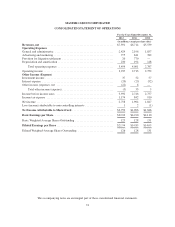
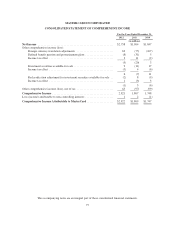
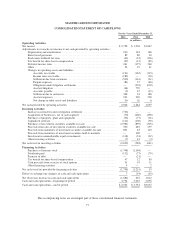
MasterCard 2012 Annual Report Download - page 82
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 82 of the 2012 MasterCard annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.MASTERCARD INCORPORATED
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 1. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Organization
MasterCard Incorporated and its consolidated subsidiaries, including MasterCard International Incorporated
(“MasterCard International” and together with MasterCard Incorporated, “MasterCard” or the “Company”), is a
technology company in the global payments industry that connects consumers, financial institutions, merchants,
governments and businesses worldwide, enabling them to use electronic forms of payment instead of cash and
checks. MasterCard primarily (1) offers a wide range of payment solutions, which enable its customers and other
parties with which we work (which include financial institutions and other entities that act as “issuers” and
“acquirers”, merchants, governments, telecommunications companies and other businesses) to develop and
implement credit, debit, prepaid, commercial and related payment programs for consumers; (2) manages a family
of well-known, widely-accepted payment brands, including MasterCard®, Maestro®and Cirrus®, which it
licenses to its customers for use in their payment programs and solutions; (3) processes payment transactions
over the MasterCard Worldwide Network; and (4) provides support services to its customers and others.
Significant Accounting Policies
Consolidation and basis of presentation—The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of
MasterCard and its majority-owned and controlled entities, including any variable interest entities (“VIEs”) for
which the Company is the primary beneficiary. Intercompany transactions and balances have been eliminated in
consolidation. Certain prior period amounts have been reclassified to conform to the 2012 presentation. The
Company follows accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”).
The Company is a variable interest holder in certain entities. These variable interests arise from contractual,
ownership or other monetary interests in the entities. The Company evaluates if the entity has sufficient equity at
risk to finance their activities without additional subordinated financial support from other parties, if equity
investors lack the ability to control the entity’s most significant activities, have voting rights that are
disproportionate to their ownership interest, or lack the ability to absorb expected losses or receive expected
returns (referred to as VIEs). The Company consolidates a VIE if it is the primary beneficiary, defined as the
entity that has both (i) the power to direct the activities that most significantly impact the VIE’s economic
performance and (ii) the obligation to absorb the losses and/or the right to receive benefits from the VIE that
could potentially be significant to the VIE. To determine whether we qualify as the primary beneficiary, the
Company considers both qualitative and quantitative factors regarding the nature, size and form of the
Company’s involvement with the VIE. The Company assesses whether or not it is the primary beneficiary of a
VIE on an ongoing basis. Investments in VIEs for which the Company is not considered the primary beneficiary
are not consolidated and are accounted for as equity method or cost method investments and recorded in other
assets on the consolidated balance sheet. At December 31, 2012 and 2011, there were no VIEs which required
consolidation.
Non-controlling interests represent the equity interest not owned by the Company and is recorded for
consolidated entities in which the Company owns less than 100% of the interests. Non-controlling interests are
reported as a component of equity. In addition, changes in a parent’s ownership interest while the parent retains
its controlling interest are accounted for as equity transactions, and upon a gain or loss of control, retained
ownership interests are remeasured at fair value, with any gain or loss recognized in earnings.
The Company accounts for investments in common stock or in-substance common stock under the equity
method of accounting when it has the ability to exercise significant influence over the investee, generally when it
holds between 20% and 50% ownership in the entity. In addition, investments in flow-through entities such as
78