HP 2014 Annual Report Download - page 151
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 151 of the 2014 HP annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
HEWLETT-PACKARD COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
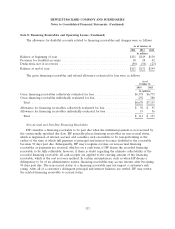
Note 11: Financial Instruments (Continued)
All highly liquid investments with original maturities of three months or less at the date of
acquisition are considered cash equivalents. As of October 31, 2014 and October 31, 2013, the carrying
amount of cash equivalents approximated fair value due to the short period of time to maturity.
Interest income related to cash, cash equivalents and debt securities was approximately $136 million in
fiscal 2014, $148 million in fiscal 2013 and $155 million in fiscal 2012. Time deposits were primarily
issued by institutions outside the U.S. as of October 31, 2014 and October 31, 2013. The estimated fair
value of the available-for-sale investments may not be representative of values that will be realized in
the future.
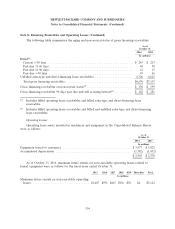
The gross unrealized loss as of October 31, 2014 and October 31, 2013 was due primarily to
decline in the fair value of a debt security of $14 million and $15 million, respectively, that has been in
a continuous loss position for more than twelve months. HP does not intend to sell this debt security,
and it is not likely that HP will be required to sell this debt security prior to the recovery of the
amortized cost.
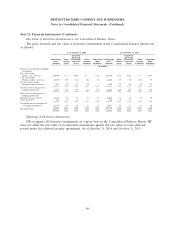
Contractual maturities of investments in available-for-sale debt securities were as follows:
As of October 31, 2014
Amortized
Cost Fair Value
In millions
Due in one year ................................................ $129 $129
Due in one to five years .......................................... 3 3
Due in more than five years ....................................... 360 436
$492 $568
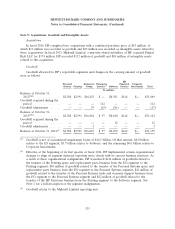
Equity securities in privately held companies include cost basis and equity method investments and
are included in Long-term financing receivables and other assets in the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
These amounted to $97 million and $50 million at October 31, 2014 and October 31, 2013, respectively.
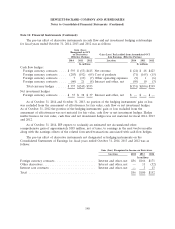
Derivative Instruments
HP is a global company exposed to foreign currency exchange rate fluctuations and interest rate
changes in the normal course of its business. As part of its risk management strategy, HP uses
derivative instruments, primarily forward contracts, option contracts, interest rate swaps and total
return swaps, to hedge certain foreign currency, interest rate and, to a lesser extent, equity exposures.
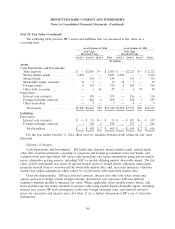
HP’s objective is to offset gains and losses resulting from these exposures with losses and gains on the
derivative contracts used to hedge them, thereby reducing volatility of earnings or protecting the fair
value of assets and liabilities. HP does not have any leveraged derivatives and does not use derivative
contracts for speculative purposes. HP may designate its derivative contracts as fair value hedges, cash
flow hedges or hedges of the foreign currency exposure of a net investment in a foreign operation
(‘‘net investment hedges’’). Additionally, for derivatives not designated as hedging instruments, HP
categorizes those economic hedges as other derivatives. HP recognizes all derivative instruments at fair
value in the Consolidated Balance Sheets. HP classifies cash flows from its derivative programs as
operating activities in the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows.
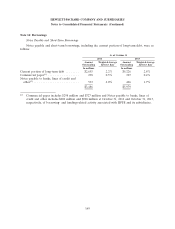
As a result of its use of derivative instruments, HP is exposed to the risk that its counterparties
will fail to meet their contractual obligations. To mitigate counterparty credit risk, HP has a policy of
only entering into derivative contracts with carefully selected major financial institutions based on their
143