Pizza Hut 2012 Annual Report Download - page 127
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 127 of the 2012 Pizza Hut annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
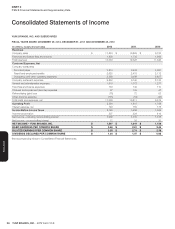
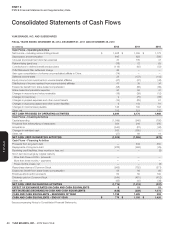
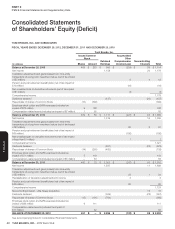
YUM! BRANDS, INC.-2012 Form10-K 35
Form 10-K
PART II
ITEM7A Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures
About Market Risk
The Company is exposed to fi nancial market risks associated with interest rates, foreign currency exchange rates and commodity prices.In the normal
course of business and in accordance with our policies, we manage these risks through a variety of strategies, which may include the use of fi nancial
and commodity derivative instruments to hedge our underlying exposures.Our policies prohibit the use of derivative instruments for trading purposes,
and we have processes in place to monitor and control their use.
Interest Rate Risk
We have a market risk exposure to changes in interest rates, principally in
the U.S.We attempt to minimize this risk and lower our overall borrowing
costs through the utilization of derivative fi nancial instruments, primarily
interest rate swaps.These swaps are entered into with fi nancial institutions
and have reset dates and critical terms that match those of the underlying
debt.Accordingly, any change in fair value associated with interest rate
swaps is offset by the opposite impact on the related debt.
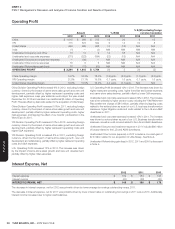
At December29, 2012 and December31, 2011 a hypothetical 100 basis-
point increase in short-term interest rates would result, over the following
twelve-month period, in a reduction of approximately $3million and $5million,
respectively, in income before income taxes.The estimated reductions
are based upon the current level of variable rate debt and assume no
changes in the volume or composition of that debt and include no impact
from interest income related to cash and cash equivalents.In addition,
the fair value of our derivative fi nancial instruments at December29, 2012
and December31, 2011 would decrease approximately $10million and
$16million, respectively, as a result of the same hypothetical 100 basis-point
increase andthe fair value of our Senior Unsecured Notes at December29,
2012 and December31, 2011 would decrease approximately $225million
and $228million, respectively.Fair value was determined based on the
present value of expected future cash fl ows considering the risks involved
and using discount rates appropriate for the duration.
Foreign Currency Exchange Rate Risk
Changes in foreign currency exchange rates impact the translation of
our reported foreign currency denominated earnings, cash fl ows and net
investments in foreign operations and the fair value of our foreign currency
denominated fi nancial instruments. Historically, we have chosen not to
hedge foreign currency risks related to our foreign currency denominated
earnings and cash fl ows through the use of fi nancial instruments. We
attempt to minimize the exposure related to our net investments in foreign
operations by fi nancing those investments with local currency debt when
practical.In addition, we attempt to minimize the exposure related to foreign
currency denominated fi nancial instruments by purchasing goods and
services from third parties in local currencies when practical. Consequently,
foreign currency denominated fi nancial instruments consist primarily of
intercompany short-term receivables and payables.At times, we utilize
forward contracts to reduce our exposure related to these intercompany
short-term receivables and payables.The notional amount and maturity
dates of these contracts match those of the underlying receivables or
payables such that our foreign currency exchange risk related to these
instruments is minimized.
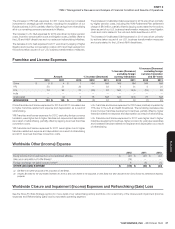
The combined Operating Profi ts of China, YRI and India constitute more
than 70% of our segment Operating Profi t in 2012, excluding unallocated
income (expenses).In addition, the Company’s foreign currency net asset
exposure (defi ned as foreign currency assets less foreign currency liabilities)
totaled approximately $4.2billion as of December29, 2012. Operating
in international markets exposes the Company to movements in foreign
currency exchange rates.The Company’s primary exposures result from
our operations in Asia-Pacifi c, Europe and the Americas.For the fi scal
year ended December29, 2012 Operating Profi t would have decreased
approximately $190million if all foreign currencies had uniformly weakened
10% relative to the U.S. dollar.This estimated reduction assumes no
changes in sales volumes or local currency sales or input prices.
Commodity Price Risk
We are subject to volatility in food costs as a result of market risk associated with commodity prices.Our ability to recover increased costs through
higher pricing is, at times, limited by the competitive environment in which we operate.We manage our exposure to this risk primarily through pricing
agreements with our vendors.