MoneyGram 2007 Annual Report Download - page 31
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 31 of the 2007 MoneyGram annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Table of Contents
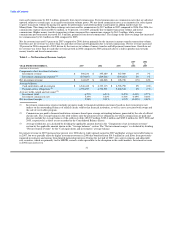
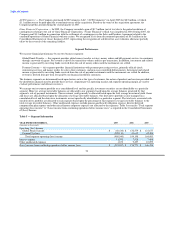
Components of Net Revenue
Our net revenue consists of fee and other revenue, investment revenue and net securities gains and losses, less commission expense. We
generate net revenue primarily by charging transaction fees in excess of third-party agent commissions, managing foreign currency
exchange and managing our investments to provide returns in excess of commissions paid to financial institution customers.
We derive revenue primarily through service fees charged to consumers and through our investments. Fee and other revenue consist of
transaction fees, foreign exchange and miscellaneous revenue. Transaction fees are fees earned on the sale of money transfers, retail
money order and bill payment products and official check transactions. Money transfer transaction fees are fixed per transaction and may
vary based upon the face value of the amount of the transaction and the location in which the money transfer originates and to which it is
sent. Money order and bill payment transaction fees are fixed per transaction. Foreign exchange revenue is derived from the management
of currency exchange spreads on international money transfer transactions. Miscellaneous revenue primarily consists of processing fees
on rebate checks and controlled disbursements, service charges on aged outstanding money orders and money order dispenser fees.
Investment revenue consists of interest and dividends generated through the investment of cash balances received from the sale of official
checks, money orders and other payment instruments. These cash balances are available to us for investment until the payment instrument
is presented for payment. Investment revenue varies depending on the level of investment balances and the yield on our investments.
Investment balances vary based on the number of payment instruments sold, the average face amount of those payment instruments and
the average length of time that passes until the instruments are presented for payment. Net securities gains and losses consist of realized
gains and losses on the sale of investments and other-than-temporary impairments of investments.
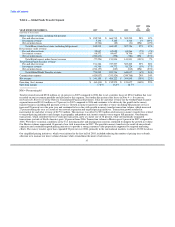
We incur commission expense on our money transfer products and our investments. We pay fee commissions to our third-party agents for
money transfer services. In a money transfer transaction, both the agent initiating the transaction and the agent disbursing the funds
receive a commission. The commission amount generally is based on a percentage of the fee charged to the consumers. We generally do
not pay commissions to agents on the sale of money orders. Fee commissions also include the amortization of capitalized incentive
payments to agents.
Investment commissions are amounts paid to financial institution customers based on the average outstanding cash balances generated by
the sale of official checks, as well as costs associated with swaps and the sale of receivables program. In December 2007, the Company
made a decision to cease selling receivables through a gradual reduction in the balances sold each period. As of January 2008, the
Company did not have a sold receivables balance remaining (see further discussion on our sale of receivables program in Note 6 — Sale
of Receivables of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements). In connection with our interest rate swaps, we pay a fixed amount to a
counterparty and receive a variable rate payment in return. To the extent that the fixed rate exceeds the variable rate, we incur an expense
related to the swap; conversely, if the variable rate exceeds the fixed rate, we receive income related to the swap. Under our receivables
program, we sold our receivables at a discount to accelerate our cash flow; this discount was recorded as an expense. Commissions paid
to financial institution customers generally are variable based on short-term interest rates. We utilize interest rate swaps, as described
above, to convert a portion of our variable rate commission payments to fixed rate payments. These swaps assist us in managing the
interest rate risk associated with the variable rate commissions paid to our financial institution customers.
28