Burger King 2010 Annual Report Download - page 79
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 79 of the 2010 Burger King annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Table of Contents
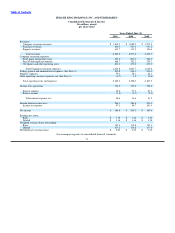
BURGER KING HOLDINGS, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Note 1. Description of Business and Organization
Description of Business
Burger King Holdings, Inc. (“BKH” or the “Company”) is a Delaware corporation formed on July 23, 2002. The Company is the
parent of Burger King Corporation (“BKC”), a Florida corporation that franchises and operates fast food hamburger restaurants,
principally under the Burger King brand (the “Brand”).
The Company generates revenues from three sources: (i) retail sales at Company restaurants; (ii) franchise revenues, consisting of
royalties based on a percentage of sales reported by franchise restaurants and franchise fees paid by franchisees; and (iii) property
income from restaurants that the Company leases or subleases to franchisees.
Restaurant sales are affected by the timing and effectiveness of the Company’s advertising, new products and promotional
programs. The Company’s results of operations also fluctuate from quarter to quarter as a result of seasonal trends and other factors,
such as the timing of restaurant openings and closings and the acquisition of franchise restaurants, as well as variability of the weather.
Restaurant sales are typically higher in the spring and summer months (our fourth and first fiscal quarters) when the weather is warmer
than in the fall and winter months (our second and third fiscal quarters). Restaurant sales during the winter are typically highest in
December, during the holiday shopping season. Our restaurant sales and Company restaurant margin are typically lowest during our
third fiscal quarter, which occurs during the winter months and includes February, the shortest month of the year. Furthermore, adverse
weather conditions can have material adverse effects on restaurant sales. The timing of religious holidays may also impact restaurant
sales.
Note 2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Basis of Presentation and Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its wholly−owned subsidiaries. All material
intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation. Investments in affiliates owned 50% or less are
accounted for by the equity method. These investments were not significant as of June 30, 2010.
Certain prior year amounts in the accompanying Financial Statements and Notes to the Financial Statements have been reclassified
in order to be comparable with the current year classifications. These reclassifications had no effect on previously reported net income.
(See significant accounting policies for “Retirement Plans”.)
Concentrations of Risk
The Company’s operations include Company and franchise restaurants located in 76 countries and U.S. territories. Of the 12,174
restaurants in operation as of June 30, 2010, 1,387 were Company restaurants and 10,787 were franchise restaurants.
Four distributors service approximately 85% of our U.S. system restaurants and the loss of any one of these distributors would
likely adversely affect our business. In many of the Company’s international markets, a single distributor services all the Burger King
restaurants in the market. The loss of any of one of these distributors would likely have an adverse effect on the market impacted, and
depending on the market, could have an adverse impact on the Company’s financial results.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States
(“GAAP”) requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in the Company’s consolidated
financial statements and accompanying notes. Management adjusts such estimates and assumptions when facts and circumstances
dictate. Volatile credit, equity, foreign currency, and energy markets
76