MasterCard 2012 Annual Report Download - page 83
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 83 of the 2012 MasterCard annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.MASTERCARD INCORPORATED
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
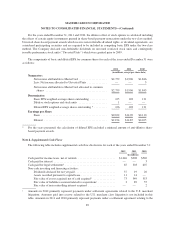
limited partnerships and limited liability companies are also accounted for under the equity method when the
Company has the ability to exercise significant influence over the investee, generally when the investment
ownership percentage is equal to or greater than 5% of the outstanding ownership interest. The excess of the cost
over the underlying net equity of investments accounted for under the equity method is allocated to identifiable
tangible and intangible assets and liabilities based on fair values at the date of acquisition. The amortization of
the excess of the cost over the underlying net equity of investments and MasterCard’s share of net earnings or
losses of entities accounted for under the equity method of accounting is included in other income (expense) on
the consolidated statement of operations.
The Company accounts for investments in common stock or in-substance common stock under the cost
method of accounting when it does not exercise significant influence, generally when it holds less than 20%
ownership in the entity. Investments in companies that MasterCard does not control, but that are not in the form
of common stock or in-substance common stock, are also accounted for under the cost method of accounting.
When the interest in a limited partnership or limited liability company is less than 5% and the Company has no
significant influence over the operation of the investee, the cost method is used. Investments for which the equity
method or cost method of accounting is used are recorded in other assets on the consolidated balance sheet.
Use of estimates—The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management
to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of
contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenue and
expenses during the reporting periods. Future events and their effects cannot be predicted with certainty;
accordingly, accounting estimates require the exercise of judgment. The accounting estimates used in the
preparation of the Company’s consolidated financial statements may change as new events occur, as more
experience is acquired, as additional information is obtained and as the Company’s operating environment
changes. Actual results may differ from these estimates.
Revenue recognition—Revenues are recognized when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists,
delivery has occurred or services have been rendered, the price is fixed or determinable, and collectibility is
reasonably assured. Revenues are generally based upon transactional information accumulated by our systems or
reported by our customers. The Company’s revenues are based on the volume of activity on cards that carry the
Company’s brands, the number of transactions processed or the nature of other payment-related services.
Volume-based revenues (domestic assessments and cross-border volume fees) are recorded as revenue in the
period they are earned, which is when the related volume is generated on the cards. Certain quarterly revenues
are estimated based upon aggregate transaction information and historical and projected customer quarterly
volumes. Actual results may differ from these estimates. Transaction-based revenues (transaction processing
fees) are calculated by multiplying the number and type of transactions by the contractual price for each service.
Transaction-based fees are recognized as revenue in the same period as the related transactions occur. Other
payment-related services are dependent on the nature of the products or services provided to our customers and
are recognized as revenue in the same period as the related transactions occur or services are rendered.
MasterCard has business agreements with certain customers that provide for fee rebates when the customers
meet certain volume hurdles as well as other support incentives such as marketing, which are tied to
performance. Rebates and incentives are recorded as a reduction of revenue in the same period as the revenue is
earned or performance has occurred. Rebates and incentives are calculated on a monthly basis based upon
estimated performance and the terms of the related business agreements. In addition, MasterCard may incur costs
directly related to entering into such an agreement, which are deferred and amortized over the life of the
agreement on a straight-line basis.
79