ICICI Bank 2005 Annual Report Download - page 88
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 88 of the 2005 ICICI Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
F28
forming part of the Accounts (Contd.)
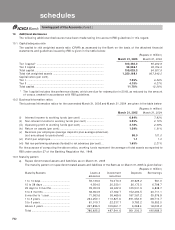
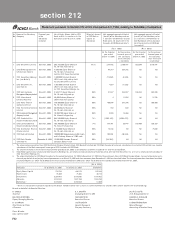
10.10 Credit exposure
As at March 31, 2005 the Bank has taken single borrower exposure above 15% with the approval of the Board of
Directors in the following cases:
Name of Borrower March 31, 2005
% to capital funds
Borrower A .................................................................................. 19.50%
Borrower B .................................................................................. 17.46%
Borrower C .................................................................................. 16.73%
Borrower D .................................................................................. 16.20%
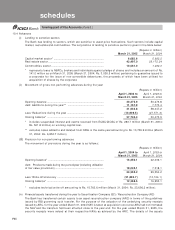
10.11 Risk category-wise country-wise exposure
As per the extant RBI guidelines, the country exposure of the Bank is categorised into various risk categories
listed in the following table. Since the country exposure (net) of the Bank in respect of each country does not
exceed 1% of the total funded assets, no provision is required to be maintained on country exposures.
(Rupees in million)
Risk category Exposure (net) as on Exposure (net) as on
March 31, 2005 March 31, 2004
Insignificant................................................................................. 54,349.8 62,651.1
Low .............................................................................................. 11,408.4 2,217.7
Moderate ..................................................................................... 4,592.1 1,735.4
High............................................................................................ .. —8.6
Very High ................................................................................... .. ——
Off-Credit ..................................................................................... 656.2 —
Total.............................................................................................. 71,006.5 66,612.8
- of which funded........................................................................ 38,885.7 46,950.6
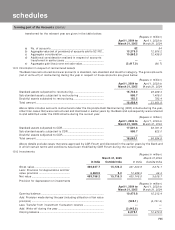
10.12 Interest rate swaps (“IRS”)
The notional principal amount of Rupee IRS contracts as at March 31, 2005 is Rs. 51.10 billion for hedging
contracts (March 31, 2004: Rs. 34.15 billion) and Rs. 1,114.30 billion for trading contracts (March 31, 2004:
Rs. 947.83 billion).
The fair value represents the estimated replacement cost of swap contracts as at balance sheet date. At
March 31, 2005 the fair value of trading rupee interest rate swap contracts is Rs. 0.33 billion (March 31, 2004 : Rs.
0.67 billion).
Associated credit risk is the loss that the Bank would incur in case all the counter-parties to these swaps fail to
fulfil their contractual obligations. As at March 31, 2005, the associated credit risk on trading rupee interest rate
swap contracts is Rs. 9.87 billion (March 31, 2004: Rs. 8.96 billion).
Market risk is monitored as the loss that would be incurred by the Bank for a 100 basis points rise in the interest
rates. As at March 31, 2005 the market risk on trading rupee interest rate swap contracts amounts to Rs. 0.14
billion (March 31, 2004: Rs. 0.06 billion).
Credit risk concentration is measured as the highest net receivable under swap contracts from a particular
counter party. As at March 31, 2005 there is a credit risk concentration of Rs. 0.27 billion (March 31, 2004: Rs. 0.68
billion) under rupee interest rate swap contracts, with ICICI Securities Ltd. As per the prevailing market practice,
the Bank does not insist on collateral from the counter parties of these contracts.
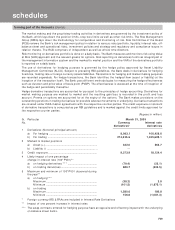
10.13 Rupee and foreign currency derivatives
ICICI Bank is a leading participant in the financial derivatives market. The Bank deals in derivatives for balance
sheet management and market making purposes whereby the Bank offers derivative products to its customers,
enabling them to hedge their risks.
Dealing in derivatives is centralised in the treasury of the Bank. Derivative transactions are entered into by the
treasury front office. Treasury middle office conducts an independent check of the transactions entered into by
the front office and also undertakes activities such as confirmation, settlement, accounting, risk monitoring and
reporting and ensures compliance with various internal and regulatory guidelines.
schedules