HSBC 2005 Annual Report Download - page 155
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 155 of the 2005 HSBC annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.-
 1
1 -
 2
2 -
 3
3 -
 4
4 -
 5
5 -
 6
6 -
 7
7 -
 8
8 -
 9
9 -
 10
10 -
 11
11 -
 12
12 -
 13
13 -
 14
14 -
 15
15 -
 16
16 -
 17
17 -
 18
18 -
 19
19 -
 20
20 -
 21
21 -
 22
22 -
 23
23 -
 24
24 -
 25
25 -
 26
26 -
 27
27 -
 28
28 -
 29
29 -
 30
30 -
 31
31 -
 32
32 -
 33
33 -
 34
34 -
 35
35 -
 36
36 -
 37
37 -
 38
38 -
 39
39 -
 40
40 -
 41
41 -
 42
42 -
 43
43 -
 44
44 -
 45
45 -
 46
46 -
 47
47 -
 48
48 -
 49
49 -
 50
50 -
 51
51 -
 52
52 -
 53
53 -
 54
54 -
 55
55 -
 56
56 -
 57
57 -
 58
58 -
 59
59 -
 60
60 -
 61
61 -
 62
62 -
 63
63 -
 64
64 -
 65
65 -
 66
66 -
 67
67 -
 68
68 -
 69
69 -
 70
70 -
 71
71 -
 72
72 -
 73
73 -
 74
74 -
 75
75 -
 76
76 -
 77
77 -
 78
78 -
 79
79 -
 80
80 -
 81
81 -
 82
82 -
 83
83 -
 84
84 -
 85
85 -
 86
86 -
 87
87 -
 88
88 -
 89
89 -
 90
90 -
 91
91 -
 92
92 -
 93
93 -
 94
94 -
 95
95 -
 96
96 -
 97
97 -
 98
98 -
 99
99 -
 100
100 -
 101
101 -
 102
102 -
 103
103 -
 104
104 -
 105
105 -
 106
106 -
 107
107 -
 108
108 -
 109
109 -
 110
110 -
 111
111 -
 112
112 -
 113
113 -
 114
114 -
 115
115 -
 116
116 -
 117
117 -
 118
118 -
 119
119 -
 120
120 -
 121
121 -
 122
122 -
 123
123 -
 124
124 -
 125
125 -
 126
126 -
 127
127 -
 128
128 -
 129
129 -
 130
130 -
 131
131 -
 132
132 -
 133
133 -
 134
134 -
 135
135 -
 136
136 -
 137
137 -
 138
138 -
 139
139 -
 140
140 -
 141
141 -
 142
142 -
 143
143 -
 144
144 -
 145
145 -
 146
146 -
 147
147 -
 148
148 -
 149
149 -
 150
150 -
 151
151 -
 152
152 -
 153
153 -
 154
154 -
 155
155 -
 156
156 -
 157
157 -
 158
158 -
 159
159 -
 160
160 -
 161
161 -
 162
162 -
 163
163 -
 164
164 -
 165
165 -
 166
166 -
 167
167 -
 168
168 -
 169
169 -
 170
170 -
 171
171 -
 172
172 -
 173
173 -
 174
174 -
 175
175 -
 176
176 -
 177
177 -
 178
178 -
 179
179 -
 180
180 -
 181
181 -
 182
182 -
 183
183 -
 184
184 -
 185
185 -
 186
186 -
 187
187 -
 188
188 -
 189
189 -
 190
190 -
 191
191 -
 192
192 -
 193
193 -
 194
194 -
 195
195 -
 196
196 -
 197
197 -
 198
198 -
 199
199 -
 200
200 -
 201
201 -
 202
202 -
 203
203 -
 204
204 -
 205
205 -
 206
206 -
 207
207 -
 208
208 -
 209
209 -
 210
210 -
 211
211 -
 212
212 -
 213
213 -
 214
214 -
 215
215 -
 216
216 -
 217
217 -
 218
218 -
 219
219 -
 220
220 -
 221
221 -
 222
222 -
 223
223 -
 224
224 -
 225
225 -
 226
226 -
 227
227 -
 228
228 -
 229
229 -
 230
230 -
 231
231 -
 232
232 -
 233
233 -
 234
234 -
 235
235 -
 236
236 -
 237
237 -
 238
238 -
 239
239 -
 240
240 -
 241
241 -
 242
242 -
 243
243 -
 244
244 -
 245
245 -
 246
246 -
 247
247 -
 248
248 -
 249
249 -
 250
250 -
 251
251 -
 252
252 -
 253
253 -
 254
254 -
 255
255 -
 256
256 -
 257
257 -
 258
258 -
 259
259 -
 260
260 -
 261
261 -
 262
262 -
 263
263 -
 264
264 -
 265
265 -
 266
266 -
 267
267 -
 268
268 -
 269
269 -
 270
270 -
 271
271 -
 272
272 -
 273
273 -
 274
274 -
 275
275 -
 276
276 -
 277
277 -
 278
278 -
 279
279 -
 280
280 -
 281
281 -
 282
282 -
 283
283 -
 284
284 -
 285
285 -
 286
286 -
 287
287 -
 288
288 -
 289
289 -
 290
290 -
 291
291 -
 292
292 -
 293
293 -
 294
294 -
 295
295 -
 296
296 -
 297
297 -
 298
298 -
 299
299 -
 300
300 -
 301
301 -
 302
302 -
 303
303 -
 304
304 -
 305
305 -
 306
306 -
 307
307 -
 308
308 -
 309
309 -
 310
310 -
 311
311 -
 312
312 -
 313
313 -
 314
314 -
 315
315 -
 316
316 -
 317
317 -
 318
318 -
 319
319 -
 320
320 -
 321
321 -
 322
322 -
 323
323 -
 324
324 -
 325
325 -
 326
326 -
 327
327 -
 328
328 -
 329
329 -
 330
330 -
 331
331 -
 332
332 -
 333
333 -
 334
334 -
 335
335 -
 336
336 -
 337
337 -
 338
338 -
 339
339 -
 340
340 -
 341
341 -
 342
342 -
 343
343 -
 344
344 -
 345
345 -
 346
346 -
 347
347 -
 348
348 -
 349
349 -
 350
350 -
 351
351 -
 352
352 -
 353
353 -
 354
354 -
 355
355 -
 356
356 -
 357
357 -
 358
358 -
 359
359 -
 360
360 -
 361
361 -
 362
362 -
 363
363 -
 364
364 -
 365
365 -
 366
366 -
 367
367 -
 368
368 -
 369
369 -
 370
370 -
 371
371 -
 372
372 -
 373
373 -
 374
374 -
 375
375 -
 376
376 -
 377
377 -
 378
378 -
 379
379 -
 380
380 -
 381
381 -
 382
382 -
 383
383 -
 384
384 -
 385
385 -
 386
386 -
 387
387 -
 388
388 -
 389
389 -
 390
390 -
 391
391 -
 392
392 -
 393
393 -
 394
394 -
 395
395 -
 396
396 -
 397
397 -
 398
398 -
 399
399 -
 400
400 -
 401
401 -
 402
402 -
 403
403 -
 404
404 -
 405
405 -
 406
406 -
 407
407 -
 408
408 -
 409
409 -
 410
410 -
 411
411 -
 412
412 -
 413
413 -
 414
414 -
 415
415 -
 416
416 -
 417
417 -
 418
418 -
 419
419 -
 420
420 -
 421
