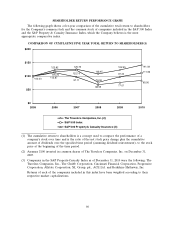
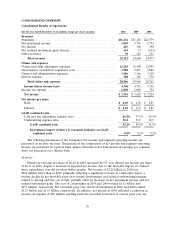
Travelers 2010 Annual Report Download - page 74
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 74 of the 2010 Travelers annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.also explore opportunities in other countries, including other emerging markets such as India and
China.
While our business outside of the United States currently constitutes a relatively small portion of
our revenues, in conducting such business we are subject to a number of significant risks, particularly in
emerging economies. These risks include restrictions such as price controls, capital controls, currency
exchange limits, ownership limits and other restrictive or anti-competitive governmental actions, which
could have an adverse effect on our business and our reputation. Our investments outside the United
States may also subject us to currency risk, and, in some markets, it may be difficult to effectively
hedge that risk. In addition, in some markets, we may invest as part of a joint venture with a local
counterparty. Because our governance rights may be limited, we may not have control over the ability
of the joint venture to make certain decisions and/or mitigate risks it faces, and significant
disagreements with a joint venture counterparty may adversely impact our investment. Investments
outside the United States also subject us to additional domestic and foreign laws and regulations,
including the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act and similar laws in other countries that prohibit the
making of improper payments to foreign officials. Although we have policies and controls in place that
are designed to ensure compliance with these laws, if those controls are ineffective and an employee or
intermediary fails to comply with applicable laws and regulations, we could suffer civil and criminal
penalties and our business and our reputation could be adversely affected. Some countries, particularly
emerging economies, have laws and regulations that lack clarity and, even with local expertise and
effective controls, it can be difficult to determine the exact requirements of, and potential liability
under, the local laws. For example, in some jurisdictions, including Brazil, parties to a joint venture
may, in some circumstances, have liability for some obligations of the venture and that liability may
extend beyond the capital invested. Failure to comply with local laws in a particular market may result
in substantial liability and could have a significant and negative effect not only on our business in that
market but also on our reputation generally.
Our business success and profitability depend, in part, on effective information technology systems
and on continuing to develop and implement improvements in technology. We depend in large part
on our technology systems for conducting business and processing claims, and thus our business success
is dependent on maintaining the effectiveness of existing technology systems and on continuing to
develop and enhance technology systems that support our business processes and strategic initiatives in
a cost and resource efficient manner. Some system development projects are long-term in nature, may
negatively impact our expense ratios as we invest in the projects and may cost more than we expect to
complete. In addition, system development projects may not deliver the benefits we expect once they
are complete, or may be replaced or become obsolete more quickly than expected, which could result
in accelerated recognition of expenses. If we do not effectively and efficiently manage and upgrade our
technology portfolio, or if the costs of doing so are higher than we expect, our ability to provide
competitive services to new and existing customers in a cost effective manner and our ability to
implement our strategic initiatives could be adversely impacted.
If we experience difficulties with technology, data security and/or outsourcing relationships our
ability to conduct our business could be negatively impacted. While technology can streamline many
business processes and ultimately reduce the cost of operations, technology initiatives present significant
risks. Our business is highly dependent upon our employees’ ability to perform, in an efficient and
uninterrupted fashion, necessary business functions. A shut-down of, or inability to access, one or more
of our facilities; a power outage; or a failure of one or more of our information technology,
telecommunications or other systems could significantly impair our ability to perform such functions on
a timely basis. In the event of a disaster such as a natural catastrophe, terrorist attack or industrial
accident, or due to a computer virus, our systems could be inaccessible for an extended period of time.
In addition, because our information technology and telecommunications systems interface with and
depend on third-party systems, we could experience service denials or failures of controls if demand for
62