ICICI Bank 2005 Annual Report Download - page 72
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 72 of the 2005 ICICI Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
F12
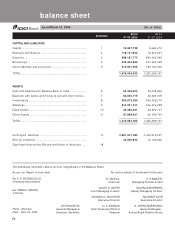
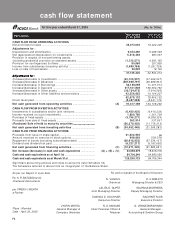
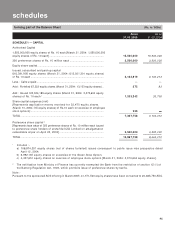
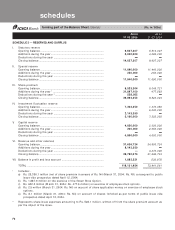
forming part of the Accounts (Contd.)
schedules
SCHEDULE 18
SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES AND NOTES TO ACCOUNTS
Overview
ICICI Bank Limited (“ICICI Bank” or “the Bank”), incorporated in Vadodara, India is a publicly held bank engaged in
providing a wide range of banking and financial services including commercial banking and treasury operations. ICICI
Bank is a banking company governed by the Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
Basis of preparation
The accounting and reporting policies of ICICI Bank used in the preparation of these financial statements conform to
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (“GAAP”) in India, the guidelines issued by Reserve Bank of India (“RBI”) from
time to time and practices generally prevailing within the banking industry in India. The Bank follows the accrual method
of accounting, except where otherwise stated, and the historical cost convention.
The preparation of financial statements requires the management to make estimates and assumptions considered in the
reported amounts of assets and liabilities (including contingent liabilities) as of the date of the financial statements and
the reported income and expenses during the reporting period. Management believes that the estimates used in the
preparation of the financial statements are prudent and reasonable. Future results could differ from these estimates.
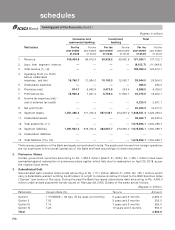
Equity issue
During the year, the Bank made an issue of 115,920,758 equity shares (including 6,992,187 equity shares issued by
exercise of green shoe option) of Rs.10 each at a premium of Rs. 270 per share aggregating Rs. 32,457.8 million under
the Prospectus dated April 12, 2004. The expenses of the issue have been charged to the Share Premium Account, in
accordance with the objects of the Issue stated in the Prospectus.
ICICI Bank had sponsored American Depositary Shares (ADSs) Offering which opened for participation on March 7, 2005 and
closed on March 11, 2005. In terms of the Offering, 20,685,750 ADSs representing 41,371,500 equity shares had been sold
at a price of US$ 21.1 per ADS. The gross proceeds from the ADS Offering were approximately US$ 436.7 million (Rs.19,099.6
million). The net consideration per share (after deduction of expenses in connection with the offering) was Rs. 453.16.
A. SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
1. Revenue Recognition
a) Interest income is recognised in the profit and loss account as it accrues except in the case of non-performing assets
where it is recognised, upon realisation, as per the prudential norms of RBI. Accrual of income is also suspended
considering economic conditions and other risk factors, on certain other loans, including certain projects under
implementation, where the implementation has been significantly delayed or in the opinion of the management
significant uncertainties exist as to the final financial closure and/or date of completion of the project.
b) Commissions paid to direct marketing agents (“DMAs”) for auto loans, is recorded upfront in the profit and loss
account net of subvention income received from them.
c) Income from hire purchase operations is accrued by applying the interest rate implicit on outstanding balances.
d) Income from leases is calculated by applying the interest rate implicit in the lease to the net investment outstanding
on the lease over the primary lease period. Leases effected from April 1, 2001 have been accounted as per
Accounting Standard 19 on “Accounting for Leases” issued by Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (“ICAI”).
Accordingly, leases effective from April 1, 2001 are accounted as advances at an amount equal to the net investment
in the lease. The lease rentals are apportioned between principal and finance income based on a pattern reflecting
a constant periodic return on the net investment of outstanding in respect of finance lease. The principal amount
is recognised as repayment of advances and the finance income is reported as interest income.
e) Income on discounted instruments is recognised over the tenure of the instrument on a constant yield basis.
f) Dividend is accounted on an accrual basis when the right to receive the dividend is established.
g) Fees received as a compensation of future interest sacrifice is amortised over the remaining period of the facility.
h) Arranger’s fee is accrued proportionately where more than 75% of the total amount of finance has been arranged.
i) All other fee income is recognised upfront on their becoming due.
j) Income arising from sell down/securitisation of loan assets is recognised upfront, net of future servicing cost
for assets sold, expected prepayment and projected delinquencies and included in interest income.
k) Guarantee commission is recognised over the period of the guarantee.
2. Investments
Investments are valued in accordance with the extant RBI guidelines on investment classification and valuation as under:
a) All investments are categorised into ‘Held to Maturity‘, ’Available for Sale’ and ‘Trading‘. Reclassifications, if
any, in any category are accounted for as per RBI guidelines. Under each category, the investments are further
classified under (a) government securities (b) other approved securities (c) shares (d) bonds and debentures, (e)
subsidiaries and joint ventures and (f) others.
b) ‘Held to Maturity’ securities are carried at their acquisition cost or at amortised cost, if acquired at a premium
over the face value. A provision is made for other than temporary diminution.
c) ‘Available for Sale’ and ‘Trading’ securities are valued periodically as per RBI guidelines. The market/fair value
for the purpose of periodical valuation of quoted investments included in the “Available for Sale” and “Trading”