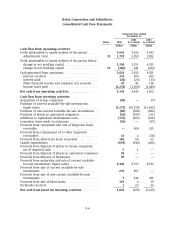
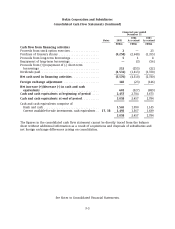
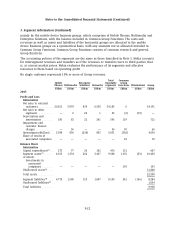
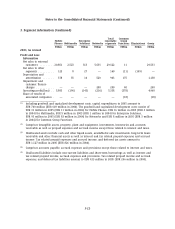
Nokia 2005 Annual Report Download - page 151
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 151 of the 2005 Nokia annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
1. Accounting principles (Continued)
The Group’s customer contracts may include the provision of separately identifiable components of
a single transaction, for example the construction of a network solution and subsequent network
maintenance services. Accordingly, for these arrangements, revenue recognition requires proper
identification of the components of the transaction and evaluation of their commercial effect in
order to reflect the substance of the transaction. If the components are considered separable,
revenue is allocated across the identifiable components based upon relative fair values.
All the Group’s material revenue streams are recorded according to the above policies.
Shipping and handling costs
The costs of shipping and distributing products are included in cost of sales.
Research and development
Research and development costs are expensed as they are incurred, except for certain
development costs, which are capitalized when it is probable that a development project will
generate future economic benefits, and certain criteria, including commercial and technical
feasibility, have been met. Capitalized development costs, comprising direct labor and related
overhead, are amortized on a systematic basis over their expected useful lives between two and
five years.
Capitalized development costs are subject to regular assessments of recoverability based on
anticipated future revenues, including the impact of changes in technology. Unamortized
capitalized development costs determined to be in excess of their recoverable amounts are
expensed immediately.
Other intangible assets
Expenditures on acquired patents, trademarks and licenses are capitalized and amortized using the
straight-line method over their useful lives, but not exceeding 20 years. Where an indication of
impairment exists, the carrying amount of any intangible asset is assessed and written down to
its recoverable amount. Costs of software licenses associated with internal-use software are
capitalized. These costs are included within other intangible assets and are amortized over a
period not to exceed three years.
Pensions
The Group companies have various pension schemes in accordance with the local conditions and
practices in the countries in which they operate. The schemes are generally funded through
payments to insurance companies or to trustee-administered funds as determined by periodic
actuarial calculations.
The Group’s contributions to defined contribution plans and to multi-employer and insured plans
are charged to the profit and loss account in the period to which the contributions relate.
For defined benefit plans, principally the reserved portion of the Finnish TEL system, pension costs
are assessed using the projected unit credit method: the cost of providing pensions is charged to
the profit and loss account so as to spread the service cost over the service lives of employees. The
pension obligation is measured as the present value of the estimated future cash outflows using
interest rates on government securities that have terms to maturity approximating the terms of
F-13