Berkshire Hathaway 2008 Annual Report Download - page 45
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 45 of the 2008 Berkshire Hathaway annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
(11) Derivatives
Derivative contracts of Berkshire’s finance and financial products businesses, with limited exceptions, are not designated
as hedges for financial reporting purposes. Changes in the fair values of such contracts that do not qualify as hedges are reported
in the Consolidated Statements of Earnings as derivative gains/losses. A summary of these contracts as of December 31, 2008
and 2007 follows (in millions).
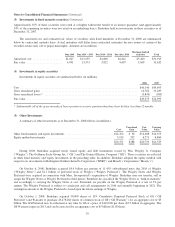
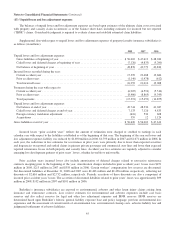
2008 2007
Assets (4) Liabilities
Notional
Value (1) Assets (4) Liabilities
Notional
Value (1)
Equity index put options ................................. $— $10,022 $37,134(2) $— $4,610 $35,043(2)
Credit default obligations:
High yield indexes ................................. — 3,031 7,892(3) — 1,838 4,660(3)
Individual corporate ................................ — 105 3,900(3) ———
States/municipalities ................................ — 958 18,364(3) ———
Other ................................................ 503 528 749 489
Counterparty netting and funds held as collateral .............. (295) (32) (50) (50)
$ 208 $14,612 $699 $6,887
(1) Not discounted for time value.
(2) Represents the aggregate undiscounted amount payable at the contract expiration dates assuming that the value of each
index is zero at the contract expiration date.
(3) Represents the maximum undiscounted future value of losses payable under the contracts, assuming a sufficient number of
credit defaults occur. The number of losses required to exhaust contract limits under substantially all of the contracts is
dependent on the loss recovery rate related to the specific obligor at the time of the default.
(4) Included in other assets of finance and financial products businesses.
As of December 31, 2008, Berkshire has written equity index put option contracts on four major equity indexes, including
three indexes outside of the United States. These contracts are European style options (exercisable only at the expiration date)
and at inception had durations of 15 to 20 years. At December 31, 2008, the weighted average remaining life of these contracts
was approximately 13.5 years with expiration dates between September 2019 and January 2028. Substantially all of these
contracts were written on an at-the-money basis (i.e. strike price equaled market price when contract was written). Future
payments, if any, under these contracts will be based on the decline in the underlying index value below the strike price at the
contract expiration date. Premiums on these contracts were received at the contract inception dates and therefore Berkshire has
no counterparty credit risk.
At December 31, 2008, the intrinsic value of the equity index put option contracts was $10.8 billion. The intrinsic value
represents Berkshire’s undiscounted liability at December 31, 2008, assuming these contracts are settled on their future
expiration dates based on the December 31, 2008 index values. However, these contracts generally may not be terminated or
fully settled before the expiration dates and therefore the ultimate amount of cash basis gains or losses on these contracts will
not be known for years.
Berkshire has written credit default contracts on various “high-yield indexes,” state/municipal debt issuers and individual
corporations. These contracts cover the loss in value of specified debt obligations of the issuers arising from default events
which are usually for non-payment or bankruptcy. Loss amounts are subject to contract limits.
High yield indexes are comprised of specified corporate issuers (usually 100 in number) in North America whose
obligations are rated below investment grade. These contracts generally cover the loss in value of a referenced obligation upon a
default by an issuer over the contract period (usually 5 years). The weighted average contract duration at December 31, 2008
was approximately 2
1
⁄
3
years. Payments by Berkshire under these contracts are limited to specified amounts per issuer as well
as aggregate limits.
In 2008, Berkshire also wrote a small number of contracts providing for payments upon defaults on debt issued by several
states and municipalities. The weighted average contract duration at December 31, 2008 was approximately 12 years.
43