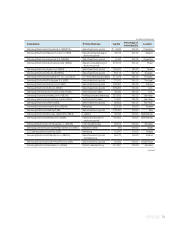
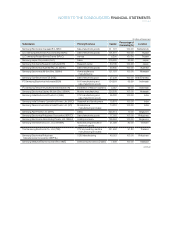
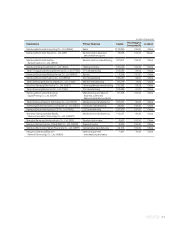
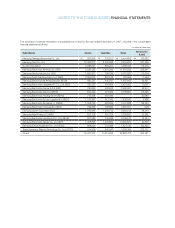
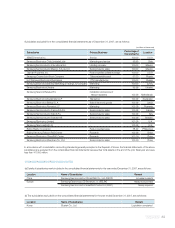
Samsung 2007 Annual Report Download - page 87
Download and view the complete annual report
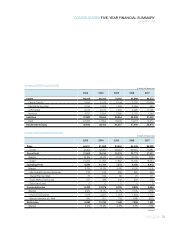
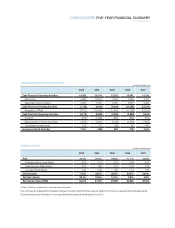
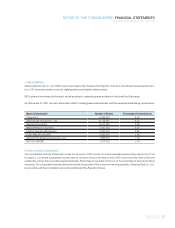
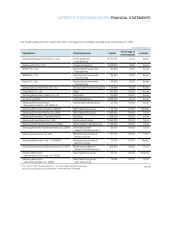
Please find page 87 of the 2007 Samsung annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.85
investees, are fully eliminated, and charged to the equity of the
controlling interests and minority interests, based on the percent-
age of ownership.
SEC and its consolidated subsidiaries follow the same fiscal year
end. Differences in accounting policies between the Company and
its consolidated subsidiaries are adjusted during consolidation.
MARKETABLE SECURITIES
Investments in equity securities or debt securities are classified
into trading securities, available-for-sale securities and held-to-
maturity securities, depending on the acquisition and holding
purpose. Trading securities are classified as current assets while
available-for-sale securities and held-to-maturity securities are
classified as long-term investments, except those securities that
mature or are certain to be disposed of within one year, which are
classified as current assets.
Cost is measured at the market value upon acquisition, including
incidental costs, and is determined using the average cost
method.
Available-for-sale securities are stated at fair value, while non-
marketable equity securities are stated at cost. Unrealized holding
gains and losses on available-for-sale securities are reported
in a separate component of shareholders’ equity under capital
adjustments, which are to be included in current operations
upon the disposal or impairment of the securities. In the case
of available-for-sale debt securities, the difference between the
acquisition cost after amortization, using the effective interest rate
method, and the fair value is reported as a capital adjustment.
Impairment resulting from the decline in realizable value below
the acquisition cost, net of amortization, are included in current
operations.
EQUITY-METHOD INVESTMENTS
Investments in business entities in which the Company has con-
trol or the ability to exercise significant influence over the operating
and financial policies are accounted for using the equity method of
accounting.
Under the equity method, the original investment is recorded at
cost and adjusted by the Company’s share in the net book value
of the investee with a corresponding charge to current opera-
tions, a separate component of shareholders’ equity, or retained
earnings, depending on the nature of the underlying change in
the net book value. All significant unrealized profits arising from
intercompany transactions between the Company and its equity-
method investee and subsidiaries are fully eliminated.
Differences between the investment amounts and correspond-
ing capital amounts of the investee at the date of acquisition
of the investment are recorded as part of investments and are
amortized over five years using the straight-line method. However,
differences which occur from additional investments made after
the Company obtains control and the investment becomes a
subsidiary are reported in a separate component of shareholders’
equity, and are not included in the determination of the results of
operations.
Assets and liabilities of the Company’s foreign investees are
translated at current exchange rates, while income and expense
are translated at average rates for the period. Adjustments
resulting from the translation process are reported in a separate
component of shareholders’ equity, and are not included in the
determination of the results of operations.
Certain equity-method investments are accounted for based on
unaudited or unreviewed financial statements as the audited or
reviewed financial statements of these entities are not available as
of the date of this audit report.
ALLOWANCE FOR DOUBTFUL ACCOUNTS
The Company provides an allowance for doubtful accounts and
notes receivable based on the aggregate estimated collectibility of
the receivables.
INVENTORY VALUATION
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or net realizable value.
Cost is determined using the average cost method, except for
materials-in-transit which are stated at actual cost as determined
using the specific identification method. Losses on valuation of
inventories and losses on inventory obsolescence are recorded as
part of cost of sales.
PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT AND
RELATED DEPRECIATION
Property, plant and equipment are stated at cost, except for
certain assets subject to upward revaluation in accordance with
the Asset Revaluation Law of Korea. The revaluation presents
production facilities and other buildings at their depreciated
replacement cost, and land at the prevailing market price, as of
the effective date of revaluation. The revaluation increment, net
of revaluation tax, is first applied to offset accumulated deficit
and deferred foreign exchange losses, if any. The remainder may
be credited to other capital surplus or transferred to common
stock. A new basis for calculating depreciation is established for
revalued assets.