ICICI Bank 2005 Annual Report Download - page 75
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 75 of the 2005 ICICI Bank annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
F15
forming part of the Accounts (Contd.)
encashment liability are determined as per actuarial valuation at year-end. Defined contributions for provident fund
are charged to the profit and loss account based on contributions made in terms of the scheme.
The Bank provides for pension, a deferred retirement plan, covering certain employees. The plan provides for a
pension payment on a monthly basis to these employees on their retirement based on the respective employee’s
salary and years of employment with the Bank. Employees covered by the pension plan are not eligible for benefits
under the provident fund plan, a defined contribution plan. The pension plan is funded through periodic contributions
to a fund set-up by the Bank and administered by a Board of Trustees. Such contributions are actuarially determined.
10. Income Taxes
Income tax expense is the aggregate amount of current tax and deferred tax charge. Current year taxes are determined
in accordance with the Income Tax Act, 1961. Deferred tax adjustments comprise of changes in the deferred tax
assets or liabilities during the period.
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognised for the future tax consequences of timing differences arising
between the carrying values of assets and liabilities and their respective tax basis and operating carry forward
losses. Deferred tax assets are recognised only after giving due consideration to prudence. Deferred tax assets and
liabilities are measured using tax rates and tax laws that have been enacted or substantially enacted by the balance
sheet date. The impact on account of changes in the deferred tax assets and liabilities is also recognised in the profit
and loss account.
Deferred tax assets are recognised and reassessed at each reporting date, based upon management’s judgement
as to whether realisation is considered reasonably certain. Deferred tax assets are recognised on carry forward of
unabsorbed depreciation and tax losses only if there is virtual certainty that such deferred tax asset can be realised
against future profits.
11. Impairment of assets
Long-lived assets and certain intangible assets are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in
circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. Recoverability of assets to be
held and used is measured by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset to future net discounted cash flows
expected to be generated by the asset. If such assets are considered to be impaired, the impairment to be recognized
is measured by the amount by which the carrying amount of the assets exceeds the fair value of the assets.
As on March 31, 2005 there were no events or changes in circumstances which indicate any impairment in the
carrying value of the assets covered by AS 28.
12. Accounting for contingencies
The Bank estimates the probability of any loss that might be incurred on outcome of contingencies on the basis of
information available up to the date on which the financial statements are prepared. A provision is recognized when
an enterprise has a present obligation as a result of past event and it is probable that an outflow of resources will be
required to settle the obligation, in respect of which a reliable estimate can be made. Provisions are determined
based on management estimate required to settle the obligation at the balance sheet date, supplemented by
experience of similar transactions. These are reviewed at each balance sheet date and adjusted to reflect the
current management estimates. In cases where the available information indicates that the loss on the contingency
is reasonably possible but the amount of loss cannot be reasonably estimated, a disclosure is made in the financial
statements. In case of remote possibility neither provision nor disclosure is made in the financials.
13. Earnings per share
Basic and diluted earnings per share are calculated by dividing the net profit or loss for the period attributable to
equity shareholders by the weighted average number of equity shares outstanding during the period. Diluted
earnings per equity share has been computed using the weighted average number of equity shares and dilutive
potential equity shares outstanding during the period, except where the results are anti-dilutive.
14. Cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents include cash in hand, balances with RBI, balances with other banks and money at call and
short notice.
B. NOTES FORMING PART OF THE ACCOUNTS
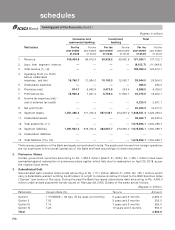
1. Information about business and geographical segments
The Bank reports its operations under the following business segments:
•Consumer and Commercial Banking
comprising the retail and corporate banking operations of the Bank.
•Investment Banking comprising the treasury of the Bank.
Inter-segment transactions are generally based on transfer pricing measures as determined by management. Income,
expenses, assets and liabilities are either specifically identified with individual segments or are allocated to segments
on a systematic basis.
Based on such allocations, segmental balance sheet as on March 31, 2005 and March 31, 2004 and segmental profit
& loss account for the year ended March 31, 2005 and for the year ended March 31, 2004 have been prepared.
schedules