Xcel Energy 2014 Annual Report Download - page 26
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 26 of the 2014 Xcel Energy annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
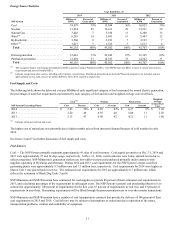
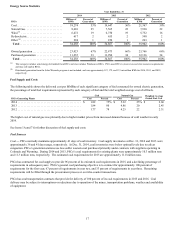
8
Hampton, Minn. to Rochester, Minn. to La Crosse, Wis. 345 KV transmission line
Construction on the project started in Minnesota in January 2013 and the project is expected to go into service in 2016, although
segments are being placed in service as they are completed.
Monticello, Minn. to Fargo, N.D. 345 KV transmission line
In December 2011, the Monticello, Minn. to St. Cloud, Minn. portion of the Monticello, Minn. to Fargo, N.D. project was placed in
service. In April 2014, the St. Cloud, Minn. to Alexandria, Minn. portion of the project was placed in service. In January 2013,
construction started on the project in North Dakota. The final phase of the project, Alexandria, Minn. to Fargo, N.D. is expected to go
into service in 2015.
Brookings County, S.D. to Hampton, Minn. 345 KV transmission line
In December 2011, MISO granted the final approval of the project as a MVP. Construction started on the project in Minnesota in May
2012. The project is expected to go fully into service in 2015, although segments are being placed in service as they are completed.
Bemidji, Minn. to Grand Rapids, Minn. 230 KV transmission line
The Bemidji, Minn. to Grand Rapids, Minn. line was placed in service in September 2012.
Big Stone South to Brookings County, S.D. 345 KV transmission line
In December 2011, MISO granted final approval of the project as a MVP. In March 2014, the SDPUC approved a permit for
construction of the project’s southern portion. Construction is anticipated to begin in late 2015, with completion in 2017.
Minnesota Solar — Minnesota legislation requires 1.5 percent of a public utility’s total electric retail sales to retail customers be
generated using solar energy by 2020. Of the 1.5 percent, 10 percent must come from systems sized less than 20 kilowatts. There are
two customer-facing solar programs authorized by the legislature: a community solar garden program that provides bill credits to
participating subscribers, and a solar production incentive program for systems equal to or less than 20 kilowatts with authorized
payments of $5.0 million per year over five years. NSP-Minnesota launched its Solar*Rewards Community program in December
2014.
The legislation also provides for an alternative tariff based on a distributed solar value or Value of Solar (VOS) methodology. In
March 2014, a VOS methodology was approved by the MPUC. However, in September 2014 the MPUC determined that the VOS is
not in the public interest for use with community solar gardens. The MPUC instead approved a retail rate based credit ranging from
9.5 to 15 cents per kilowatt hour. The actual bill credit amount is dependent on customer class as well as customers’ willingness to
transfer the RECs to NSP-Minnesota.
Annual Automatic Adjustment (AAA) of Charges — In June 2013, the DOC proposed that the MPUC adopt a fuel clause incentive
that would normalize FCA recovery using monthly patterns derived from averages of the prior three-year period, setting and fixing
this level during a rate case with no adjustment between rate cases. NSP-Minnesota and other utilities opposed this proposal. The
DOC proposal is pending MPUC action.
Additionally, the DOC has indicated it will review prudence of replacement power costs associated with the Sherco Unit 3 outage
event within the 2013 AAA docket. The 2013 and 2012 AAA dockets remain pending.
Minneapolis, Minn. Franchise Agreement — In October 2014, the City of Minneapolis and Xcel Energy signed a 10 year franchise
agreement. The City of Minneapolis has the option to end the agreement any time after the first five years and the option to extend it
to a maximum of 20 years if both parties agree. A separate clean energy partnership agreement with the City of Minneapolis was also
signed, which establishes a board comprised of city and utility officials tasked with creating a work plan to promote energy efficiency,
the use of renewable energy, and the reduction of carbon emissions.
Nuclear Power Operations and Waste Disposal
NSP-Minnesota owns two nuclear generating plants: the Monticello plant and the PI plant. Nuclear power plant operations produce
gaseous, liquid and solid radioactive wastes which are controlled by federal regulation. High-level radioactive wastes primarily
include used nuclear fuel. LLW consists primarily of demineralizer resins, paper, protective clothing, rags, tools and equipment that
have become contaminated through use in a plant.
NRC Regulation — The NRC regulates the nuclear operations of NSP-Minnesota. Decisions by the NRC can significantly impact the
operations of the nuclear generating plants.