Wells Fargo 2010 Annual Report Download - page 174
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 174 of the 2010 Wells Fargo annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
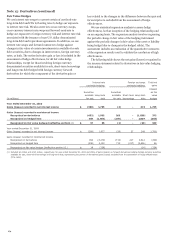
We use derivatives to manage exposure to market risk, interest
rate risk, credit risk and foreign currency risk, to generate profits
from proprietary trading and to assist customers with their risk
management objectives. Derivative transactions are measured in
terms of the notional amount, but this amount is not recorded
on the balance sheet and is not, when viewed in isolation, a
meaningful measure of the risk profile of the instruments. The
notional amount is generally not exchanged, but is used only as
the basis on which interest and other payments are determined.
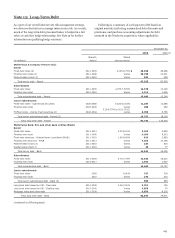
Note 15: Derivatives
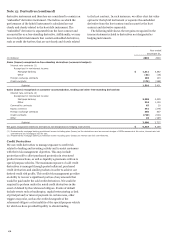
Our asset/liability management approach to interest rate,
foreign currency and certain other risks includes the use of
derivatives. Such derivatives are typically designated as fair
value or cash flow hedges, or economic hedge derivatives for
those that do not qualify for hedge accounting. This helps
minimize significant, unplanned fluctuations in earnings, fair
values of assets and liabilities, and cash flows caused by interest
rate, foreign currency and other market value volatility. This
approach involves modifying the repricing characteristics of
certain assets and liabilities so that changes in interest rates,
foreign currency and other exposures do not have a significant
adverse effect on the net interest margin, cash flows and
earnings. As a result of fluctuations in these exposures, hedged
assets and liabilities will gain or lose market value. In a fair value
or economic hedge, the effect of this unrealized gain or loss will
generally be offset by the gain or loss on the derivatives linked to
the hedged assets and liabilities. In a cash flow hedge, where we
manage the variability of cash payments due to interest rate
fluctuations by the effective use of derivatives linked to hedged
assets and liabilities, the unrealized gain or loss on the
derivatives or the hedged asset or liability is generally not
reflected in earnings.
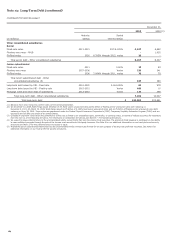
We also offer various derivatives, including interest rate,
commodity, equity, credit and foreign exchange contracts, to our
customers but usually offset our exposure from such contracts by
purchasing other financial contracts. The customer
accommodations and any offsetting financial contracts are
treated as free-standing derivatives. Free-standing derivatives
also include derivatives we enter into for risk management that
do not otherwise qualify for hedge accounting, including
economic hedge derivatives. To a lesser extent, we take positions
based on market expectations or to benefit from price
differentials between financial instruments and markets.
Additionally, free-standing derivatives include embedded
derivatives that are required to be separately accounted for from
their host contracts.
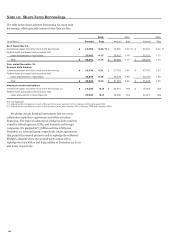
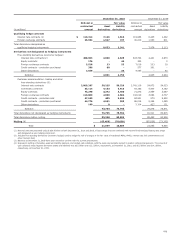
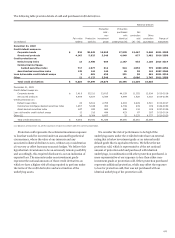
The following table presents the total notional or contractual
amounts and fair values for derivatives, the fair values of
derivatives designated as qualifying hedge contracts, which are
used as asset/liability management hedges, and free-standing
derivatives (economic hedges) not designated as hedging
instruments are recorded on the balance sheet in other assets or
other liabilities. Customer accommodation, trading and other
free-standing derivatives are recorded on the balance sheet at
fair value in trading assets or other liabilities.
172