income statement if it does
not involve an equity instrument.
Earned or paid interest attributable to these assets is recognized in
the income statement as part of net financial items in accordance with
the effective interest method. Dividends received attributable to these
assets are recognized in the income statement as Income from other
investments.
Volvo reports shares and participations in listed companies at mar-
ket value on the balance-sheet date, with the exception of investments
classified as associated companies and joint ventures. Holdings in
unlisted companies for which a market value is unavailable are recog-
nized at acquisition value. Volvo classifies these types of investments
as assets available for sale. See note 15 for Volvo’s holdings of shares
and participations in listed companies.
Assessment of impairment – available-for-sale assets
If an asset available for sale is to be impaired, it shall be effected by
taking the difference between the asset’s acquisition value (adjusted
for any accrued interest if it involves that type of asset) and its fair
value. If it instead involves equity instruments such as shares, a com-
pleted impairment shall not be reversed in the income statement. On
the other hand, impairments that have been made on debt instruments
(interest-bearing instruments) shall in whole or part be reversed in the
income statement, in those instances where an event that is proven to
have occurred after the impairment was performed is identified and
impacts the valuation of that asset.
Hedge accounting
In order to apply hedge accounting in accordance with IAS 39, the
following criteria must be met: the position being hedged is identified
and exposed to market value movements, for instance related to
exchange-rate or interest-rate movements, the purpose of the loan/
instrument is to serve as a hedge and the hedging effectively protects
the underlying position against changes in the fair value. Financial
instruments used for the purpose of hedging future currency flows are
accounted for as hedges if the currency flows are considered highly
probable to occur.
– During 2009 Volvo has partly applied hedge accounting for hedg-
ing against currency-rate risk and interest-rate risks pertaining to
commercial assets and liabilities. Financial instruments used to hedge
forecasted internal commercial cash flows and forecasted electricity
consumption are reported at fair value in the balance sheet. The fair
value is debited or credited to a separate component of equity pro-
vided that hedge accounting is applied and to the extent the require-
ments for cash-flow hedge accounting are fulfilled. To the extent that
hedge accounting is not applied or the requirements are not met, the
unrealized gain or loss will be charged to the income statement. Unre-
alized and realized gains and losses on hedges are reported in gross
income.
– During 2009 Volvo has partly applied hedge accounting for finan-
cial instruments used to hedge interest and currency risks on loans only
for cases when hedge accounting requirements are fulfilled. For cases
73