Volvo 2008 Annual Report Download - page 51
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 51 of the 2008 Volvo annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
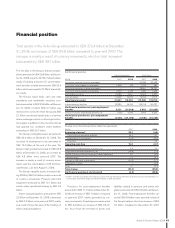
Financial risk
In its operations, the Volvo Group is exposed to
various types of fi nancial risks. Group-wide
policies, which are updated and decided upon
annually, form the basis of each Group compa-
ny’s management of these risks. The objectives
of the Group’s policies for management of
fi nancial risks are to optimize the Group’s cap-
ital costs by utilizing economies of scale, to
minimize negative effects on income as a
result of changes in currency or interest rates,
to optimize risk exposure and to clarify areas
of responsibility. Monitoring and control that
established policies are adhered to is continu-
ously conducted. Most of the Volvo Group’s
fi nancial transactions are carried out through
Volvo’s in-house bank, Volvo Treasury, which
conducts its operations within established risk
mandates and limits. Credit risks are mainly
managed by the different business areas.
The nature of the various fi nancial risks and
objectives and policies for the management of
these risks are described in detail in notes 36
and 37. Volvo’s accounting policies for fi nan-
cial instruments are described in note 1. Vari-
ous aspects of fi nancial risk are described
separately in the following paragraphs. The
overall impact on a company’s competitive-
ness is also affected however by how various
macro-economic factors interact.
Currency-related risk
More than 90% of the net sales of the Volvo
Group are generated in countries other than
Sweden. Changes in exchange rates have a
direct impact on the Volvo Group’s operating
income, balance sheet and cash fl ow, as well
as an indirect impact on Volvo’s competitive-
ness, which over time affects the Group’s
earnings. Currency-associated risk in Volvo’s
business operations relates to changes in the
value of contracted and expected future pay-
ment fl ows (commercial currency exposure),
changes in the value of loans and investments
(fi nancial currency exposure) and changes in
the value of assets and liabilities of foreign
subsidiaries (currency exposure of sharehold-
ers’ equity). In addition, currency movements
can affect Volvo’s pricing of products sold and
materials purchased in foreign currencies.
Since Volvo has substantial manufacturing
operations in Sweden and generates a sub-
stantial portion of its revenues in currencies
other than the Swedish krona, Volvo’s earnings
in Swedish kronor could be positively affected
short-term by an depreciation of the Swedish
krona against other currencies.
The objective of the Volvo Group’s currency
risk management is to minimize the short-term
negative effects. The Volvo Group employs
forward contracts and currency options to
hedge the value of future payment fl ows in for-
eign currencies.
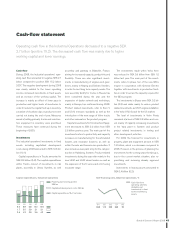
Interest-related risk
Interest-related risk includes risks that
changes in interest rates will impact the
Group’s income and cash fl ow (cash fl ow risks)
or the fair value of fi nancial assets and liabil-
ities (price risks). Interest-rate risk can be
minimized through “matching” of the fi xed
interest terms of fi nancial assets and liabilities.
Interest rate swaps are used to adjust the fi xed
interest terms of the Group’s fi nancial assets
and liabilities. Currency interest rate swaps
make it possible to borrow from different mar-
kets in foreign currencies without assuming
currency-associated risk. Volvo also holds
standardized futures and forward rate agree-
ments. The majority of these contracts are
used to hedge interest rate levels for short-
term borrowing or investment.
Market risk from investments in shares
or similar instruments
The Volvo Group is indirectly exposed to mar-
ket risks from shares and other similar instru-
ments as a result of managed capital trans-
ferred to independent pension plans being
partly invested in instruments of these types.
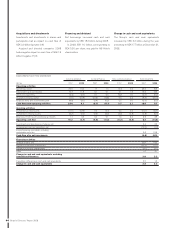
Credit-related risk
Volvo’s extension of credit is governed by
Group-wide policies and rules for classifying
customers. Efforts are made to ensure that the
credit portfolio is reasonably diversifi ed among
different customer categories and industries.
Credit-associated risk is managed by actively
monitoring credit, routines for follow up and
in certain cases repossession of products.
Additionally, continuous and necessary
reserves are monitored in cases involving
uncertain receivables. An important part of the
Group’s credit risk is related to how the fi nan-
cial assets of the Group have been placed. The
majority are placed in Swedish Government
bonds and interest-bearing bonds issued by
Swedish real estate fi nancing institutions.
Liquidity risk
Volvo ensures its fi nancial preparedness by
always maintaining a certain portion of rev-
enues in liquid assets. A healthy balance between
short- and long-term borrowing and access to
credit in the form of credit facilities are intended
to meet the long-term fi nancial needs.
Operational risk
The profi tability depends on successful
new products
The Volvo Group’s long-term profi tability
depends on the Company’s ability to success-
fully launch and market its new products.
Product life cycles continue to shorten, putting
increased focus on the success of the Group’s
product development.
Reliance on suppliers
Volvo purchases raw materials, parts and com-
ponents from numerous external suppliers.
A signifi cant part of the Group’s requirements
for raw materials and supplies is fi lled by
single-source suppliers. The effects of delivery
interruptions vary depending on the item or
component. Certain items and components
are standard throughout the industry, whereas
others are internally developed and require
unique tools that are time-consuming to
replace.
The Volvo Group’s costs for raw materials
and components can vary signifi cantly over a
47
Board of Directors’ Report 2008