421 -
 422
422 -
 423
423 -
 424
424
 |
 |
153
technique that estimates the potential losses that
could occur on risk positions as a result of
movements in market rates and prices over a
specified time horizon and to a given level of
confidence (for HSBC, 99 per cent). HSBC
calculates VAR daily. The VAR model used by
HSBC is predominantly based on historical
simulation. The historical simulation model derives
plausible future scenarios from historical market rate
time series, taking account of inter-relationships
between different markets and rates, for example,
between interest rates and foreign exchange rates.
Potential movements in market prices are calculated
with reference to market data from the last two
years. The model incorporates the impact of option
features in the underlying exposures. HSBC has
changed the assumed holding period from a 10-day
period to a 1-day period as this reflects the way the
risk positions are managed. Comparative VAR
numbers have been restated to reflect this change.
Although a valuable guide to risk, VAR should
always be viewed in the context of its limitations.
For example:
• the use of historical data as a proxy for
estimating future events may not encompass all
potential events, particularly those which are
extreme in nature;
• the use of a 1-day holding period assumes that
all positions can be liquidated or hedged in one
day. This may not fully reflect the market risk
arising at times of severe illiquidity, when a
1-day holding period may be insufficient to
liquidate or hedge all positions fully;
• the use of a 99 per cent confidence level, by
definition, does not take into account losses that
might occur beyond this level of confidence;
and
• VAR is calculated on the basis of exposures
outstanding at the close of business and
therefore does not necessarily reflect intra-day
exposures.
HSBC recognises these limitations by
augmenting its VAR limits with other position and
sensitivity limit structures. Additionally, HSBC
applies a wide range of stress testing, both on
individual portfolios and on the Group’s
consolidated positions. HSBC’s stress-testing regime
provides senior management with an assessment of
the financial impact of identified extreme events on
the market risk exposures of HSBC.
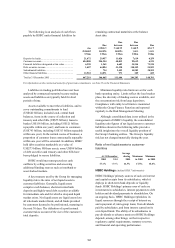
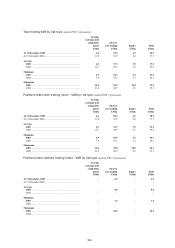
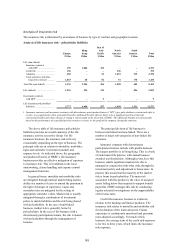
The VAR, both trading and non-trading, for
Global Markets was as follows:
Value at risk
US$m
Total
At 31 December 2005 ..................................................................................................................................................... 128.5
At 31 December 2004 ...................................................................................................................................................... 254.7
Average Minimum Maximum
US$m US$m US$m
2005 .................................................................................................................... 174.1 108.2 248.8
2004 .................................................................................................................... 172.5 101.2 304.2
Total VAR at 31 December 2005 reduced compared
with 31 December 2004. As interest rates rose
during 2005 in the major markets, the risk arising
in Global Markets’ positions was managed down to
limit exposure to further interest rate rises.
(Unaudited information)
The histogram overleaf illustrates the
frequency of daily revenue arising from all Global
Markets’ business and other trading activities. In
2005, HSBC implemented a change in the transfer
pricing of funds between the Personal Financial
Services and the Corporate, Investment Banking
and Markets segments in North America, following
a transfer of the management of all of the interest
rate risk of the held prime residential mortgage
portfolio. The numbers for 2004 have been restated
to reflect the impact of transfer pricing had it been
in place on a similar basis and to include the
Futures and Equities revenues which comprise part
of the Global Markets’ business. As a result of
these restatements, the average daily revenue in
2004 increased from US$18.3 million to
US$20.5 million.
The average daily revenue earned from Global
Markets’ business and other trading activities in
2005 was US$18.7 million, compared with
US$20.5 million in 2004. The standard deviation of
these daily revenues was US$10.4 million
compared with US$8.1 million for 2004. The
standard deviation measures the variation of daily
revenues about the mean value of those revenues.
