Berkshire Hathaway 2008 Annual Report Download - page 5
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 5 of the 2008 Berkshire Hathaway annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
BERKSHIRE HATHAWAY INC.
To the Shareholders of Berkshire Hathaway Inc.:
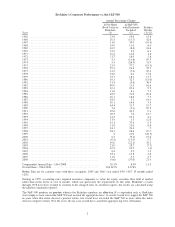
Our decrease in net worth during 2008 was $11.5 billion, which reduced the per-share book value of
both our Class A and Class B stock by 9.6%. Over the last 44 years (that is, since present management took over)
book value has grown from $19 to $70,530, a rate of 20.3% compounded annually.*
The table on the preceding page, recording both the 44-year performance of Berkshire’s book value
and the S&P 500 index, shows that 2008 was the worst year for each. The period was devastating as well for
corporate and municipal bonds, real estate and commodities. By yearend, investors of all stripes were bloodied
and confused, much as if they were small birds that had strayed into a badminton game.
As the year progressed, a series of life-threatening problems within many of the world’s great financial
institutions was unveiled. This led to a dysfunctional credit market that in important respects soon turned
non-functional. The watchword throughout the country became the creed I saw on restaurant walls when I was
young: “In God we trust; all others pay cash.”
By the fourth quarter, the credit crisis, coupled with tumbling home and stock prices, had produced a
paralyzing fear that engulfed the country. A freefall in business activity ensued, accelerating at a pace that I have
never before witnessed. The U.S. – and much of the world – became trapped in a vicious negative-feedback
cycle. Fear led to business contraction, and that in turn led to even greater fear.
This debilitating spiral has spurred our government to take massive action. In poker terms, the Treasury
and the Fed have gone “all in.” Economic medicine that was previously meted out by the cupful has recently
been dispensed by the barrel. These once-unthinkable dosages will almost certainly bring on unwelcome
aftereffects. Their precise nature is anyone’s guess, though one likely consequence is an onslaught of inflation.
Moreover, major industries have become dependent on Federal assistance, and they will be followed by cities
and states bearing mind-boggling requests. Weaning these entities from the public teat will be a political
challenge. They won’t leave willingly.
Whatever the downsides may be, strong and immediate action by government was essential last year if
the financial system was to avoid a total breakdown. Had one occurred, the consequences for every area of our
economy would have been cataclysmic. Like it or not, the inhabitants of Wall Street, Main Street and the various
Side Streets of America were all in the same boat.
Amid this bad news, however, never forget that our country has faced far worse travails in the past. In
the 20th Century alone, we dealt with two great wars (one of which we initially appeared to be losing); a dozen or
so panics and recessions; virulent inflation that led to a 21
1
⁄
2
% prime rate in 1980; and the Great Depression of
the 1930s, when unemployment ranged between 15% and 25% for many years. America has had no shortage of
challenges.
Without fail, however, we’ve overcome them. In the face of those obstacles – and many others – the
real standard of living for Americans improved nearly seven-fold during the 1900s, while the Dow Jones
Industrials rose from 66 to 11,497. Compare the record of this period with the dozens of centuries during which
humans secured only tiny gains, if any, in how they lived. Though the path has not been smooth, our economic
system has worked extraordinarily well over time. It has unleashed human potential as no other system has, and it
will continue to do so. America’s best days lie ahead.
*All per-share figures used in this report apply to Berkshire’s A shares. Figures for the B shares are
1/30th of those shown for A.
3