Berkshire Hathaway 2008 Annual Report Download - page 89
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 89 of the 2008 Berkshire Hathaway annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Management’s Discussion (Continued)
Equity Price Risk
Historically, Berkshire has maintained large amounts of invested assets in exchange traded equity securities. Strategically,
Berkshire strives to invest in businesses that possess excellent economics, with able and honest management and at sensible prices
and prefers to invest a meaningful amount in each investee. Consequently, equity investments may be concentrated in relatively
few investees. At December 31, 2008, 57% of the total fair value of equity investments was concentrated in four investees.
Berkshire prefers to hold equity investments for very long periods of time so management is not troubled by short-term
equity price volatility with respect to its investments provided that the underlying business, economic and management
characteristics of the investees remain favorable. Berkshire strives to maintain above average levels of shareholder capital to
provide a margin of safety against short-term equity price volatility.
Market prices for equity securities are subject to fluctuation and consequently the amount realized in the subsequent sale of
an investment may significantly differ from the reported market value. Fluctuation in the market price of a security may result
from perceived changes in the underlying economic characteristics of the investee, the relative price of alternative investments
and general market conditions.
Berkshire is also subject to equity price risk with respect to its equity index put option contracts. While Berkshire’s
ultimate potential loss with respect to these contracts is determined from the movement of the underlying stock index between
contract inception date and expiration, the change in fair value resulting from current changes in the index values are also
affected by changes in other factors such as interest rates, expected dividend rates and the remaining duration of the contract.
These contracts generally expire 15 to 20 years from inception and may not be settled before their respective expiration dates.
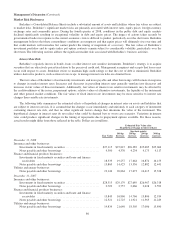
The following table summarizes Berkshire’s equity investments and derivative contract liabilities with equity price risk as
of December 31, 2008 and 2007. The effects of a hypothetical 30% increase and a 30% decrease in market prices as of those
dates is also shown. The selected 30% hypothetical change does not reflect what could be considered the best or worst case
scenarios. Indeed, results could be far worse due both to the nature of equity markets and the aforementioned concentrations
existing in Berkshire’s equity investment portfolio. Dollar amounts are in millions.
Fair Value
Hypothetical
Price Change
Estimated
Fair Value after
Hypothetical
Change in Prices
Hypothetical
Percentage
Increase (Decrease) in
Shareholders’ Equity
December 31, 2008
Equity securities ............................... $49,073 30% increase $ 63,795 8.8
30% decrease 34,351 (8.8)
Equity index put options ......................... (10,022) 30% increase (7,952) 1.2
30% decrease (12,799) (1.7)
December 31, 2007
Equity securities ............................... $74,999 30% increase $ 97,499 12.1
30% decrease 52,499 (12.1)
Equity index put options ......................... (4,610) 30% increase (3,282) 0.7
30% decrease (6,900) (1.2)
Foreign Currency Risk
Berkshire generally does not use derivative contracts to hedge foreign currency price changes primarily because of the
natural hedging that occurs between assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies in the consolidated financial
statements. Financial statements of subsidiaries that do not use the U.S. Dollar as their functional currency are translated into
U.S. Dollars using period-end exchange rates for assets and liabilities and weighted-average exchange rates for revenues and
expenses. Adjustments resulting from translating the financial statements of these subsidiaries are reported in accumulated other
comprehensive income. Foreign currency transaction gains or losses are included in earnings primarily as a result of the
translation of foreign currency denominated assets and liabilities held by U.S. subsidiaries. In addition, Berkshire holds
investments in major multinational companies that have significant foreign business and foreign currency risk of their own, such
as the Coca-Cola Company.
87