Sara Lee 2010 Annual Report Download - page 44
Download and view the complete annual report
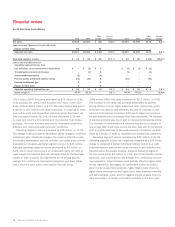
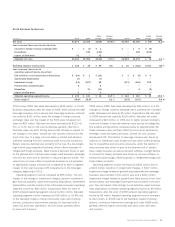
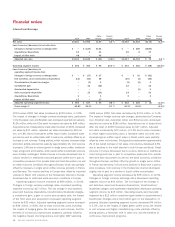
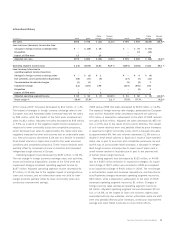
Please find page 44 of the 2010 Sara Lee annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.The material guarantees for which the maximum potential
amount of future payments can be determined, include the corpora-
tion’s contingent liability on leases on property operated by others
that is described above, and the corporation’s guarantees of certain
third-party debt. These debt guarantees require the corporation to
make payments under specific debt arrangements in the event that
the third parties default on their debt obligations. The maximum
potential amount of future payments that the corporation could be
required to make in the event that these third parties default on
their debt obligations is approximately $14 million. At the present
time, the corporation does not believe it is probable that any of
these third parties will default on the amount subject to guarantee.
Risk Management
Geographic Risks The corporation maintains a presence in a large
number of nations in the world. This includes geographic locations
where the corporation has a direct economic presence through owned
manufacturing or distribution facilities, or companies where Sara Lee
maintains a direct equity investment. The corporation also has an
indirect economic presence in many geographic locations through
third-party suppliers who provide inventory, distribution services or
business process outsourcing services. In most cases, alternative
sources of supply are available for inventory products that are man-
ufactured or purchased from these foreign locations. However, the
general insurance coverage that is maintained by the corporation
does not cover losses resulting from acts of war or terrorism. As
a result, a loss of a significant direct or indirect manufacturing or
distribution location could impact the corporation’s operations,
cash flows and liquidity.
Foreign Exchange, Interest and Commodity Risks The corporation
is exposed to market risk from changes in foreign currency exchange
rates, interest rates and commodity prices. To mitigate the risk from
interest rate, foreign currency exchange rate and commodity price
fluctuations, the corporation enters into various hedging transactions
that have been authorized pursuant to the corporation’s policies
and procedures. The corporation does not use financial instruments
for trading purposes and is not a party to any leveraged derivatives.
Foreign Exchange
The corporation primarily uses foreign currency
forward and option contracts to hedge its exposure to adverse changes
in foreign currency exchange rates. The corporation’s exposure to
foreign currency exchange rates exists primarily with the European
euro, British pound, Brazilian real, Danish krone, Hungarian forint,
Russian ruble and Australian dollar against the U.S. dollar. Hedging
is accomplished through the use of financial instruments as the
gain or loss on the hedging instrument offsets the gain or loss on
an asset, a liability or a basis adjustment to a firm commitment.
Hedging of anticipated transactions is accomplished with financial
instruments as the realized gain or loss on the hedge occurs on
or near the maturity date of the anticipated transactions.
Interest Rates
The corporation uses interest rate swaps to modify
its exposure to interest rate movements, reduce borrowing costs and
to lock in interest rates on anticipated debt issuances. The corpo -
ration’s net exposure to interest rate risk consists of floating-rate
instruments that are benchmarked to U.S. and European short-term
money market interest rates. Interest rate risk management is
accomplished through the use of swaps to modify interest payments
under these instruments.
Commodities
The corporation is a purchaser of certain commodities
such as beef, pork, coffee, wheat, corn, corn syrup, soybean and
corn oils, butter, sugar, natural gas and diesel fuel. The corporation
generally buys these commodities based upon market prices that
are established with the vendor as part of the purchase process.
In circumstances where commodity derivative instruments are used,
there is a high correlation between the commodity costs and the
derivative instrument.
Risk Management Activities The corporation maintains risk
management control systems to monitor the foreign exchange,
interest rate and commodity risks, and the corporation’s offsetting
hedge positions. The risk management control system uses analyti-
cal techniques including market value, sensitivity analysis and
value at risk estimations.
Value at Risk
The value at risk estimations are intended to
measure the maximum amount the corporation could lose from
adverse market movements in interest rates and foreign currency
exchange rates, given a specified confidence level, over a given
period of time. Loss is defined in the value at risk estimation as
fair market value loss. As a result, foreign exchange gains or losses
that are charged directly to translation adjustments in common
stockholders’ equity are included in this estimate. The value at risk
estimation utilizes historical interest rates and foreign currency
exchange rates from the past year to estimate the volatility and
correlation of these rates in the future. The model uses the vari-
42 Sara Lee Corporation and Subsidiaries
Financial review