Vodafone 2008 Annual Report Download - page 19
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 19 of the 2008 Vodafone annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.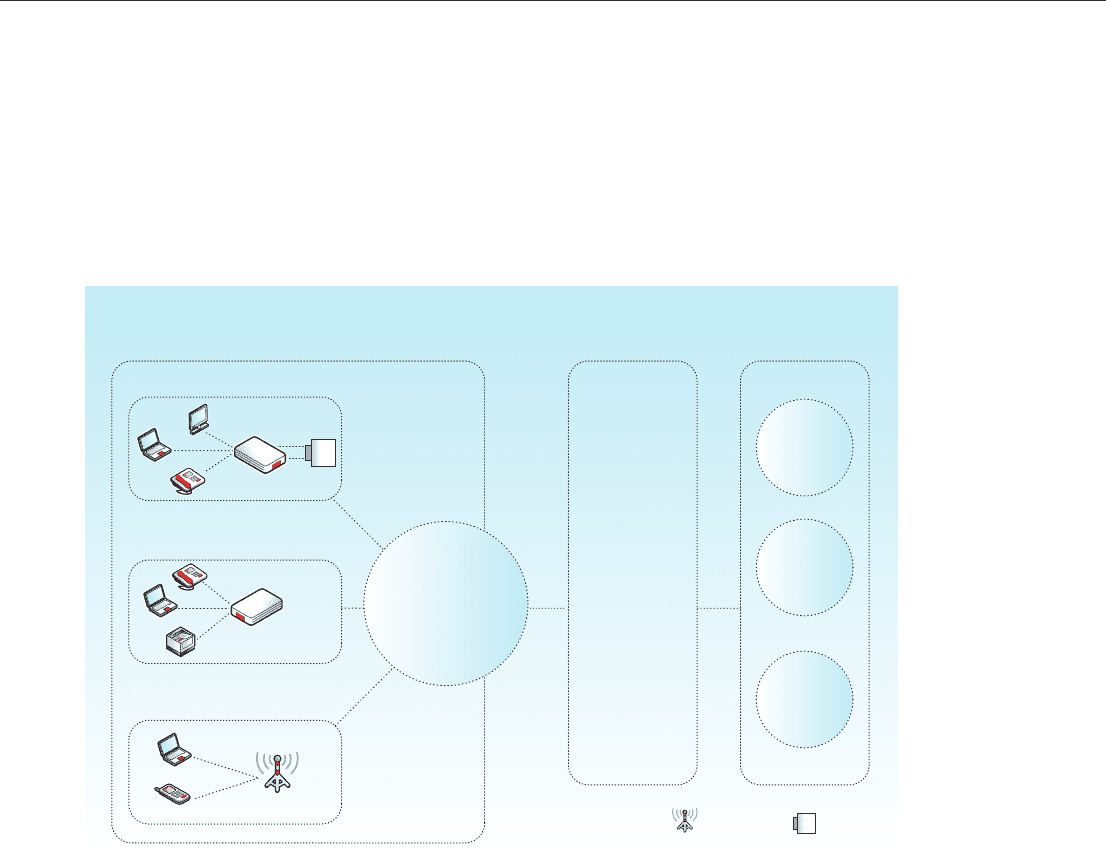
The Packet Switched domain allows customers to use
data services. Its key nodes are responsible for a variety of
functions, such as the delivery of data packets to and from
mobile devices within a geographical service area, setting
up data connections and providing the gateway between
the Vodafone network and external data networks, including
the internet and customers’ corporate networks.
The IP Multimedia Subsystem (“IMS”) domain is the first step
of a wider evolutionary path from the current core network
to an all internet protocol (“IP”) next generation network.
It enables delivery of advanced multimedia services, both
mobile and fixed, leveraging the flexibility and effectiveness
of internet technologies. IMS is expected to be a key element
in the future infrastructure to support Vodafone’s total
communications strategy, exploiting the technology of
convergence between the mobile telecommunications and
the internet world.
If the voice call or data transmission is intended for delivery
to another device which is not on the Vodafone network in
the same country, the information is transferred through a
public or private fixed line telephone network or the internet.
Mobile network technology
2G
Vodafone operates 2G networks in all its mobile operating
subsidiaries, through Global System for Mobile (“GSM”) networks,
offering customers services such as voice, text messaging and
basic data services. In addition, all of the Group’s controlled
networks operate General Packet Radio Services (“GPRS”), often
referred to as 2.5G. GPRS allows mobile devices to be used for
sending and receiving data over an IP based network, enabling
wireless access to data networks like the internet.
•
•
The GPRS data service offering includes internet and email
access, allowing the customer to always be connected at
download speeds slightly below a dial-up modem. In some
markets, Vodafone continues to further evolve data speeds
with 2G evolutions beyond GPRS capability.
3G
Vodafone’s 3G networks, operating the Wideband Code Division
Multiple Access (“W-CDMA”) standard, provide customers with
faster data access. Vodafone has expanded its service offering on
3G networks with high speed internet and email access, video
telephony, full track music downloads, mobile TV and other data
services in addition to existing voice and data services.
High speed packet access (“HSPA”)
HSPA is a 3G wireless technology enhancement enabling
significant increases in data transmission speeds. It allows
increased mobile data traffic and improves the customer
experience through the availability of 3G broadband services
and significantly shorter data transfer times.
High Speed Downlink Packet Access (“HSDPA”) has been widely
deployed on Vodafone 3G networks at up to 3.6 Mbps (“Mega
bits per second”) peak speed. In addition, starting in hotspots,
the first upgrades to up to 7.2 Mbps peak speed have already
started to be deployed in several operating subsidiaries. The
figures are theoretical peak rates deliverable by the technology
in ideal radio conditions with no customer contention for
resources. This is providing customers with faster access
speeds than historically experienced on 3G networks.
Vodafone Group Plc Annual Report 2008 17
Access & transmission network
Fixed broadband networks
Core network Other networks
Private corporate networks
2G/3G mobile networks
Access
transmission
infrastructure
(e.g. microwave, leased
line or DSL)
Router
Modem Service
platforms
IMS
Packet
switched
Circuit
switched
Fixed line
operators
Internet
Other
mobile
operators
Base station DSLAM