HP 2014 Annual Report Download - page 152
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 152 of the 2014 HP annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.HEWLETT-PACKARD COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
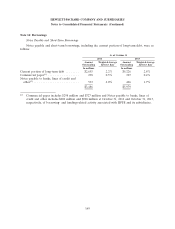
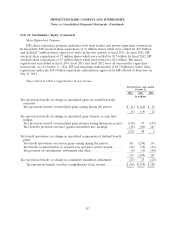
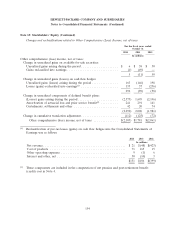
Note 11: Financial Instruments (Continued)
credit ratings and other factors, and HP maintains dollar risk limits that correspond to each financial
institution’s credit rating and other factors. HP’s established policies and procedures for mitigating
credit risk include reviewing and establishing limits for credit exposure and periodically re-assessing the
creditworthiness of its counterparties. Master netting agreements further mitigate credit exposure to
counterparties by permitting HP to net amounts due from HP to counterparty against amounts due to
HP from the same counterparty under certain conditions.
To further mitigate credit exposure to counterparties, HP has collateral security agreements that
allow HP to hold collateral from, or require HP to post collateral to, counterparties when aggregate
derivative fair values exceed contractually established thresholds which are generally based on the credit
ratings of HP and its counterparties. If HP’s or the counterparty’s credit rating falls below a specified
credit rating, either party has the right to request full collateralization of the derivatives’ net liability
position. Collateral is generally posted within two business days. The fair value of derivatives with
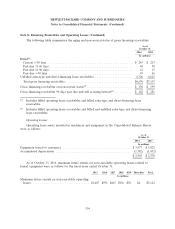
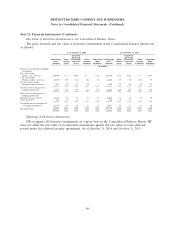
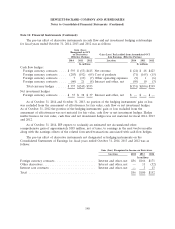
credit contingent features in a net liability position was $38 million and $207 million at October 31,
2014 and October 31, 2013, respectively, all of which were fully collateralized within two business days.
Under HP’s derivative contracts, the counterparty can terminate all outstanding trades following a
covered change of control event affecting HP that results in the surviving entity being rated below a
specified credit rating. This credit contingent provision did not affect HP’s financial position or cash
flows as of October 31, 2014 and October 31, 2013.
Fair Value Hedges
HP issues long-term debt in U.S. dollars based on market conditions at the time of financing. HP
may enter into fair value hedges, such as interest rate swaps, to reduce the exposure of its debt
portfolio to changes in fair value resulting from changes in interest rates by achieving a primarily U.S.
dollar LIBOR-based floating interest expense. The swap transactions generally involve principal and
interest obligations for U.S. dollar-denominated amounts. Alternatively, HP may choose not to swap
fixed for floating interest payments or may terminate a previously executed swap if it believes a larger
proportion of fixed-rate debt would be beneficial.
When investing in fixed-rate instruments, HP may enter into interest rate swaps that convert the
fixed interest payments into variable interest payments and may designate these swaps as fair value
hedges.
For derivative instruments that are designated and qualify as fair value hedges, HP recognizes the
change in fair value of the derivative instrument, as well as the offsetting change in the fair value of
the hedged item, in Interest and other, net in the Consolidated Statements of Earnings in the period of
change.
Cash Flow Hedges
HP uses a combination of forward contracts and option contracts designated as cash flow hedges
to protect against the foreign currency exchange rate risks inherent in its forecasted net revenue and, to
a lesser extent, cost of sales, operating expenses, and intercompany loans denominated in currencies
other than the U.S. dollar. HP’s foreign currency cash flow hedges mature generally within twelve
months; however, hedges related to longer term procurement arrangements extend several years and
forward contracts associated with sales-type and direct-financing leases and intercompany loans extend
for the duration of the lease or loan term, which typically range from two to five years.
144