Berkshire Hathaway 2008 Annual Report Download - page 52
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 52 of the 2008 Berkshire Hathaway annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
(17) Fair value measurements
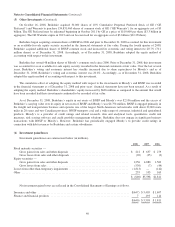
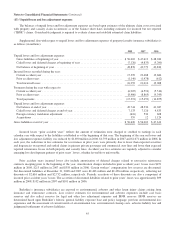
The estimated fair values of Berkshire’s financial instruments as of December 31, 2008 and 2007 are shown in the
following table (in millions). The carrying values of cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable and accounts payable,
accruals and other liabilities are deemed to be reasonable estimates of their fair values.
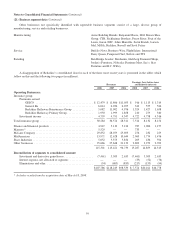
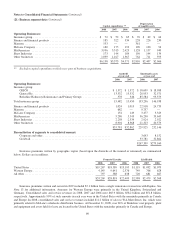
Carrying Value Fair Value
2008 2007 2008 2007
Insurance and other:
Investments in fixed maturity securities ................................. $27,115 $28,515 $27,115 $28,515
Investments in equity securities ....................................... 49,073 74,999 49,073 74,999
Other investments .................................................. 21,535 — 20,759 —
Notes payable and other borrowings .................................... 4,349 2,680 4,300 2,709
Finance and financial products:
Investments in fixed maturity securities ................................. 4,517 3,056 4,517 3,231
Derivative contract assets (1) .......................................... 208 699 208 699
Loans and finance receivables ......................................... 13,942 12,359 14,016 12,612
Notes payable and other borrowings .................................... 13,388 12,144 13,820 12,317
Derivative contract liabilities ......................................... 14,612 6,887 14,612 6,887
Utilities and energy:
Derivative contract assets (1) .......................................... 324 397 324 397
Notes payable and other borrowings .................................... 19,145 19,002 19,144 19,834
Derivative contract liabilities (2) ....................................... 729 765 729 765
(1) Included in Other assets
(2) Included in Accounts payable, accruals and other liabilities
Fair value is the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between
market participants as of the measurement date. Fair value measurements assume the asset or liability is exchanged in an orderly
manner; the exchange is in the principal market for that asset or liability (or in the most advantageous market when no principal
market exists); and the market participants are independent, knowledgeable, able and willing to transact an exchange.
Nonperformance risk (credit risk) is considered in valuing liabilities.
Fair values for substantially all of Berkshire’s financial instruments were measured using market or income approaches.
Considerable judgment may be required in interpreting market data used to develop the estimates of fair value. Accordingly, the
estimates presented herein are not necessarily indicative of the amounts that could be realized in an actual current market
exchange. The use of different market assumptions and/or estimation methodologies may have a material effect on the estimated
fair value.
SFAS 157 establishes a framework for measuring fair value by creating a hierarchy for observable independent market inputs and
unobservable market assumptions. The hierarchy consists of three levels, ranging from the category the FASB deems to be most
reliable to a category where fair value is measured using significant unobservable inputs because of the lack of observable market
prices for the instrument, or Levels 1 through 3, respectively. A further description of the inputs used in the valuation of assets and
liabilities under the three levels are as follows.
Level 1 – Inputs represent unadjusted quoted prices for identical assets or liabilities exchanged in active markets.
Substantially all of Berkshire’s equity investments are traded on an exchange in active markets and fair value is based on
the closing price as of the balance sheet date.
Level 2 – Inputs include directly or indirectly observable inputs other than Level 1 inputs such as quoted prices for similar
assets or liabilities exchanged in active or inactive markets; quoted prices for identical assets or liabilities exchanged in
inactive markets; other inputs that are considered in fair value determinations of the assets or liabilities, such as interest
rates and yield curves that are observable at commonly quoted intervals, volatilities, prepayment speeds, loss severities,
credit risks and default rates; and inputs that are derived principally from or corroborated by observable market data by
correlation or other means. Fair values for Berkshire’s investments in fixed maturity securities are primarily based on
market prices and market data available for instruments with similar characteristics since active markets are not common
for many instruments. Pricing evaluations are based on yield curves for instruments with similar characteristics, such as
credit rating, estimated duration, and yields for other instruments of the issuer or entities in the same industry sector.
50