MasterCard 2012 Annual Report Download - page 12
Download and view the complete annual report
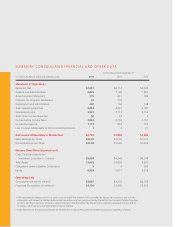
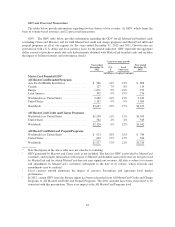
Please find page 12 of the 2012 MasterCard annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.In addition, some payment cards and devices are equipped with an RFID (radio frequency identification)
microchip, which provides an advanced authentication technique, and technology that allows contactless
payments requiring neither signature nor PIN under established maximum transaction amounts.
MasterCard Worldwide Network Architecture and Operations. We believe the architecture of the
MasterCard Worldwide Network is unique, featuring a globally integrated structure that provides scalability for
our customers and enables them to expand into regional and global markets. Our network also features an
intelligent architecture that enables it to adapt to the needs of each transaction by blending two distinct
processing structures-distributed (peer-to-peer) and centralized (hub-and-spoke). Transactions that require fast,
reliable processing, such as those submitted using a contactless card or device at a toll booth, can use the
network’s distributed processing structure, ensuring they are processed close to where the transaction occurred.
Transactions that require value-added processing, such as real-time access to transaction data for fraud scoring or
rewards at the point-of-sale, or customization of transaction data for unique consumer-spending controls, use the
network’s centralized processing structure, ensuring advanced processing services are applied to the transaction.
Through the unique architecture of our network, we are able to connect all parties with respect to payments
transactions regardless of whether the transaction is occurring at a traditional physical location, at an ATM, on
the internet or through a mobile device.
The network typically operates at under 80% capacity and has the capacity to handle more than 160 million
transactions per hour with an average network response time of 130 milliseconds. The network can also
substantially scale capacity to meet demand. Our transaction processing services are available 24 hours per day,
every day of the year. Our global payments network provides multiple levels of back-up protection and related
continuity procedures should the issuer, acquirer or payments network experience a service interruption.
Moreover, the network features multiple layers of protection against hacking or other cyber-attacks. See our risk
factor in “Risk Factors—Business Risks” in Part I, Item 1A of this Report related to a failure or breach of our
security systems or infrastructure as a result of cyber-attacks. We supplement this protection with mitigation
efforts to strengthen our protection against such threats, both in terms of operability of the network and
protection of the information transmitted through the network. To date, we have consistently maintained
availability of our global processing systems more than 99.9% of the time.
Processing Capabilities.
•Transaction Switching—Authorization, Clearing and Settlement. We provide transaction switching
(authorization, clearing and settlement) through the MasterCard Worldwide Network.
OAuthorization. Authorization refers to the process by which a transaction is routed to the issuer for
approval and then a decision whether or not to approve the transaction is made by the issuer or, in
certain circumstances such as when the issuer’s systems are unavailable or cannot be contacted, by
MasterCard or others on behalf of the issuer in accordance with either the issuer’s instructions or
applicable rules (also known as “stand-in”). Our standards, which may vary across regions, establish
the circumstances under which merchants and acquirers must seek authorization of transactions.
OClearing. Clearing refers to the exchange of financial transaction information between issuers and
acquirers after a transaction has been successfully conducted at the point of interaction. We clear
transactions among customers through our processing systems.
OSettlement. Once transactions have been authorized and cleared, we help to settle the transactions
by facilitating the exchange of funds between parties. Once clearing is completed, a daily
reconciliation is provided to each customer involved in settlement, detailing the net amounts by
clearing cycle and a final settlement position. The actual exchange of funds takes place between a
settlement bank, designated by the customer and approved by us, and a settlement bank chosen by
us. Customer settlement occurs generally in U.S. dollars or in a limited number of other currencies
in accordance with our established rules.
8