Burger King 2010 Annual Report Download - page 5
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 5 of the 2010 Burger King annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Table of Contents
Item 1. Business
Overview
Burger King Holdings, Inc. (“we” or the “Company”) is a Delaware corporation formed on July 23, 2002. Our restaurant system
includes restaurants owned by the Company and by franchisees. We are the world’s second largest fast food hamburger restaurant, or
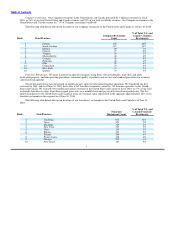
FFHR, chain as measured by the total number of restaurants and system−wide sales. As of June 30, 2010, we owned or franchised a
total of 12,174 restaurants in 76 countries and U.S. territories, of which 1,387 restaurants were Company restaurants and 10,787 were
owned by our franchisees. Of these restaurants, 7,258 or 60% were located in the United States and 4,916 or 40% were located in our
international markets. Our restaurants feature flame−broiled hamburgers, chicken and other specialty sandwiches, french fries, soft
drinks and other affordably−priced food items. During our more than 50 years of operating history, we have developed a scalable and
cost−efficient quick service hamburger restaurant model that offers customers fast food at affordable prices.
We generate revenues from three sources: (1) retail sales at Company restaurants; (2) franchise revenues, consisting of royalties
based on a percentage of sales reported by franchise restaurants and franchise fees paid by franchisees; and (3) property income from
restaurants that we lease or sublease to franchisees. Approximately 90% of our current restaurants are franchised and we have a higher
percentage of franchise restaurants to Company restaurants than our major competitors in the FFHR category. We expect that the
percentage of franchise restaurants will increase as franchisees open new restaurants and as we accelerate sales of Company restaurants
to franchisees, or “refranchisings,” over the next five years. We believe that this restaurant ownership mix provides us with a strategic
advantage because the capital required to grow and maintain the Burger King® system is funded primarily by franchisees, while still
giving us a base of Company restaurants to demonstrate credibility with franchisees in launching new initiatives. As a result of the high
percentage of franchise restaurants in our system, we believe we have lower capital requirements compared to our major competitors.
However, our franchise dominated business model also presents a number of drawbacks and risks, such as our limited control over
franchisees and limited ability to facilitate changes in restaurant ownership. In addition, our operating results are closely tied to the
success of our franchisees, and we are dependent on franchisees to open new restaurants as part of our growth strategy.
Our History
Burger King Corporation, which we refer to as BKC, was founded in 1954 when James McLamore and David Edgerton opened
the first Burger King restaurant in Miami, Florida. The Whopper® sandwich was introduced in 1957. BKC opened its first international
restaurant in the Bahamas in 1966. BKC also established its brand identity with the introduction of the “bun halves” logo in 1969 and
the launch of the first Have It Your Way® campaign in 1974. BKC introduced drive−thru service, designed to satisfy customers
“on−the−go” in 1975.
In 1967, Mr. McLamore and Mr. Edgerton sold BKC to Minneapolis−based The Pillsbury Company, taking it from a small
privately−held franchised chain to a subsidiary of a large food conglomerate. The Pillsbury Company was purchased by Grand
Metropolitan plc which, in turn, merged with Guinness plc to form Diageo plc, a British spirits company. In December 2002, BKC was
acquired by private equity funds controlled by TPG Capital, Bain Capital Partners and the Goldman Sachs Funds, which we refer to as
our “Sponsors.” In May 2006, we consummated our initial public offering. The private equity funds controlled by the Sponsors
currently own approximately 31% of our outstanding common stock.
Our Industry
We operate in the FFHR category of the quick service restaurant, or QSR, segment of the restaurant industry. In the United States,
the QSR segment is the largest segment of the restaurant industry and has demonstrated steady growth over a long period of time.
According to The NPD Group, Inc., which prepares and disseminates CREST data, QSR sales have grown at an annual rate of 3% over
the past 10 years, totaling approximately $230.5 billion for the 12−month period ended May 2010 and are projected to increase at an
annual rate of 3% between 2010 and 2015.
3